The Role of Forests in Carbon Cycles, Sequestration, and Storage
... Resources Canada, Canadian Forest Service, Atlantic Forestry Centre, P.O. Box 4000, Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada E3B 5P7 2 Institute of Forest Ecology, Austrian Federal Office and Research Centre for Forests, Seckendorff- Gudent-Weg 8, A-1131 Vienna, Austria 3 Natural Resources Canada, Canadia ...
... Resources Canada, Canadian Forest Service, Atlantic Forestry Centre, P.O. Box 4000, Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada E3B 5P7 2 Institute of Forest Ecology, Austrian Federal Office and Research Centre for Forests, Seckendorff- Gudent-Weg 8, A-1131 Vienna, Austria 3 Natural Resources Canada, Canadia ...
The Earth February 7 − Why does Earth support life?
... Lots of scientific debate about the details…. ...
... Lots of scientific debate about the details…. ...
Study Guide
... Fossils are the same age as the rock layers they are found in. Fossils are NOT found in igneous rock or metamorphic rock because these processes are so hot that remains of organisms are destroyed. Fossils show how life has changed over time. Life on earth has become more complex and diverse over tim ...
... Fossils are the same age as the rock layers they are found in. Fossils are NOT found in igneous rock or metamorphic rock because these processes are so hot that remains of organisms are destroyed. Fossils show how life has changed over time. Life on earth has become more complex and diverse over tim ...
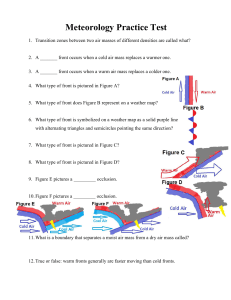
Meteorology Practice Test
... 40. True or false: Weather near a large body of water tends to be warmer in the summer and colder in the winter than the surrounding land area. 41. The Maunder Minimum occurred at the same time as the middle of what climatological event? 42. True or false: the Dalton Minimum lasted approximately fro ...
... 40. True or false: Weather near a large body of water tends to be warmer in the summer and colder in the winter than the surrounding land area. 41. The Maunder Minimum occurred at the same time as the middle of what climatological event? 42. True or false: the Dalton Minimum lasted approximately fro ...
Adopt-A-Drifter Program Lesson
... temperatures to western Ireland and Great Britain, resulting in a subtropical climate with mild winters. ...
... temperatures to western Ireland and Great Britain, resulting in a subtropical climate with mild winters. ...
HNRS 228 Astrobiology Chap.4 Geology Bennett et al.
... Climate Regulation and Change (4.5) Greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, ice ages, Snowball Earth, long term habitability ...
... Climate Regulation and Change (4.5) Greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, ice ages, Snowball Earth, long term habitability ...
Visualization of Ocean Currents and Eddies in a High
... meshes based on Voronoi tessellations [4]. MPAS-Ocean has several next-generation features as a climate model. In addition to the multi-resolution capabilities, it includes conservation properties required for century-long climate simulations: conservation of volume and volume-weighted tracers; ener ...
... meshes based on Voronoi tessellations [4]. MPAS-Ocean has several next-generation features as a climate model. In addition to the multi-resolution capabilities, it includes conservation properties required for century-long climate simulations: conservation of volume and volume-weighted tracers; ener ...
2nd Semester Final Exam - Murrieta Valley Unified
... 88. More solar energy reaches the equatorial regions than the polar regions because the equatorial regions are covered by a greater area of land. have more vegetation to absorb sunlight. have days with more hours of light. receive sun rays closest to vertical. 89. Which diagram below is the best mod ...
... 88. More solar energy reaches the equatorial regions than the polar regions because the equatorial regions are covered by a greater area of land. have more vegetation to absorb sunlight. have days with more hours of light. receive sun rays closest to vertical. 89. Which diagram below is the best mod ...
Name
... 4. What is the difference between mass and weight? Mass is the amount of matter in an object, where weight is a measure of the gravitational pull on an object ...
... 4. What is the difference between mass and weight? Mass is the amount of matter in an object, where weight is a measure of the gravitational pull on an object ...
C1.7 Earth and its a..
... To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ...
... To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ...
