Unit 03 Lab - TTU Physics
... 1.1 Suppose you had an object that had a positive charge of 100C. a. If there were an object with 5C of charge 5m away from the 100C object, what would be the magnitude of the force that object would experience? What value do you get, if you divide the magnitude of the force the object experiences b ...
... 1.1 Suppose you had an object that had a positive charge of 100C. a. If there were an object with 5C of charge 5m away from the 100C object, what would be the magnitude of the force that object would experience? What value do you get, if you divide the magnitude of the force the object experiences b ...
Function of Conserved Tryptophans in the Aspergillus niger
... In this paper, we have followed the binding site numbering convention of Lawson et al. (1994) in domain E of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase. This is opposite to the numbering adopted by Klein and Schulz (1991) and Coutinho and Reilly (1994b). Production of the Variants. The three variants, W615K, ...
... In this paper, we have followed the binding site numbering convention of Lawson et al. (1994) in domain E of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase. This is opposite to the numbering adopted by Klein and Schulz (1991) and Coutinho and Reilly (1994b). Production of the Variants. The three variants, W615K, ...
ReviewWavesO
... We now want to expand the picture in the following way: EM waves propagate in 3D not just 1D as we have considered. - Diffraction - waves coming from a finite source spread out. EM waves propagate through material and are modified. - Dispersion - waves are slowed down by media, different frequency ...
... We now want to expand the picture in the following way: EM waves propagate in 3D not just 1D as we have considered. - Diffraction - waves coming from a finite source spread out. EM waves propagate through material and are modified. - Dispersion - waves are slowed down by media, different frequency ...
chapter37
... In constructive interference the amplitude of the resultant wave is greater than that of either individual wave In destructive interference the amplitude of the resultant wave is less than that of either individual wave All interference associated with light waves arises when the electromagnetic fie ...
... In constructive interference the amplitude of the resultant wave is greater than that of either individual wave In destructive interference the amplitude of the resultant wave is less than that of either individual wave All interference associated with light waves arises when the electromagnetic fie ...
Print
... chains are often cross-linked, most commonly by two cysteine residues linked together to form a cystine unit. 2. Secondary structure: The folding of a polypeptide backbone by means of internal hydrogen bonds between nearby amino acid residues giving rise to a regular arrangement defines the secondar ...
... chains are often cross-linked, most commonly by two cysteine residues linked together to form a cystine unit. 2. Secondary structure: The folding of a polypeptide backbone by means of internal hydrogen bonds between nearby amino acid residues giving rise to a regular arrangement defines the secondar ...
Energy Efficient Coils for Magnetic Stimulation of Peripheral Nerves
... Abstract — The preoccupation for improving the quality of life, for persons with different handicaps, led to extended research in the area of functional stimulation. Due to its advantages compared to electrical stimulation, the technique of magnetic stimulation of nerve fibers represents a new direc ...
... Abstract — The preoccupation for improving the quality of life, for persons with different handicaps, led to extended research in the area of functional stimulation. Due to its advantages compared to electrical stimulation, the technique of magnetic stimulation of nerve fibers represents a new direc ...
Lecture 1 ELEC 3105 OLD slides
... Given a group of charges we find the net electric field at any point in space by using the principle of superposition. This is a general principle that says a net effect is the sum of the individual effects. Here, the principle means that we first compute the electric field at the point in space due ...
... Given a group of charges we find the net electric field at any point in space by using the principle of superposition. This is a general principle that says a net effect is the sum of the individual effects. Here, the principle means that we first compute the electric field at the point in space due ...
Electricity Part 1 (ppt)
... • Charge is measured in Coulombs [unit: C] • Proton and electron have equal and opposite elementary charge = 1.6 x 10-19 C • Charge on proton = +1.6 x 10-19 C • Charge on electron = -1.6 x 10-19 C ...
... • Charge is measured in Coulombs [unit: C] • Proton and electron have equal and opposite elementary charge = 1.6 x 10-19 C • Charge on proton = +1.6 x 10-19 C • Charge on electron = -1.6 x 10-19 C ...
