Chapter 1 Planet Earth
... Heating of the Atmosphere Solar energy reaches the Earth as electromagnetic radiation, which includes visible light, infrared radiation, and ultraviolet light. About half of the solar energy that enters the atmosphere passes through it and reaches the Earth’s surface, while the rest of the energ ...
... Heating of the Atmosphere Solar energy reaches the Earth as electromagnetic radiation, which includes visible light, infrared radiation, and ultraviolet light. About half of the solar energy that enters the atmosphere passes through it and reaches the Earth’s surface, while the rest of the energ ...
Answers to Spring Final Review
... Where are the metals on the Periodic Table? the nonmetals? Metals are on the left side of the staircase and nonmetals are in the upper right side of the Periodic Table. ...
... Where are the metals on the Periodic Table? the nonmetals? Metals are on the left side of the staircase and nonmetals are in the upper right side of the Periodic Table. ...
New model better estimates mantle melt percentage
... understand the evolution and dynamics of the planet. To quantify the fraction of mantle melting, scientists analyze seismic waves that travel through the mantle and crust, or they conduct a magnetotelluric (MT) survey, which measures the natural variations of the mantle’s electrical and magnetic fie ...
... understand the evolution and dynamics of the planet. To quantify the fraction of mantle melting, scientists analyze seismic waves that travel through the mantle and crust, or they conduct a magnetotelluric (MT) survey, which measures the natural variations of the mantle’s electrical and magnetic fie ...
Earth PowerPoint
... • Surface re-radiates as infrared thermal radiation • Atmosphere absorbs some infrared, causing further heating ...
... • Surface re-radiates as infrared thermal radiation • Atmosphere absorbs some infrared, causing further heating ...
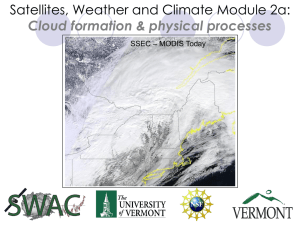
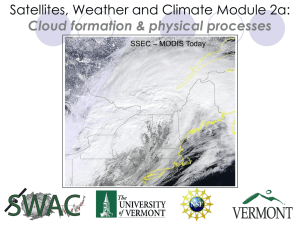
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module 2a: Cloud formation & physical processes SSEC
... Heat added to water increases internal energy (latent heat) and breaks molecular bonds resulting in evaporation to gas or vapor Rising air is cooled through work of expansion and heat is given off with molecular bonds reforming leading to condensation and clouds as noted in ...
... Heat added to water increases internal energy (latent heat) and breaks molecular bonds resulting in evaporation to gas or vapor Rising air is cooled through work of expansion and heat is given off with molecular bonds reforming leading to condensation and clouds as noted in ...
Satellite Weather And Climate (SWAC) Initial Training Modules
... Exact track of storm determines cloud and precipitation type Sea breeze is a localized combination of convection and convergence ...
... Exact track of storm determines cloud and precipitation type Sea breeze is a localized combination of convection and convergence ...
CV - Blake Dyer
... The goal of my research is to better understand how sediments record the Earth-system response to changing boundary conditions. The information stored in the sedimentary rock record offers a broad range of past environmental variability that serves as a powerful baseline to differentiate naturally o ...
... The goal of my research is to better understand how sediments record the Earth-system response to changing boundary conditions. The information stored in the sedimentary rock record offers a broad range of past environmental variability that serves as a powerful baseline to differentiate naturally o ...
Changes in the Earth and its Atmosphere
... • There are many theories about how the atmosphere was formed. • One of these suggests that during the first billion years the atmosphere was mainly CO2 with little or no O2 (like Mars and Venus). There was probably also methane and ammonia. • What process could have created the oxygen? ...
