protein structure - MBBS Students Club
... proceed in the same direction (i.e. the direction of N-terminal to C-terminal ends is the same). • In antiparallel sheets adjacent chains are aligned in opposite directions. ...
... proceed in the same direction (i.e. the direction of N-terminal to C-terminal ends is the same). • In antiparallel sheets adjacent chains are aligned in opposite directions. ...
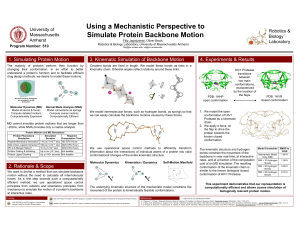
PROTEIN STRUCTURE
... proceed in the same direction (i.e. the direction of N-terminal to C-terminal ends is the same). • In antiparallel sheets adjacent chains are aligned in opposite directions. ...
... proceed in the same direction (i.e. the direction of N-terminal to C-terminal ends is the same). • In antiparallel sheets adjacent chains are aligned in opposite directions. ...
•How vision works •What is light •Wavelength and Frequency: c = f λ
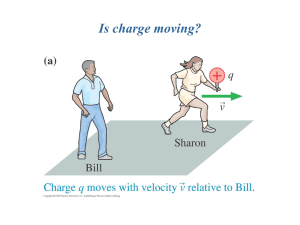
... Faraday showed: a changing magnetic field can create an electric field. (aside: this is how electric generators work--they move a magnet near a wire; moving the magnetic varies the magnetic field, creating an electric field, which moves electrons in the wire). Have you noticed symmetry in physics? F ...
... Faraday showed: a changing magnetic field can create an electric field. (aside: this is how electric generators work--they move a magnet near a wire; moving the magnetic varies the magnetic field, creating an electric field, which moves electrons in the wire). Have you noticed symmetry in physics? F ...
1. dia
... AA feature space: AAindex database http://www.genome.jp/aaindex A number is associated with every amino acid, which quantitatively describes how characteristic the given feature is to the AA (has 517 different scales at present) ...
... AA feature space: AAindex database http://www.genome.jp/aaindex A number is associated with every amino acid, which quantitatively describes how characteristic the given feature is to the AA (has 517 different scales at present) ...
2.2 KeyTerms
... of 1 g of water by 1°C; also the amount of heat energy that 1 g of water releases when it cools by 1°C. The Calorie (with a capital C), usually used to indicate the energy content of food, is a kilocalorie. A sugar in the form of a monosaccharide, disaccharide or polysaccharide. An attractive force ...
... of 1 g of water by 1°C; also the amount of heat energy that 1 g of water releases when it cools by 1°C. The Calorie (with a capital C), usually used to indicate the energy content of food, is a kilocalorie. A sugar in the form of a monosaccharide, disaccharide or polysaccharide. An attractive force ...
1B11 Foundations of Astronomy Star names and magnitudes
... 1B11 The electromagnetic spectrum When an electric charge is accelerated, electromagnetic energy is produced. This energy can be thought of as propagating as a wave – or, equally as a particle. The waves are usually referred to as light waves or radiation. The particles are known as photons. ...
... 1B11 The electromagnetic spectrum When an electric charge is accelerated, electromagnetic energy is produced. This energy can be thought of as propagating as a wave – or, equally as a particle. The waves are usually referred to as light waves or radiation. The particles are known as photons. ...
Biochemistry I
... Enzymology is the study of the macromolecules acting as catalysts for the processes that sustain life, in particular their structure, kinetics and function. Molecular biology focuses on deciphering the interactions between DNA, RNA and protein, which are responsible for DNA replication, gene express ...
... Enzymology is the study of the macromolecules acting as catalysts for the processes that sustain life, in particular their structure, kinetics and function. Molecular biology focuses on deciphering the interactions between DNA, RNA and protein, which are responsible for DNA replication, gene express ...
File - BHS Chemistry
... Describe how excessive heating can severely affect the plant protein’s ability to function correctly. Heat provides energy to the bonds in the protein and may enable some of them to break. By altering any of the bonds in the protein, its shape will be changed and it can no longer perform its ...
... Describe how excessive heating can severely affect the plant protein’s ability to function correctly. Heat provides energy to the bonds in the protein and may enable some of them to break. By altering any of the bonds in the protein, its shape will be changed and it can no longer perform its ...
Organic Chemistry Standards
... manufactured polymers used in daily life (e.g., polyester, nylon, and polyethylene). 10. c. Students know amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Proteins are large single-stranded polymers often made up of thousands of relatively small subunits called amino acids. The bond attaching two am ...
