Lecture 16a_Electromagnetic 1
... In the region surrounding a permanent magnet there exists a magnetic field, which can be represented by magnetic flux lines similar to electric flux lines. ...
... In the region surrounding a permanent magnet there exists a magnetic field, which can be represented by magnetic flux lines similar to electric flux lines. ...
Force on a Current-Carrying Wire in a Magnetic Field F = ILB
... displays, tape recorders, and computer hard drives all depend on the magnetic effects of electric currents ...
... displays, tape recorders, and computer hard drives all depend on the magnetic effects of electric currents ...
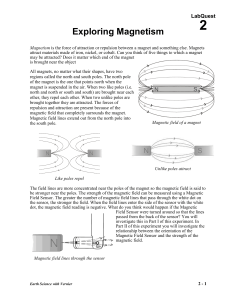
02 Expl Magnet LQ
... 4. Zero the Magnetic Field Sensor. This reduces the effect of the surrounding environment on the magnetic field reading. a. Move all magnets far away from the Magnetic Field Sensor. b. When the readings on the screen stabilize, choose Zero from the Sensors menu. When the process is complete, the rea ...
... 4. Zero the Magnetic Field Sensor. This reduces the effect of the surrounding environment on the magnetic field reading. a. Move all magnets far away from the Magnetic Field Sensor. b. When the readings on the screen stabilize, choose Zero from the Sensors menu. When the process is complete, the rea ...
VERSION C 1. Short Answer Problems (5 points each) (a) (5 points
... What is the direction of the field if it is a pure magnetic field aligned along one of the coordinate axes? i. −x ii. +x iii. −y iv. +y v. −z vi. +z ~ the answer is −z. Answer: From the Lorentz force law F~ = q~v × B, (b) (5 points) You are given two identical inductors, each with inductance L. In o ...
... What is the direction of the field if it is a pure magnetic field aligned along one of the coordinate axes? i. −x ii. +x iii. −y iv. +y v. −z vi. +z ~ the answer is −z. Answer: From the Lorentz force law F~ = q~v × B, (b) (5 points) You are given two identical inductors, each with inductance L. In o ...
B page I into
... field exerts a force on the current given by F~ = I ~` × B. The field produced by an infinite solenoid is parallel to the axis of the solenoid. The direction is given by the right hand rule where the fingers of your right hand curl in the direction of the current and your thumb points in the directi ...
... field exerts a force on the current given by F~ = I ~` × B. The field produced by an infinite solenoid is parallel to the axis of the solenoid. The direction is given by the right hand rule where the fingers of your right hand curl in the direction of the current and your thumb points in the directi ...
“A Design for an efficient cylindrical ma with rotating magnets and
... * The target tube is rotated about its longitudinal axis. A magnetic structure is arranged inside the tube but does not rotate with it. * The rotation of the target surface through the stationary plasma sputters the top layer of material from entire surface as that surface is rotated through the ma ...
... * The target tube is rotated about its longitudinal axis. A magnetic structure is arranged inside the tube but does not rotate with it. * The rotation of the target surface through the stationary plasma sputters the top layer of material from entire surface as that surface is rotated through the ma ...
PPT
... E sinq = |p x E| • The dipole tends to “align” itself with the field lines. • ICPP: What happens if the field is NOT UNIFORM?? ...
... E sinq = |p x E| • The dipole tends to “align” itself with the field lines. • ICPP: What happens if the field is NOT UNIFORM?? ...
Quantum diffusion of electromagnetic fields of ultrarelativistic spin
... It has been known for a while that very intense electromagnetic fields are created in ultrarelativistic hadronic and nuclear collisions [1–5]. However, no convincing experimental evidence of their impact on the scattering dynamics has been observed. In recent years, a renewed interest to this subjec ...
... It has been known for a while that very intense electromagnetic fields are created in ultrarelativistic hadronic and nuclear collisions [1–5]. However, no convincing experimental evidence of their impact on the scattering dynamics has been observed. In recent years, a renewed interest to this subjec ...
CHATTANOOGA STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE
... 76. Given appropriate values for a series wound motor, determine its mechanical power and efficiency. CHAPTER 29 Sources of Magnetic Field 77. Discuss the historical development of our understanding of magnetism. 78. Trace the origin of magnetism to its atomic basis. 79. Define all the key terms lis ...
... 76. Given appropriate values for a series wound motor, determine its mechanical power and efficiency. CHAPTER 29 Sources of Magnetic Field 77. Discuss the historical development of our understanding of magnetism. 78. Trace the origin of magnetism to its atomic basis. 79. Define all the key terms lis ...
Chapter 16 Engineering Magnetism: Magnetic Field Calculations and Inductors 16.1 Homework # 140
... 09. In a laboratory, an electric field of 3.0 x103 V/m and a magnetic field of 1.5 T are produced. a.) What is the energy density for the electric field? b.) What is the energy density for the magnetic field? c.) What electric field strength would be needed to produce the same energy density as the ...
... 09. In a laboratory, an electric field of 3.0 x103 V/m and a magnetic field of 1.5 T are produced. a.) What is the energy density for the electric field? b.) What is the energy density for the magnetic field? c.) What electric field strength would be needed to produce the same energy density as the ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.