... • There are many theories about how the atmosphere was formed. • One of these suggests that during the first billion years the atmosphere was mainly CO2 with little or no O2 (like Mars and Venus). There was probably also methane and ammonia. • What process could have created the oxygen? ...
careers in atmospheric sciences is a career in atmospheric sciences
... major employers include universities and private industry. University atmospheric scientists teach and work in atmospheric research programs. There are increasing employment opportunities for atmospheric scientists in industry, research organizations, and private consulting firms offering specialize ...
... major employers include universities and private industry. University atmospheric scientists teach and work in atmospheric research programs. There are increasing employment opportunities for atmospheric scientists in industry, research organizations, and private consulting firms offering specialize ...
CHAPTER 17
... EX TWO CUPS OF COFFEE, ONE LARGE ONE SMALL AT THE SAME TEMP OR ICECUBE MELTING THERMOMETER – MEASURES TEMP NOT HEAT (CELCIUS) TEMPERATURE GRADIENT HOT ...
... EX TWO CUPS OF COFFEE, ONE LARGE ONE SMALL AT THE SAME TEMP OR ICECUBE MELTING THERMOMETER – MEASURES TEMP NOT HEAT (CELCIUS) TEMPERATURE GRADIENT HOT ...
HNRS 228 Astrobiology Chap.4 Geology Bennett et al.
... Climate Regulation and Change (4.5) Greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, ice ages, Snowball Earth, long term habitability ...
... Climate Regulation and Change (4.5) Greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, ice ages, Snowball Earth, long term habitability ...
Document
... atmosphere before being removed by mixing into the ocean or by photosynthesis. Carbon Dioxide: lifetime cannot be specified and has GWP of one. Methane: lifetime of 12 +/-3 years and GWP of 72. Nitrous Oxide: life time 114 years and GWP 289. CFCs: vary in lifetimes from 12-50,000 years GWP 5,16015,0 ...
... atmosphere before being removed by mixing into the ocean or by photosynthesis. Carbon Dioxide: lifetime cannot be specified and has GWP of one. Methane: lifetime of 12 +/-3 years and GWP of 72. Nitrous Oxide: life time 114 years and GWP 289. CFCs: vary in lifetimes from 12-50,000 years GWP 5,16015,0 ...
HNRS 228 Astrobiology Chap.4 Geology Bennett et al.
... Climate Regulation and Change (4.5) Greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, ice ages, Snowball Earth, long term habitability ...
... Climate Regulation and Change (4.5) Greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, ice ages, Snowball Earth, long term habitability ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Climate Regulation and Change (4.5) Greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, ice ages, Snowball Earth, long term habitability ...
... Climate Regulation and Change (4.5) Greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, ice ages, Snowball Earth, long term habitability ...
Meteorology Part 1
... Test the results against the range of normal atmospheric pressures 919.6 is below the range of normal pressures…. REJECTED! 1019.6 is within the range of normal pressures…. ACCEPTED! ...
... Test the results against the range of normal atmospheric pressures 919.6 is below the range of normal pressures…. REJECTED! 1019.6 is within the range of normal pressures…. ACCEPTED! ...
Climate: The Two Ports What is the climate of Cabo San Lucas and
... terrain more closely resembles that of a tropical rainforest than a tropical grassland; the mountain causes rain to fall out of the rising air, and as the air descends the northwestern slopes of the ridges towards the airport’s weather station, it dries out a bit and has less rain to drop on the air ...
... terrain more closely resembles that of a tropical rainforest than a tropical grassland; the mountain causes rain to fall out of the rising air, and as the air descends the northwestern slopes of the ridges towards the airport’s weather station, it dries out a bit and has less rain to drop on the air ...
Meteorology
... Traps in heat which causes Earth’s surface temperatures to increase About 50 percent of the solar energy that strikes the top of the atmosphere reaches Earth’s surface and is absorbed. ...
... Traps in heat which causes Earth’s surface temperatures to increase About 50 percent of the solar energy that strikes the top of the atmosphere reaches Earth’s surface and is absorbed. ...
