UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Rotational Motion
... • Length of the velocity vector does not change (speed stays constant), but the vector’s direction constantly changes • Since acceleration = Change in velocity, the object accelerates as it moves around the track ...
... • Length of the velocity vector does not change (speed stays constant), but the vector’s direction constantly changes • Since acceleration = Change in velocity, the object accelerates as it moves around the track ...
Circular Motion and Rotation
... fact, if the forces are balanced, then an object in motion continues in motion in a straight line at constant speed. ...
... fact, if the forces are balanced, then an object in motion continues in motion in a straight line at constant speed. ...
Chap6. Circular Motion
... ii) If you spin the rock fast enough, there could be a point where the string snaps. If so, then a) the string would likely snap when the rock is at the bottom b) the string would likely snap when the rock is at the top v ...
... ii) If you spin the rock fast enough, there could be a point where the string snaps. If so, then a) the string would likely snap when the rock is at the bottom b) the string would likely snap when the rock is at the top v ...
vertical circles banked curves
... direction of Fnet & acceleration. It is NOT itself a force. • Any force applied at 90o to displacement or forces can cause curved or circular motion. • Fc is the amount of force required to keep an object of mass m, moving at speed v, in a circle of radius r. ...
... direction of Fnet & acceleration. It is NOT itself a force. • Any force applied at 90o to displacement or forces can cause curved or circular motion. • Fc is the amount of force required to keep an object of mass m, moving at speed v, in a circle of radius r. ...
PPT
... Newton's 2nd Law provides us the insight we need to explain why circular motion occurs. •An object accelerates toward the center of a circle due to the action of a net force in that direction. •This force is referred to as the Centripetal Force. •THIS IS NOT A NEW FORCE! ...
... Newton's 2nd Law provides us the insight we need to explain why circular motion occurs. •An object accelerates toward the center of a circle due to the action of a net force in that direction. •This force is referred to as the Centripetal Force. •THIS IS NOT A NEW FORCE! ...
Centrip to post - Physics: 1(AE) 2(B,D)
... • What is the magnitude of the centripetal force on the cart from the previous slide? __________ • If the mass of the cart is doubled, what happens to the centripetal force acting on the cart? • If the speed of the cart is doubled, what happens to the magnitude of the centripetal force of the on the ...
... • What is the magnitude of the centripetal force on the cart from the previous slide? __________ • If the mass of the cart is doubled, what happens to the centripetal force acting on the cart? • If the speed of the cart is doubled, what happens to the magnitude of the centripetal force of the on the ...
Circular motion notes
... out per unit time. This definition directly analogous to that of normal velocity v = dr dt . In what follows, we shall specialise to uniform circular motion, and so ω does not change with time. The period T for one revolution is the time taken to describe an angle 2π radians, thus using Definition ( ...
... out per unit time. This definition directly analogous to that of normal velocity v = dr dt . In what follows, we shall specialise to uniform circular motion, and so ω does not change with time. The period T for one revolution is the time taken to describe an angle 2π radians, thus using Definition ( ...
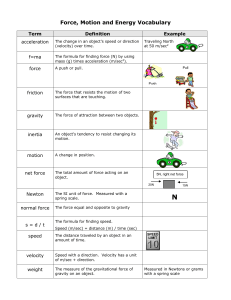
FORCE and MOTION UNIT VOCABULARY
... The force equal and opposite to gravity The formula for finding speed. Speed (m/sec) = distance (m) / time (sec) The distance traveled by an object in an amount of time. ...
... The force equal and opposite to gravity The formula for finding speed. Speed (m/sec) = distance (m) / time (sec) The distance traveled by an object in an amount of time. ...
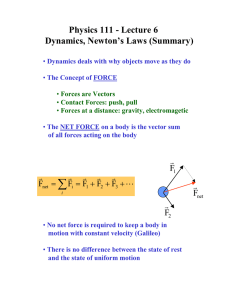
Physics 111 - Lecture 6 Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary)
... • Contact Forces: push, pull • Forces at a distance: gravity, electromagetic • The NET FORCE on a body is the vector sum of all forces acting on the body ...