Atmosphere - Spring Branch ISD
... Physical weathering happens when large masses of rock are broken down into smaller pieces. ...
... Physical weathering happens when large masses of rock are broken down into smaller pieces. ...
Novice HighSpeedRailNeg
... (May 24, “China’s Actions are Crucial on Climate Change,” http://web.mit.edu/newsoffice/2012/chinafocus-addressing-climate-change.html) The report — titled "The Role of China in Mitigating Climate Change" — published in the journal Energy Economics, compares the impact of a stringent emissions reduc ...
... (May 24, “China’s Actions are Crucial on Climate Change,” http://web.mit.edu/newsoffice/2012/chinafocus-addressing-climate-change.html) The report — titled "The Role of China in Mitigating Climate Change" — published in the journal Energy Economics, compares the impact of a stringent emissions reduc ...
Application of a forest succession model to a continentality gradient
... Other authors have also pointed out that unrealistic threshold effects may occur, e.g. at the southern range limit of tree species (Prentice et al., 1993) or when gap models are applied to environmental gradients (Bugmann, 1994). Further research is needed to identify physiologically based growth li ...
... Other authors have also pointed out that unrealistic threshold effects may occur, e.g. at the southern range limit of tree species (Prentice et al., 1993) or when gap models are applied to environmental gradients (Bugmann, 1994). Further research is needed to identify physiologically based growth li ...
1. What are the two most abundant permanent gasses, and roughly
... 26.Can you think of another planet beside Earth whose surface temperature is much more strongly affected by the greenhouse effect? 27.Do greenhouse gases warm the earth by absorbing sunlight? 28.What are the two most important greenhouse gases on Earth? 29.Why do we expect increasing concentrations ...
... 26.Can you think of another planet beside Earth whose surface temperature is much more strongly affected by the greenhouse effect? 27.Do greenhouse gases warm the earth by absorbing sunlight? 28.What are the two most important greenhouse gases on Earth? 29.Why do we expect increasing concentrations ...
solid rock
... change Continental drift - all continents were once together in a single landmass and have since drifted apart Pangaea – “all lands” ...
... change Continental drift - all continents were once together in a single landmass and have since drifted apart Pangaea – “all lands” ...
Little Ice Age Module: Cycle A Group
... role. Scientists have found that aerosols produced by large volcanic eruptions accelerate ozone destruction by providing a surface upon which chemical reactions can take place, enhancing chlorine-driven ozone depletion. These effects from volcanoes are short lived and will settle out of the atmosphe ...
... role. Scientists have found that aerosols produced by large volcanic eruptions accelerate ozone destruction by providing a surface upon which chemical reactions can take place, enhancing chlorine-driven ozone depletion. These effects from volcanoes are short lived and will settle out of the atmosphe ...
UNIT TITLE: Readers Theater
... 6. The process of weathering breaks down rocks to form sediment. 7. Erosion is the process that moves sediment. The three agents of erosion are water, wind, and ice (or glaciers). 8. The interior of Earth is hot. Convection currents in the mantle cause tectonic plates to move. This causes earthquak ...
... 6. The process of weathering breaks down rocks to form sediment. 7. Erosion is the process that moves sediment. The three agents of erosion are water, wind, and ice (or glaciers). 8. The interior of Earth is hot. Convection currents in the mantle cause tectonic plates to move. This causes earthquak ...
“greenhouse” periods
... and amplitudes of the variability of atmospheric circulation patterns, hydrological cycles, and terrestrial desert distributions in response to global climate change. Hypothesis: drastic shrinking of the Hadley circulation during the mid-Cretaceous Our resent research results concerning the long-te ...
... and amplitudes of the variability of atmospheric circulation patterns, hydrological cycles, and terrestrial desert distributions in response to global climate change. Hypothesis: drastic shrinking of the Hadley circulation during the mid-Cretaceous Our resent research results concerning the long-te ...
File - Earth Science With Mrs. Locke
... lithosphere is broken into pieces called tectonic plates. • The plates move very slowly and don’t last forever ...
... lithosphere is broken into pieces called tectonic plates. • The plates move very slowly and don’t last forever ...