Formation of the Atmosphere
... interconnected Earth System. While the surface features of the Earth developed, volcanic activity and other processes injected large amounts of gaseous materials into the atmosphere. These events determined the evolving albedo and greenhouse properties of the early Earth. In ways not yet well unders ...
... interconnected Earth System. While the surface features of the Earth developed, volcanic activity and other processes injected large amounts of gaseous materials into the atmosphere. These events determined the evolving albedo and greenhouse properties of the early Earth. In ways not yet well unders ...
Earth Science Common Core Curriculum Standards
... due to variations in the perihelion and aphilionTracing and tracking glacial history and present-day data for Ohio, the United States and globally is an emphasis for this unit. Scientific data found in the analysis of the geologic record, ice cores and surficial geology should be used to provide the ...
... due to variations in the perihelion and aphilionTracing and tracking glacial history and present-day data for Ohio, the United States and globally is an emphasis for this unit. Scientific data found in the analysis of the geologic record, ice cores and surficial geology should be used to provide the ...
U.S. EPA`s Models-3 : An Integrated “One
... black carbon) could be a viable alternative to CO2 reduction to curb global warming. A key strategy suggested was to focus on air pollution to benefit regional and local air quality and global climate simultaneously (Hansen et al., PNAS, 2000); ...
... black carbon) could be a viable alternative to CO2 reduction to curb global warming. A key strategy suggested was to focus on air pollution to benefit regional and local air quality and global climate simultaneously (Hansen et al., PNAS, 2000); ...
Discovery Education: Earth`s Spheres interactive text
... The atmosphere consists of a gaseous mixture of air that surrounds the surface of the planet. Volcanoes released many of the gases that make up the atmosphere. Nitrogen dominates the mixture because it does not react with minerals and rocks at Earth’s surface. The concentration of nitrogen has incre ...
... The atmosphere consists of a gaseous mixture of air that surrounds the surface of the planet. Volcanoes released many of the gases that make up the atmosphere. Nitrogen dominates the mixture because it does not react with minerals and rocks at Earth’s surface. The concentration of nitrogen has incre ...
Earth and Atmosphere Week 6 10th
... Suggest one reason why scientists now know that the Earth is much older than 400 million years. ...
... Suggest one reason why scientists now know that the Earth is much older than 400 million years. ...
Slides - Powerpoint - University of Toronto Physics
... greenhouse gases and re-emitted back to Earth. • Equilibrium temperature determined by concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere • More greenhouse gases means higher temperature earth ...
... greenhouse gases and re-emitted back to Earth. • Equilibrium temperature determined by concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere • More greenhouse gases means higher temperature earth ...
History of climate change science

The history of the scientific discovery of climate change began in the early 19th century when ice ages and other natural changes in paleoclimate were first suspected and the natural greenhouse effect first identified. In the late 19th century, scientists first argued that human emissions of greenhouse gases could change the climate. Many other theories of climate change were advanced, involving forces from volcanism to solar variation. In the 1960s, the warming effect of carbon dioxide gas became increasingly convincing, although some scientists also pointed out that human activities, in the form of atmospheric aerosols (e.g., ""pollution""), could have cooling effects as well. During the 1970s, scientific opinion increasingly favored the warming viewpoint. By the 1990s, as a result of improving fidelity of computer models and observational work confirming the Milankovitch theory of the ice ages, a consensus position formed: greenhouse gases were deeply involved in most climate changes, and human emissions were bringing serious global warming.Since the 1990s, scientific research on climate change has included multiple disciplines and has expanded, significantly increasing our understanding of causal relations, links with historic data and ability to numerically model climate change. The most recent work has been summarized in the Assessment Reports by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions, or in the distribution of weather around the average conditions (i.e., more or fewer extreme weather events). Climate change is caused by factors that include oceanic processes (such as oceanic circulation), biotic processes, variations in solar radiation received by Earth, plate tectonics and volcanic eruptions, and human-induced alterations of the natural world; these latter effects are currently causing global warming, and ""climate change"" is often used to describe human-specific impacts.