... manufactured polymers used in daily life (e.g., polyester, nylon, and polyethylene). 10. c. Students know amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Proteins are large single-stranded polymers often made up of thousands of relatively small subunits called amino acids. The bond attaching two am ...
Protein Origami
... Meanwhile, TeraGrid computational resources, and a TeraGrid Science Gateway called the Robetta Portal, are making it possible for thousands of researchers to look at the structures of thousands of proteins at once. These resources are helping move the field toward accurately predicting and designing ...
... Meanwhile, TeraGrid computational resources, and a TeraGrid Science Gateway called the Robetta Portal, are making it possible for thousands of researchers to look at the structures of thousands of proteins at once. These resources are helping move the field toward accurately predicting and designing ...
Lecture 4 - Université d`Ottawa
... • Sequence of amino acids in a protein is determined by the order of nucleotide bases in a gene (Primary structure) • One can deduce aa sequence from the sequence of nucleotides in the gene (or mRNA) • 3-D conformation is critical to proteins function • What determines the 3-D structure of proteins? ...
... • Sequence of amino acids in a protein is determined by the order of nucleotide bases in a gene (Primary structure) • One can deduce aa sequence from the sequence of nucleotides in the gene (or mRNA) • 3-D conformation is critical to proteins function • What determines the 3-D structure of proteins? ...
Repetitive Patterns in Proteins
... • Crossover during sexual recombination (“exon shuffling”) • (Retro)-Transposition -> These processes result in novel domain compositions, circularly permuted proteins (includes loss), or repetitive proteins ...
... • Crossover during sexual recombination (“exon shuffling”) • (Retro)-Transposition -> These processes result in novel domain compositions, circularly permuted proteins (includes loss), or repetitive proteins ...
Introduction to the Universe
... You are in a spaceship flying away from a star. When you were stationary, the starlight was in the visible light part of the electromagnetic spectrum. What part of the electromagnetic spectrum might the starlight appear to be in now? (A) Gamma ray (B) X ray (C) Ultraviolet (D) Infrared ...
... You are in a spaceship flying away from a star. When you were stationary, the starlight was in the visible light part of the electromagnetic spectrum. What part of the electromagnetic spectrum might the starlight appear to be in now? (A) Gamma ray (B) X ray (C) Ultraviolet (D) Infrared ...
Peptide Bonds - Newcastle University
... At the left hand side of the protein chain, there will be an amino acid with an unchanged –NH2 group. In this example it is leucine, and this is called the protein’s N-terminal. At the other end of the protein chain is and unchanged –COOH group, in this example it belongs to glycine. This is known a ...
... At the left hand side of the protein chain, there will be an amino acid with an unchanged –NH2 group. In this example it is leucine, and this is called the protein’s N-terminal. At the other end of the protein chain is and unchanged –COOH group, in this example it belongs to glycine. This is known a ...
Biochemistry- Ch 11. Carbohydrates
... Formation of a Mannose 6phosphate Marker I-cell Disease: deficient in the phosphotransferase. ...
... Formation of a Mannose 6phosphate Marker I-cell Disease: deficient in the phosphotransferase. ...
Organic Compounds
... •Hydrocarbons contain only _____________________ and __________________. Uses of Hydrocarbons •Many hydrocarbons are composed of a long polymer chain so they can be used to make ____________________ and _______________ ________________. •Many are __________________________________ so they are used f ...
... •Hydrocarbons contain only _____________________ and __________________. Uses of Hydrocarbons •Many hydrocarbons are composed of a long polymer chain so they can be used to make ____________________ and _______________ ________________. •Many are __________________________________ so they are used f ...
Scientific Notation Introduction Activity
... [note: conversion from m to km is three decimal places to the left 1000m = 1.0 km [standard] so 103m = 100km [exponent] and 1.0 x 103m = 1.0 x 100 km [scientific notation] always remember that 100 is equal to 1] ...
... [note: conversion from m to km is three decimal places to the left 1000m = 1.0 km [standard] so 103m = 100km [exponent] and 1.0 x 103m = 1.0 x 100 km [scientific notation] always remember that 100 is equal to 1] ...
Ch33 - Siena College
... was the first to understand that light is an oscillation of the electromagnetic field. Maxwell was able to predict that • Electromagnetic waves can exist at any frequency, not just at the frequencies of visible light. This prediction was the harbinger of radio waves. • All electromagnetic waves trav ...
... was the first to understand that light is an oscillation of the electromagnetic field. Maxwell was able to predict that • Electromagnetic waves can exist at any frequency, not just at the frequencies of visible light. This prediction was the harbinger of radio waves. • All electromagnetic waves trav ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.