7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... B) Electric motor: Class activity: Showing a real electric motor and describing how current changes direction when torque becomes zero. 10) Force acting on a charge moving in magnetic field: [Force on current is sum of magnetic forces on moving charges in the wire] ...
... B) Electric motor: Class activity: Showing a real electric motor and describing how current changes direction when torque becomes zero. 10) Force acting on a charge moving in magnetic field: [Force on current is sum of magnetic forces on moving charges in the wire] ...
PHYS 221 Exam 2 10 July 2015 Physics 221 – Exam 2 Lorentz
... N1 = 5 turns and the transformer secondary has N2 = 10 turns. Assuming a that the magnetic flux linkage is 100%, what is the voltage across R? a. 0 V b. 6 V c. 48 V d. 12 V Transformers rely on Faraday’s law of induction to operate. Faraday’s law of induction requires a magnetic field that changes o ...
... N1 = 5 turns and the transformer secondary has N2 = 10 turns. Assuming a that the magnetic flux linkage is 100%, what is the voltage across R? a. 0 V b. 6 V c. 48 V d. 12 V Transformers rely on Faraday’s law of induction to operate. Faraday’s law of induction requires a magnetic field that changes o ...
... Or in other words in that case the sources of the magnetic H-field are equal to those area that have a non-zero divergence. Note that the divergence is zero in a homogeneously magnetized object. Also note that the divergence is unequal to zero if the normal component of M has a non-zero component. C ...
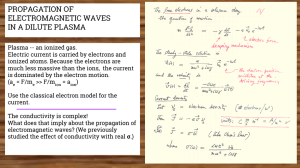
Lecture #23 04/26/05
... current I (don’t worry if you get it wrong, the result will be correct just negative) •You must be consistent however after you assign a direction! •Write down conservation of charge at each vertex •Write down one equation for each loop •Solve all equations You might end up with many equations, but ...
... current I (don’t worry if you get it wrong, the result will be correct just negative) •You must be consistent however after you assign a direction! •Write down conservation of charge at each vertex •Write down one equation for each loop •Solve all equations You might end up with many equations, but ...
Lecture 1: Introductory Topics
... ( = constant) fluid with velocity field because for any closed surface as much fluid flows out as flows in ...
... ( = constant) fluid with velocity field because for any closed surface as much fluid flows out as flows in ...
Problem set 3
... 1. Recall that the angular momentum raising operator is L+ = ~eiφ (∂θ + i cot θ ∂φ ). Use this to find L− . 2. Use the above formulae for L± to find the coordinate representation of the angular momentum basis states Y11 , Y10 and Y1,−1 up to normalization. 3. Write out the 9 equations summarized in ...
... 1. Recall that the angular momentum raising operator is L+ = ~eiφ (∂θ + i cot θ ∂φ ). Use this to find L− . 2. Use the above formulae for L± to find the coordinate representation of the angular momentum basis states Y11 , Y10 and Y1,−1 up to normalization. 3. Write out the 9 equations summarized in ...
1 pt
... What is the name of the term given to the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom? ...
... What is the name of the term given to the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom? ...