4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... A proton in a particle accelerator has a speed of 5.0x106 m/s. The proton encounters a magnetic field whose magnitude is 0.40 T and whose direction makes and angle of 30.0 degrees with respect to the proton’s velocity (see part (c) of the figure). Find (a) the magnitude and direction of the force on ...
... A proton in a particle accelerator has a speed of 5.0x106 m/s. The proton encounters a magnetic field whose magnitude is 0.40 T and whose direction makes and angle of 30.0 degrees with respect to the proton’s velocity (see part (c) of the figure). Find (a) the magnitude and direction of the force on ...
Chapter S34
... •Faraday’s law and the Ampere-Maxwell law are symmetrical in that the line integrals of E and B around a closed path are related to the rate of change of the respective fluxes ...
... •Faraday’s law and the Ampere-Maxwell law are symmetrical in that the line integrals of E and B around a closed path are related to the rate of change of the respective fluxes ...
Why does my circuit radiate?
... Field can only exist within a few λ of a conducting structure It will collapse once the energy source is removed The field can be dynamic or static The field can exist exclusively as an electric or magnetic field and as a combined E & H field. Can be called a reactive field ...
... Field can only exist within a few λ of a conducting structure It will collapse once the energy source is removed The field can be dynamic or static The field can exist exclusively as an electric or magnetic field and as a combined E & H field. Can be called a reactive field ...
Physics Week 6(Sem. 2) Magnetism Cont’d
... another, since a current in a conductor creates its own magnetic field. When the current is in the same direction, the two wires attract to one another. This can be confirmed by the right hand rule. If the current in the two wires are going in opposite directions, the two wires will repel ea ...
... another, since a current in a conductor creates its own magnetic field. When the current is in the same direction, the two wires attract to one another. This can be confirmed by the right hand rule. If the current in the two wires are going in opposite directions, the two wires will repel ea ...
spin-orbit coupling
... • An electron revolving about a nucleus finds itself in a magnetic field produced by the nucleus which is circling about it in its own frame of reference. • This magnetic field then acts upon the electron’s own spin magnetic moment to produce substates in terms of energy. S=1/2 could make some singl ...
... • An electron revolving about a nucleus finds itself in a magnetic field produced by the nucleus which is circling about it in its own frame of reference. • This magnetic field then acts upon the electron’s own spin magnetic moment to produce substates in terms of energy. S=1/2 could make some singl ...
DO PHYSICS ONLINE JJ THOMPSON`S e/m EXPERIMENT
... Even though Thompson used several different gases in his tube and different metals for his electrodes, he found a consistent value for the e/me ratio. From this observation he argued that there was only one type of electron which must be contained in all atoms. The basic research into electrical di ...
... Even though Thompson used several different gases in his tube and different metals for his electrodes, he found a consistent value for the e/me ratio. From this observation he argued that there was only one type of electron which must be contained in all atoms. The basic research into electrical di ...
DO PHYSICS ONLINE JJ THOMPSON`S e/m EXPERIMENT
... Even though Thompson used several different gases in his tube and different metals for his electrodes, he found a consistent value for the e/me ratio. From this observation he argued that there was only one type of electron which must be contained in all atoms. The basic research into electrical di ...
... Even though Thompson used several different gases in his tube and different metals for his electrodes, he found a consistent value for the e/me ratio. From this observation he argued that there was only one type of electron which must be contained in all atoms. The basic research into electrical di ...
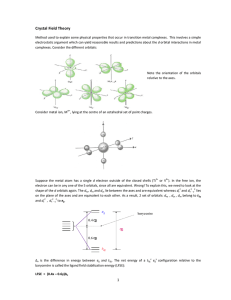
Crystal Field Theory
... [CoX(NH3)5] with X = I , Br , Cl H20 and NH3, the colours range from purple (for X = I ) through pink (X = Cl ) to yellow (with NH3). This observation indicates that energy of the lowest electronic transition increases as the ligands are varied along the series. Ligands that give rise to high energy ...
... [CoX(NH3)5] with X = I , Br , Cl H20 and NH3, the colours range from purple (for X = I ) through pink (X = Cl ) to yellow (with NH3). This observation indicates that energy of the lowest electronic transition increases as the ligands are varied along the series. Ligands that give rise to high energy ...
9 - web page for staff
... If the wired is tightly wounded, the flux linkage will be the same for the adjacent turns of toroid. If the adjacent turns are separated by some finite distance, the total flux must be calculated from the flux from each turn. ...
... If the wired is tightly wounded, the flux linkage will be the same for the adjacent turns of toroid. If the adjacent turns are separated by some finite distance, the total flux must be calculated from the flux from each turn. ...
Lecture 9 - web page for staff
... Flux linkage is the total flux passing through the surface bounded by the contour of the circuit carrying the current. Inductane L is defined as the ratio of flux linkage to the current generating the flux, Ntotal henrys or Wb/A. L I ...
... Flux linkage is the total flux passing through the surface bounded by the contour of the circuit carrying the current. Inductane L is defined as the ratio of flux linkage to the current generating the flux, Ntotal henrys or Wb/A. L I ...
Chapter 20: Magnetic field and forces What will we learn in this
... The forces that make motors turn are forces a magnetic field exerts on a current-carrying conductor. Calculation of the force: Assume positive charges in a wire of length l and cross section A in a in-plane field B. The force on a single charge is F = |q|vB sin(φ) Since the drift velocity vd, field ...
... The forces that make motors turn are forces a magnetic field exerts on a current-carrying conductor. Calculation of the force: Assume positive charges in a wire of length l and cross section A in a in-plane field B. The force on a single charge is F = |q|vB sin(φ) Since the drift velocity vd, field ...
January 2004
... Let the magnetic field, B, have the configuration which is used in mass spectrometers: B = 0 for x < 0, while for x > 0 it is uniform, B = B0 ẑ. A spherical ball with radius R, total mass M and total charge Q approaches the plane x = 0 from the left and enters the magnetic field region x > 0 with c ...
... Let the magnetic field, B, have the configuration which is used in mass spectrometers: B = 0 for x < 0, while for x > 0 it is uniform, B = B0 ẑ. A spherical ball with radius R, total mass M and total charge Q approaches the plane x = 0 from the left and enters the magnetic field region x > 0 with c ...
magnetic field - University of Utah Physics
... Mass of wire : M = ρ ( volume) = ρAL M = (8.94 × 10 3 kg/m3 )( 2.50 × 10 −6 m 2 )(36.0 m) = 0.805 kg FG = Mg = (0.805 kg)(9.81 m/s 2 ) = 7.89 N FG / FB = 199 ...
... Mass of wire : M = ρ ( volume) = ρAL M = (8.94 × 10 3 kg/m3 )( 2.50 × 10 −6 m 2 )(36.0 m) = 0.805 kg FG = Mg = (0.805 kg)(9.81 m/s 2 ) = 7.89 N FG / FB = 199 ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.