M-8 - University of Iowa Physics
... 4. What is the difference between static and kinetic friction? 5. An object moves in a circular path with constant speed. Is its velocity constant? 6. A child swings a ball attached to a string in a circle at a constant speed. Is the ball accelerating and if so what force provides this acceler ...
... 4. What is the difference between static and kinetic friction? 5. An object moves in a circular path with constant speed. Is its velocity constant? 6. A child swings a ball attached to a string in a circle at a constant speed. Is the ball accelerating and if so what force provides this acceler ...
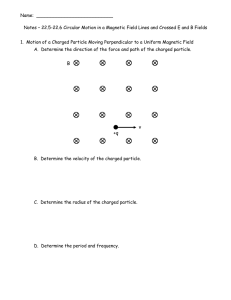
Name: Notes – 22.5-22.6 Circular Motion in a Magnetic Field Lines
... A proton with just the right velocity will pass straight through the apparatus shown below from left to right that has crossed E and B fields that are perpendicular to each other. The electric charges on the upper and lower plates are shown. ...
... A proton with just the right velocity will pass straight through the apparatus shown below from left to right that has crossed E and B fields that are perpendicular to each other. The electric charges on the upper and lower plates are shown. ...
Advanced Physics
... 5-6 Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation 5-7 Gravity near the Earth's Surface 5-8 Satellites and “Weightlessness” 5-10 Types of Forces in Nature ...
... 5-6 Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation 5-7 Gravity near the Earth's Surface 5-8 Satellites and “Weightlessness” 5-10 Types of Forces in Nature ...
11.2 Questions Force and Mass Determine Acceleration 1. What 3
... 1. What 3 concepts are involved in Newton’s second law? 8. A mass is 2kg. What other information do you need to calculate acceleration? 2. Look at the picture on page 354. What do the arrows in the diagrams show? 9. If an object moves at a constant speed, but it accelerates, what changes? 3. What ha ...
... 1. What 3 concepts are involved in Newton’s second law? 8. A mass is 2kg. What other information do you need to calculate acceleration? 2. Look at the picture on page 354. What do the arrows in the diagrams show? 9. If an object moves at a constant speed, but it accelerates, what changes? 3. What ha ...
Physics
... 4. a) Diagram the forces that acted on the airplanes in my airplane swing; explain what provides the centripetal force. b) If the planes have a mass of 60g and travel in a circle of radius 20 cm at a speed of 30 cm/sec what angle do they make with the vertical? 5. A ferris wheel whose radius is 10.0 ...
... 4. a) Diagram the forces that acted on the airplanes in my airplane swing; explain what provides the centripetal force. b) If the planes have a mass of 60g and travel in a circle of radius 20 cm at a speed of 30 cm/sec what angle do they make with the vertical? 5. A ferris wheel whose radius is 10.0 ...
Quiz #3 - Dawson College
... b) in the direction of motion. c) directed upward. d) opposite its velocity. 6. An apple weighs 1 N. The magnitude of net force on the apple when it is in free-fall is a) 10 N. b) 0.1 N. c) 0 N. d) 1 N. e) none of these 7. A girl pulls on a 10-kg wagon with a constant net force of 30 N. What is the ...
... b) in the direction of motion. c) directed upward. d) opposite its velocity. 6. An apple weighs 1 N. The magnitude of net force on the apple when it is in free-fall is a) 10 N. b) 0.1 N. c) 0 N. d) 1 N. e) none of these 7. A girl pulls on a 10-kg wagon with a constant net force of 30 N. What is the ...
UCM HONORS PHYSICS 2016 2017
... Uniform Circular Motion Uniform circular motion is defined as an object moving at constant speed (not constant velocity!) around a circle with a fixed radius. As the object moves around the circle, the length of its position vector (the radius) doesn’t change, but the direction does. Same thing w ...
... Uniform Circular Motion Uniform circular motion is defined as an object moving at constant speed (not constant velocity!) around a circle with a fixed radius. As the object moves around the circle, the length of its position vector (the radius) doesn’t change, but the direction does. Same thing w ...
r (t) - VT Math
... 4 feet above the ground with an initial speed of 95 feet per second at a launch angle of 42 degrees. How high above the ground will the projectile be when it is 224 feet downrange? ...
... 4 feet above the ground with an initial speed of 95 feet per second at a launch angle of 42 degrees. How high above the ground will the projectile be when it is 224 feet downrange? ...
Chapter 5 PowerPoint
... 5-2 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Newton F=ma Object moving in a circle must be acted on by a force Fr=mar=mv2/r Net force must be directed toward the center of the circle. Centripetal force - force directed towards center of circle ...
... 5-2 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Newton F=ma Object moving in a circle must be acted on by a force Fr=mar=mv2/r Net force must be directed toward the center of the circle. Centripetal force - force directed towards center of circle ...
3, 4, 6, 9, 14 / 5, 8, 13, 18, 23, 27, 32, 52
... that on earth, the safe speed for the same curve on the moon would be less than that on earth. In other words, other things being equal, it would be more difficult to drive at high speed around an unbanked curve on the moon as compared to driving around the same curve on the earth. ...
... that on earth, the safe speed for the same curve on the moon would be less than that on earth. In other words, other things being equal, it would be more difficult to drive at high speed around an unbanked curve on the moon as compared to driving around the same curve on the earth. ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... • All points on the object have the same rotational velocity. • All points on the object do not have the same Tangential velocity ...
... • All points on the object have the same rotational velocity. • All points on the object do not have the same Tangential velocity ...