Earth`s Climate & Mankind
... Variations in earth’s orbit around the Sun affect the amount of solar radiation received on Earth’s surface. Orbital scale changes occur over tens to hundreds of thousands of years. ...
... Variations in earth’s orbit around the Sun affect the amount of solar radiation received on Earth’s surface. Orbital scale changes occur over tens to hundreds of thousands of years. ...
chapter 17 - Geoclassroom Home
... Enrichment Topic 3. Could Global Warming Start a Little Ice Age in Europe? Oddly, global warming could bring about a new ice age in Europe. Europe is warmer than it should be for its latitude. Warm water from the equator travels up North America, and then the Gulf Stream moves eastward across the At ...
... Enrichment Topic 3. Could Global Warming Start a Little Ice Age in Europe? Oddly, global warming could bring about a new ice age in Europe. Europe is warmer than it should be for its latitude. Warm water from the equator travels up North America, and then the Gulf Stream moves eastward across the At ...
MULTIDISCIPLINARY NATURE OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
... • Oceans, seas, rivers, streams, glaciers, lakes, reservoirs, polar ice caps and the shallow groundwater bodies that interflow with the surface water • 70.8% of the earth’s surface is covered with water mainly in the form of oceans • 97% of total water (1360M Km3) in the oceans and inland seas • les ...
... • Oceans, seas, rivers, streams, glaciers, lakes, reservoirs, polar ice caps and the shallow groundwater bodies that interflow with the surface water • 70.8% of the earth’s surface is covered with water mainly in the form of oceans • 97% of total water (1360M Km3) in the oceans and inland seas • les ...
Strategic Framework for Fisheries, Aquaculture and Climate Change
... • Oceans removed about 25% of The ability of major oceanic and other atmospheric carbon dioxide emitted by aquatic systems to maintain their human activities from 2000 to 2007. function under natural and human- • Oceans absorb more than 95% of the induced variability is a vitally important sun’s rad ...
... • Oceans removed about 25% of The ability of major oceanic and other atmospheric carbon dioxide emitted by aquatic systems to maintain their human activities from 2000 to 2007. function under natural and human- • Oceans absorb more than 95% of the induced variability is a vitally important sun’s rad ...
ear 203 earth system science
... 2. Identify anthropogenic greenhouse gases, their sources and their effects. 3. Explain fundamental components of the Earth system and their interactions. 4. Differentiate between global warming and the greenhouse effect. 5. Explain the relationship between surface temperature and atmospheric CO 2 c ...
... 2. Identify anthropogenic greenhouse gases, their sources and their effects. 3. Explain fundamental components of the Earth system and their interactions. 4. Differentiate between global warming and the greenhouse effect. 5. Explain the relationship between surface temperature and atmospheric CO 2 c ...
History of climate change science

The history of the scientific discovery of climate change began in the early 19th century when ice ages and other natural changes in paleoclimate were first suspected and the natural greenhouse effect first identified. In the late 19th century, scientists first argued that human emissions of greenhouse gases could change the climate. Many other theories of climate change were advanced, involving forces from volcanism to solar variation. In the 1960s, the warming effect of carbon dioxide gas became increasingly convincing, although some scientists also pointed out that human activities, in the form of atmospheric aerosols (e.g., ""pollution""), could have cooling effects as well. During the 1970s, scientific opinion increasingly favored the warming viewpoint. By the 1990s, as a result of improving fidelity of computer models and observational work confirming the Milankovitch theory of the ice ages, a consensus position formed: greenhouse gases were deeply involved in most climate changes, and human emissions were bringing serious global warming.Since the 1990s, scientific research on climate change has included multiple disciplines and has expanded, significantly increasing our understanding of causal relations, links with historic data and ability to numerically model climate change. The most recent work has been summarized in the Assessment Reports by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions, or in the distribution of weather around the average conditions (i.e., more or fewer extreme weather events). Climate change is caused by factors that include oceanic processes (such as oceanic circulation), biotic processes, variations in solar radiation received by Earth, plate tectonics and volcanic eruptions, and human-induced alterations of the natural world; these latter effects are currently causing global warming, and ""climate change"" is often used to describe human-specific impacts.