... • Contact Forces: push, pull • Forces at a distance: gravity, electromagetic • The NET FORCE on a body is the vector sum of all forces acting on the body ...
Circular Motion
... U.C.M. and The Laws Remember N.S.L., the acceleration is directly proportional to the force Since the acceleration and the force are directly related, the force must ALSO point towards the center. This is called ...
... U.C.M. and The Laws Remember N.S.L., the acceleration is directly proportional to the force Since the acceleration and the force are directly related, the force must ALSO point towards the center. This is called ...
1 - Hingham Schools
... A girl stood at first base on a level playing field and tossed a softball at an angle of 35 degrees above the horizontal. It was caught by another player over home base at the same height above the ground as it was originally thrown. 1. At which point along its trajectory was the softball traveling ...
... A girl stood at first base on a level playing field and tossed a softball at an angle of 35 degrees above the horizontal. It was caught by another player over home base at the same height above the ground as it was originally thrown. 1. At which point along its trajectory was the softball traveling ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... A ball is going around in a circle attached to a string. If the string breaks at the instant shown, which path will the ball follow? ...
... A ball is going around in a circle attached to a string. If the string breaks at the instant shown, which path will the ball follow? ...
Uniform Circular Motion HW
... Help with the following vocabulary and problems can be found in the textbook, McGraw-Hill Physics, Chapter 6, Section 2, Circular Motion. Answer the following questions using the GUESS method. (Use g=10m/s2) 1. An air puck of mass m = 0.025 kg is tied to a string and allowed to revolve in a circle o ...
... Help with the following vocabulary and problems can be found in the textbook, McGraw-Hill Physics, Chapter 6, Section 2, Circular Motion. Answer the following questions using the GUESS method. (Use g=10m/s2) 1. An air puck of mass m = 0.025 kg is tied to a string and allowed to revolve in a circle o ...
Circular Motion
... Centripetal Force Calculation Centripetal force = mass x velocity^2 / radius Any of the data values may be changed . When finished with data entry, click on the quantity you wish to calculate in the formula above. Unit conversions will be carried out as you enter data , but values will not be force ...
... Centripetal Force Calculation Centripetal force = mass x velocity^2 / radius Any of the data values may be changed . When finished with data entry, click on the quantity you wish to calculate in the formula above. Unit conversions will be carried out as you enter data , but values will not be force ...
Canvas-g02 UCM Dyn - Clayton School District
... Does the speed of the particle change? ( YES / NO ) Does the direction of motion change? ( YES / NO ) Is an object in uniform circular motion accelerating? (YES / NO) If the particle is accelerating, what must be true about the forces acting on it? (Newton I, II)__________________________________ Ho ...
... Does the speed of the particle change? ( YES / NO ) Does the direction of motion change? ( YES / NO ) Is an object in uniform circular motion accelerating? (YES / NO) If the particle is accelerating, what must be true about the forces acting on it? (Newton I, II)__________________________________ Ho ...
Please review my solution to the problem and explain in
... This is a crossed fields problem with the two fields perpendicular to each other. B is perpendicular to v, out of the page. Since B is perpendicular, it does no work on the electron but instead deflects it in a circular path. q = 1.6 x 10-19 C v = (12.0j + 15.0k) km/s = square root(12.02 + 15.02) = ...
... This is a crossed fields problem with the two fields perpendicular to each other. B is perpendicular to v, out of the page. Since B is perpendicular, it does no work on the electron but instead deflects it in a circular path. q = 1.6 x 10-19 C v = (12.0j + 15.0k) km/s = square root(12.02 + 15.02) = ...
SESSION 5
... examples of this type of motion: a car travelling around a corner or curve, a person on a merry-go-round or a satellite orbiting the Earth. In each case the motion is the same. Although the speed of the object does not change the velocity quite clearly does since the direction is constantly changing ...
... examples of this type of motion: a car travelling around a corner or curve, a person on a merry-go-round or a satellite orbiting the Earth. In each case the motion is the same. Although the speed of the object does not change the velocity quite clearly does since the direction is constantly changing ...