Molecular design of the photosystem II light
... light-harvesting complexes: they must bind sufficient pigments to maximize absorption; they must provide for the optimal orientation and configuration of pigments for energy transfer; they must tune the excited state energy levels of the pigments to promote energy transfer; and they must permit prot ...
... light-harvesting complexes: they must bind sufficient pigments to maximize absorption; they must provide for the optimal orientation and configuration of pigments for energy transfer; they must tune the excited state energy levels of the pigments to promote energy transfer; and they must permit prot ...
XII Cycle Test I - SBIOA Model Matriculation And Higher Secondary
... 1. State Gauss’s law in electrostatics. 2. Define electric flux and give its unit . 3. What is permittivity and relative permittivity? How are they related? 4. What is meant by additive nature of charges? 5. Define potential difference. 6. Give the properties of lines of force. 7. Explain the workin ...
... 1. State Gauss’s law in electrostatics. 2. Define electric flux and give its unit . 3. What is permittivity and relative permittivity? How are they related? 4. What is meant by additive nature of charges? 5. Define potential difference. 6. Give the properties of lines of force. 7. Explain the workin ...
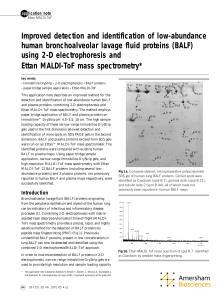
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5
... antibodies to a parallel trough along the separated proteins – The antibodies diffuse through the agar and form lines of precipitation with their respective antigens – The visible precipitant arcs can be compared to known standards to identify specific protein bands – Or to detect missing bands ...
... antibodies to a parallel trough along the separated proteins – The antibodies diffuse through the agar and form lines of precipitation with their respective antigens – The visible precipitant arcs can be compared to known standards to identify specific protein bands – Or to detect missing bands ...
Resonance-assignement-Structure-constraints
... The receiver coil picks up the signal from the sample. An analog-to-digital converter “reads” the voltage and sends it to the computer for data storage. ...
... The receiver coil picks up the signal from the sample. An analog-to-digital converter “reads” the voltage and sends it to the computer for data storage. ...
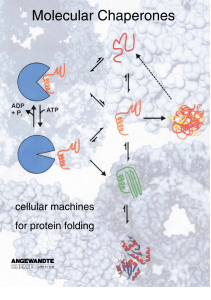
Molecular Chaperones - Cellular Machines for Protein Folding
... respectively, which are both required for the viability of E. coli.[25] Thus, at least one essential E. coli protein cannot fold without assistance from the GroE chaperone. 2.1.1. Structure of the GroE Chaperone The most striking feature of GroEL is its quaternary structure, which resembles a barrel ...
... respectively, which are both required for the viability of E. coli.[25] Thus, at least one essential E. coli protein cannot fold without assistance from the GroE chaperone. 2.1.1. Structure of the GroE Chaperone The most striking feature of GroEL is its quaternary structure, which resembles a barrel ...
Subwavelength imaging of light confinement in high-Q/small
... Additionally, we also note that the characteristic beating length is ⬃600 nm, which surprisingly corresponds to twice the separation distance between the standing wave antinodes 共or nodes兲 in the middle of the waveguide. As the alternation of the hot and dark spots along the two edges of the wavegui ...
... Additionally, we also note that the characteristic beating length is ⬃600 nm, which surprisingly corresponds to twice the separation distance between the standing wave antinodes 共or nodes兲 in the middle of the waveguide. As the alternation of the hot and dark spots along the two edges of the wavegui ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Carbon dioxide
... mode region, the shape of the band is not altered too much as can be seen on Fig. 3 (middle panel), even when the substructure appears in the 15.2 µm band. The temperature at which the bending mode shows a triple substructure is roughly related to the strength of the interaction between the acid and ...
... mode region, the shape of the band is not altered too much as can be seen on Fig. 3 (middle panel), even when the substructure appears in the 15.2 µm band. The temperature at which the bending mode shows a triple substructure is roughly related to the strength of the interaction between the acid and ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.