chapter 7 notes - School District of La Crosse
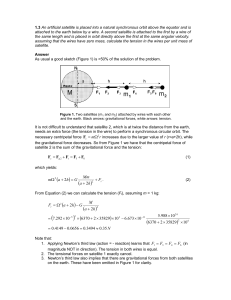
... 1. F1- the outward force of inertiatangent to the motion of the object. 2. F2- the inward force called centripetal force. ...
... 1. F1- the outward force of inertiatangent to the motion of the object. 2. F2- the inward force called centripetal force. ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... _____ 3. Which of the following is the correct equation for centripetal acceleration? ...
... _____ 3. Which of the following is the correct equation for centripetal acceleration? ...
Circular Motion - Garnet Valley School District
... circle at a constant speed – Speed is constant – Direction is changing – Acceleration vector points inward (center seeking) v ...
... circle at a constant speed – Speed is constant – Direction is changing – Acceleration vector points inward (center seeking) v ...
3 5-1 Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion
... constant the direction of the velocity is constantly changing Recall that acceleration is the change in velocity over the change in time and is a vector In circular motion, the direction is constantly changing which means an object moving in circular motion is ALWAYS accelerating, even if it’s v ...
... constant the direction of the velocity is constantly changing Recall that acceleration is the change in velocity over the change in time and is a vector In circular motion, the direction is constantly changing which means an object moving in circular motion is ALWAYS accelerating, even if it’s v ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
Circular Motion
... required to complete 96 revs is 2.40 secs. a) What is the period? b) What is the linear speed? c) Is your linear speed faster/slower/same if you move closer to the center? ...
... required to complete 96 revs is 2.40 secs. a) What is the period? b) What is the linear speed? c) Is your linear speed faster/slower/same if you move closer to the center? ...
South Pasadena • Physics Name 5 · Applications of Forces Period
... Calculate the frequency (rev / t) and speed of an object (v = 2 π r f) in circular motion. Know why the velocity vector points in the direction of motion of an object, which is tangent to the circular path, and why the acceleration and force vectors point toward the center of the circular path. ...
... Calculate the frequency (rev / t) and speed of an object (v = 2 π r f) in circular motion. Know why the velocity vector points in the direction of motion of an object, which is tangent to the circular path, and why the acceleration and force vectors point toward the center of the circular path. ...
Circular Motion
... rotations per unit of time Example: Carousel horses travel at same rotational speed but different tangential speed ...
... rotations per unit of time Example: Carousel horses travel at same rotational speed but different tangential speed ...
Document
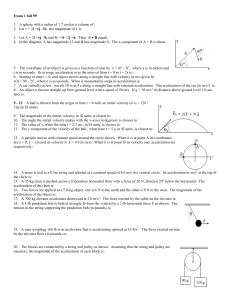
... 5. The coordinate of an object is given as a function of time by x = 4t 2 - 3t3 , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - ...
... 5. The coordinate of an object is given as a function of time by x = 4t 2 - 3t3 , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - ...
Topics covered in PH111 - Rose
... Scalars and vectors, decomposition of vectors into components, addition of vectors, cross and dot products, unit vectors. Kinematics: Position, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity and acceleration, derivation of the equations of motion at constant acceleration from velocity-time graph, ...
... Scalars and vectors, decomposition of vectors into components, addition of vectors, cross and dot products, unit vectors. Kinematics: Position, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity and acceleration, derivation of the equations of motion at constant acceleration from velocity-time graph, ...
Sects. 4.1 through 4.4
... lake. He pushes parallel to the length of the light pole, exerting on the bottom of the lake a force of 240 N. The pole lies in the vertical plane containing the keel of the boat. At one moment the pole makes an angle of 35.0° with the vertical and the water exerts a horizontal drag force of 47.5 N ...
... lake. He pushes parallel to the length of the light pole, exerting on the bottom of the lake a force of 240 N. The pole lies in the vertical plane containing the keel of the boat. At one moment the pole makes an angle of 35.0° with the vertical and the water exerts a horizontal drag force of 47.5 N ...
File
... • linear speed: distance moved per unit of time (speed). Ex: Merry Go Round • tangential speed (Vt) : the speed of an object that is moving along a circular path. The direction of motion is tangent to the circle. ...
... • linear speed: distance moved per unit of time (speed). Ex: Merry Go Round • tangential speed (Vt) : the speed of an object that is moving along a circular path. The direction of motion is tangent to the circle. ...