Week 10: Space quantization
... (G) Just as a spinning top in a gravitational field experiences precession about the gravitational field direction, a particle of charge, e, mass, m, and angular momentum, L, placed in a magnetic field, H, also experiences precession about the magnetic field direction. The magnetic moment, μ, which ...
... (G) Just as a spinning top in a gravitational field experiences precession about the gravitational field direction, a particle of charge, e, mass, m, and angular momentum, L, placed in a magnetic field, H, also experiences precession about the magnetic field direction. The magnetic moment, μ, which ...
Electric fields ppt File
... accelerate charged particles to very high speeds. Uses range from TVs to huge colliders. ...
... accelerate charged particles to very high speeds. Uses range from TVs to huge colliders. ...
Another recent exam sample #2
... 12. If the distance between the wires is 6 cm, and the distance from wire 1 to point B is 2 cm what are the direction and the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point B seen in figure. A. 3.5x10-5 T into the page B. 4.5x10-5 T into the page C. 1.6x10-4 T out of the page D. 2.0x10 -4T into the pa ...
... 12. If the distance between the wires is 6 cm, and the distance from wire 1 to point B is 2 cm what are the direction and the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point B seen in figure. A. 3.5x10-5 T into the page B. 4.5x10-5 T into the page C. 1.6x10-4 T out of the page D. 2.0x10 -4T into the pa ...
The Cyclotron…
... DO NOT confuse t with time here!!! The quantity 1/nq is what is known as the Hall Coefficient, RH Because all quantities other than n and q in the expression above can be measured the Hall coefficient is readily obtained. 1. The coefficient gives the sign of the charge carriers and their density 2. ...
... DO NOT confuse t with time here!!! The quantity 1/nq is what is known as the Hall Coefficient, RH Because all quantities other than n and q in the expression above can be measured the Hall coefficient is readily obtained. 1. The coefficient gives the sign of the charge carriers and their density 2. ...
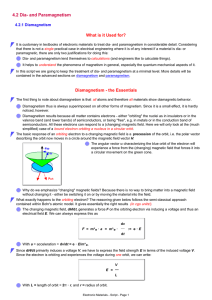
4.2 Dia- and Paramagnetism What is it Used for? 4.2.1 Diamagnetism
... a circular movement on the green cone. ...
... a circular movement on the green cone. ...
Physics Lecture #32 - WordPress for academic sites @evergreen
... Example: Applying Lenz’s Law – Fight the Flux Change! A solenoid is used to create a uniform magnetic field that points into the page. A wire loop of area A is in the magnetic field, as shown. For each of the following cases, choose one of the following for the direction of the induced current in t ...
... Example: Applying Lenz’s Law – Fight the Flux Change! A solenoid is used to create a uniform magnetic field that points into the page. A wire loop of area A is in the magnetic field, as shown. For each of the following cases, choose one of the following for the direction of the induced current in t ...
Quantum Mechanics
... The number n is called principal quantum number. So the energy of the electron is quantized and this result is the consequence of Schrödinger equation. Although the energies of the hydrogen atom states can be described by the single quantum number n, the wave functions describing these states requir ...
... The number n is called principal quantum number. So the energy of the electron is quantized and this result is the consequence of Schrödinger equation. Although the energies of the hydrogen atom states can be described by the single quantum number n, the wave functions describing these states requir ...
PHY2054 Exam 1 Formula Sheet
... E = F / q2 = k 12 rˆ (units = N/C = V/m) r r r Electric Flux (through the infinitesimal surface area dA): dΦ E = E ⋅ dA (units = Nm2/C) r Vector Area (directed area): A = Anˆ (where n̂ = normal to the surface) r r Q Gauss’ Law (net flux through closed surface S): Φ E = ∫ E ⋅ dA = enclosed (Qenclosed ...
... E = F / q2 = k 12 rˆ (units = N/C = V/m) r r r Electric Flux (through the infinitesimal surface area dA): dΦ E = E ⋅ dA (units = Nm2/C) r Vector Area (directed area): A = Anˆ (where n̂ = normal to the surface) r r Q Gauss’ Law (net flux through closed surface S): Φ E = ∫ E ⋅ dA = enclosed (Qenclosed ...
p30_m4_l02_assign
... This Assignment Booklet is worth __ marks out of the total ___ marks for the assignments in Unit B. The value of each assignment and each question is stated in the left margin. Read all parts of your assignment carefully, and record your answers in the appropriate places. If you have difficulty with ...
... This Assignment Booklet is worth __ marks out of the total ___ marks for the assignments in Unit B. The value of each assignment and each question is stated in the left margin. Read all parts of your assignment carefully, and record your answers in the appropriate places. If you have difficulty with ...