Nuclear Forces
... • An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... • An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
Review1 - UCF Physics
... Drawing a FBD of forces on an object (on, not by) 1. Choose the object to analyze. Draw it as a dot. 2. What forces physically touch this object? This object, not some other 3. What “action at a distance” forces act on the object? Gravity is the only one for this PHYS2053 4. Draw these forces as ar ...
... Drawing a FBD of forces on an object (on, not by) 1. Choose the object to analyze. Draw it as a dot. 2. What forces physically touch this object? This object, not some other 3. What “action at a distance” forces act on the object? Gravity is the only one for this PHYS2053 4. Draw these forces as ar ...
IB Mechanics objectives
... where the displacement is not in the same direction as the force. A typical example would be calculating the work done in extending a spring. See 2.3.7. ...
... where the displacement is not in the same direction as the force. A typical example would be calculating the work done in extending a spring. See 2.3.7. ...
mDv
... Why does a car skid when going too fast around a curve? I am pushing a box across the floor. How does the magnitude of the force I am pushing on the box compare to the magnitude of the force that the box is pushing on me? I am lifting a 20 kg mass by a rope with constant speed. What is the tension ...
... Why does a car skid when going too fast around a curve? I am pushing a box across the floor. How does the magnitude of the force I am pushing on the box compare to the magnitude of the force that the box is pushing on me? I am lifting a 20 kg mass by a rope with constant speed. What is the tension ...
Causes of circular motion
... Rotational motion refers to the motion of a body or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the rotation occurs. Circular motion refers to the motion of a particular point on an object that is undergoing rotational motion. Because the direction of motion is co ...
... Rotational motion refers to the motion of a body or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the rotation occurs. Circular motion refers to the motion of a particular point on an object that is undergoing rotational motion. Because the direction of motion is co ...
Forces Review
... The questions below are intended to assist you with reviewing the information previously covered on forces. This is not everything we have covered on forces but it does represent an overview of many of the topics we have studies so far. 1. Three spring scales are attached along a straight line as sh ...
... The questions below are intended to assist you with reviewing the information previously covered on forces. This is not everything we have covered on forces but it does represent an overview of many of the topics we have studies so far. 1. Three spring scales are attached along a straight line as sh ...
Newton`s Laws
... 5. An applied force of 50 N is used to accelerate an object to the right across a frictional surface. The object encounters 10 N of friction. Use the diagram to determine the normal force, the net force, the mass, and the acceleration of the object. (Neglect air resistance.) ...
... 5. An applied force of 50 N is used to accelerate an object to the right across a frictional surface. The object encounters 10 N of friction. Use the diagram to determine the normal force, the net force, the mass, and the acceleration of the object. (Neglect air resistance.) ...
Mass and Motion
... The change in motion is proportional to the net force and the change is made in the same direction as the net force. Net force gives rise to acceleration. Force = mass x acceleration (Newton’s second law). ...
... The change in motion is proportional to the net force and the change is made in the same direction as the net force. Net force gives rise to acceleration. Force = mass x acceleration (Newton’s second law). ...
Forces 2-1b0y3mn
... 7. A 3.45 g hockey puck rests on a flat, smooth table. A horizontal net force of 85.0 N acts on it for 1.10 seconds. The puck slides across the table at the end of that time and then falls off the table. The table’s top surface is 85.0 cm above the deck. Find (a) the acceleration of the puck, (b) th ...
... 7. A 3.45 g hockey puck rests on a flat, smooth table. A horizontal net force of 85.0 N acts on it for 1.10 seconds. The puck slides across the table at the end of that time and then falls off the table. The table’s top surface is 85.0 cm above the deck. Find (a) the acceleration of the puck, (b) th ...
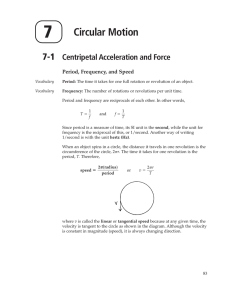
Chapter 7
... Tangential speed is the thought that as an object is traveling in a circle, with what speed is it traveling linearly. Or a more practical use would be if the object were to break its circular motion, what path would it travel? So what would the initial velocity be of the object as it breaks from the ...
... Tangential speed is the thought that as an object is traveling in a circle, with what speed is it traveling linearly. Or a more practical use would be if the object were to break its circular motion, what path would it travel? So what would the initial velocity be of the object as it breaks from the ...
Division I only 2 Division I only ATTENTION: All Division I students
... 7. A mass connected to a string swings back and forth as a pendulum with snapshots of the motion seen in the figure. Ignore the friction in the system. Which of the following statements about the pendulum-Earth A system is correct? ...
... 7. A mass connected to a string swings back and forth as a pendulum with snapshots of the motion seen in the figure. Ignore the friction in the system. Which of the following statements about the pendulum-Earth A system is correct? ...
Document
... by one equation alone. Acceleration - Force / Mass. This law governs acceleration and is simple to understand. You can lower the acceleration which is produced by your body in a collision by using safety features like crumple zones and air bags. "The acceleration a of a mass m by an unbalanced force ...
... by one equation alone. Acceleration - Force / Mass. This law governs acceleration and is simple to understand. You can lower the acceleration which is produced by your body in a collision by using safety features like crumple zones and air bags. "The acceleration a of a mass m by an unbalanced force ...
Motion and Simple Machines TEST Study Guide 2014 (Key
... the left with the description of motion on the right. C ...
... the left with the description of motion on the right. C ...