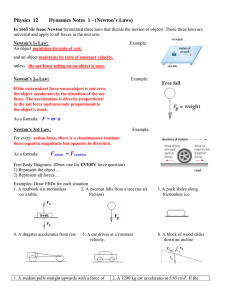
Experiment 1G Uniform Circular Motion
... Static Test of the Centripetal Force Consider the bob hanging from the crossarm with the stretched spring and a cord with suspended weights attached to it as in Figure 1. The horizontal forces on the bob are provided by the spring and the tension in the spring due to the suspended weights. If the bo ...
... Static Test of the Centripetal Force Consider the bob hanging from the crossarm with the stretched spring and a cord with suspended weights attached to it as in Figure 1. The horizontal forces on the bob are provided by the spring and the tension in the spring due to the suspended weights. If the bo ...
How much force is required to inflate a high pressure
... During your travels through deep space you discover a new solar system. You land on the outermost planet and determine that the acceleration due to gravity is 2.7 m/s^2. If your mass back on Earth is 72 kg, what force would you exert on a scale in pounds while standing on the planet's surface? The ...
... During your travels through deep space you discover a new solar system. You land on the outermost planet and determine that the acceleration due to gravity is 2.7 m/s^2. If your mass back on Earth is 72 kg, what force would you exert on a scale in pounds while standing on the planet's surface? The ...
Semester Exam Review
... 1. What is a contact force? force that result from physical contact between objects 2. What is a field force? force that do not involve physical contact such as magnetism and gravity 3. What is inertia? The tendency of an object not to accelerate. Inertia means that objects at rest tend to stay at r ...
... 1. What is a contact force? force that result from physical contact between objects 2. What is a field force? force that do not involve physical contact such as magnetism and gravity 3. What is inertia? The tendency of an object not to accelerate. Inertia means that objects at rest tend to stay at r ...
Unit 5 Force and Motion Vocabulary
... direction, or motion; net force equals zero Unbalanced force – unequal forces on an object that may result in a change in position, direction or motion; net force does not equal zero Inertia ...
... direction, or motion; net force equals zero Unbalanced force – unequal forces on an object that may result in a change in position, direction or motion; net force does not equal zero Inertia ...
Physics 121 Exam Sheet - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... FAB is the force exerted on body B by body A and FBA is the force exerted on body A by body B. This law is sometimes called the Law of Action and Reaction. This is a somewhat misleading title because it implicitly implies a cause-effect relation between the two forces which are associated with any i ...
... FAB is the force exerted on body B by body A and FBA is the force exerted on body A by body B. This law is sometimes called the Law of Action and Reaction. This is a somewhat misleading title because it implicitly implies a cause-effect relation between the two forces which are associated with any i ...
Name of Model
... 7. Rollercoasters use a hill for riders to gain speed followed by an upside down loop. The loops are designed with large radius bottoms and small radius tops, and such a shape is called a clothoid. Answer the following questions in order to find out why the clothoid is used. The speed of the roller ...
... 7. Rollercoasters use a hill for riders to gain speed followed by an upside down loop. The loops are designed with large radius bottoms and small radius tops, and such a shape is called a clothoid. Answer the following questions in order to find out why the clothoid is used. The speed of the roller ...
Splitting Strategy: 2 Dimensional Problems The first concern in
... The first concern in solving 2-dimensional problems is dividing them into two 1dimensional problems we can solve with our tools. Here is a general procedure for approaching these problems. ...
... The first concern in solving 2-dimensional problems is dividing them into two 1dimensional problems we can solve with our tools. Here is a general procedure for approaching these problems. ...
Study Guide Chapter 2 Motion
... 18. How does one keep up with their instantaneous speed? 19. A truck changing its speed from 23m/s to 12m/s is undergoing ________________acceleration. 20. 45m/s south is an example of __________________. 21. The slope of a distance-time graph gives the ______________________. 22. How are speed, dis ...
... 18. How does one keep up with their instantaneous speed? 19. A truck changing its speed from 23m/s to 12m/s is undergoing ________________acceleration. 20. 45m/s south is an example of __________________. 21. The slope of a distance-time graph gives the ______________________. 22. How are speed, dis ...
Forces
... • How is the motion of an object affected when a force acts on it? • How does air resistance affect the acceleration of a falling object? • Describe why a projectile follows a curved ...
... • How is the motion of an object affected when a force acts on it? • How does air resistance affect the acceleration of a falling object? • Describe why a projectile follows a curved ...
Gravitation and Rotational Motion
... Torque- is a measure of how effectively a force causes rotation. The magnitude of torque is the product of the force and the lever arm. Torque is measured in Newton-meters. p.s. (multiply by sin theta if used at an angle) Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion: states that angular acceleration is ...
... Torque- is a measure of how effectively a force causes rotation. The magnitude of torque is the product of the force and the lever arm. Torque is measured in Newton-meters. p.s. (multiply by sin theta if used at an angle) Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion: states that angular acceleration is ...
Physical Science Gravity
... stronger as the masses increase and rapidly become weaker as the distance between the masses increases, F=G(m1m2/d2) • Evaluate the concept that free-fall acceleration near Earth’s surface is independent of the mass of the falling object • Demonstrate mathematically how free-fall acceleration relate ...
... stronger as the masses increase and rapidly become weaker as the distance between the masses increases, F=G(m1m2/d2) • Evaluate the concept that free-fall acceleration near Earth’s surface is independent of the mass of the falling object • Demonstrate mathematically how free-fall acceleration relate ...
Physics Final Exam Review Packet
... 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 25.0 m/s from a height of 2.0 m. a. How long does it take to reach its highest point? b. How high does the ball rise? c. How long does the ball take to hit the ground after it reaches the highest point? d. What is the ball’s velocity when it retu ...
... 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 25.0 m/s from a height of 2.0 m. a. How long does it take to reach its highest point? b. How high does the ball rise? c. How long does the ball take to hit the ground after it reaches the highest point? d. What is the ball’s velocity when it retu ...
Centripetal acceleration
... you away from the center of the circle? • Newton’s first law: If no net force is acting on an object, it will continue with the same velocity (inertia of mass) • Velocity is a vector (points to a direction) • If no net force is acting on an object, it will not change its direction. • A force is acti ...
... you away from the center of the circle? • Newton’s first law: If no net force is acting on an object, it will continue with the same velocity (inertia of mass) • Velocity is a vector (points to a direction) • If no net force is acting on an object, it will not change its direction. • A force is acti ...
Force and Motion
... a shopping cart full of groceries has a mass of 150 kg. if you push the cart to the right with 1500 N, what will the acceleration of the cart be? ...
... a shopping cart full of groceries has a mass of 150 kg. if you push the cart to the right with 1500 N, what will the acceleration of the cart be? ...