Momentum - Issaquah Connect
... a. A VW beetle moving at a high velocity b. A big truck moving at the same ...
... a. A VW beetle moving at a high velocity b. A big truck moving at the same ...
Document
... Two boxes are connected by a cord running over a pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table is 0.20. We ignore the mass of the cord and pulley and any friction in the pulley, which means we can assume that a force applied to one end of the cord will have the same magnitu ...
... Two boxes are connected by a cord running over a pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table is 0.20. We ignore the mass of the cord and pulley and any friction in the pulley, which means we can assume that a force applied to one end of the cord will have the same magnitu ...
PHY101 - National Open University of Nigeria
... X, Y, Z are its coordinates. A new system of reference with 01 as the origin is drawn as shown where, for convenience, 01 is taken along the X axis of the first system. Let 01X, 01Y1 and 01Z1 be the corresponding axes of the new system. 01Y1 and 01Z1 are evidently parallel to 0Y and 0Z. The point, P ...
... X, