South
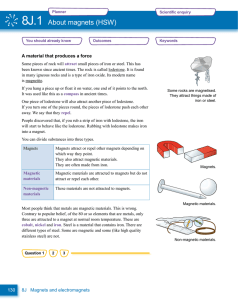
... will repel. Be prepared to tell which pole of the magnet is facing which if they are stacked on a pencil and explain (like poles with repel, unlike poles will attract). -When a steel or iron object touches a magnet, it becomes a temporary magnet. Only other iron or steel objects will then stick to t ...
... will repel. Be prepared to tell which pole of the magnet is facing which if they are stacked on a pencil and explain (like poles with repel, unlike poles will attract). -When a steel or iron object touches a magnet, it becomes a temporary magnet. Only other iron or steel objects will then stick to t ...
pptx
... Classically, we would expect that the magnetic moment vector could be pointing in any direction when we measure it. By directional quantization, they are referring to how the projection of the magnetic moment vector for the silver atoms onto any axis only comes in two discrete values [+mB or -mB], a ...
... Classically, we would expect that the magnetic moment vector could be pointing in any direction when we measure it. By directional quantization, they are referring to how the projection of the magnetic moment vector for the silver atoms onto any axis only comes in two discrete values [+mB or -mB], a ...
Energy Level diagram for a spin-1/2 nucleus as a function of
... All nuclei with spin greater than ½ are termed quadrupolar nuclei, since they posses an electrical quadrupole moment , which is due to their non-spherical charge distribution. These nuclei are difficult to observe since the electrical quadrupole moment interacts with local electric field gradients. ...
... All nuclei with spin greater than ½ are termed quadrupolar nuclei, since they posses an electrical quadrupole moment , which is due to their non-spherical charge distribution. These nuclei are difficult to observe since the electrical quadrupole moment interacts with local electric field gradients. ...
practice multiple choice questions
... E. where surface curves outward C. where curvature is least ____25. If a conductor is in electrostatic equilibrium near an electrical charge: A. the total charge on the conductor must be zero. B. the electric field inside the conductor must be zero. C. any charges on the conductor must be uniformly ...
... E. where surface curves outward C. where curvature is least ____25. If a conductor is in electrostatic equilibrium near an electrical charge: A. the total charge on the conductor must be zero. B. the electric field inside the conductor must be zero. C. any charges on the conductor must be uniformly ...
212b204
... 1.) Self inductance of a coaxial cable: A small solid conductor with radius a is supported by insulating disks on the axis of a thin walled tube with inner radius b. The inner and outer conductors carry equal currents i in opposite directions. From work done with Ampere’s Law earlier this semester, ...
... 1.) Self inductance of a coaxial cable: A small solid conductor with radius a is supported by insulating disks on the axis of a thin walled tube with inner radius b. The inner and outer conductors carry equal currents i in opposite directions. From work done with Ampere’s Law earlier this semester, ...
Introduction
... In previous chapters we have seen that an electrostatic field is produced by static or stationary charges. The relationship of the steady magnetic field to its sources is much ...
... In previous chapters we have seen that an electrostatic field is produced by static or stationary charges. The relationship of the steady magnetic field to its sources is much ...
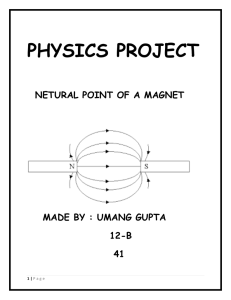
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.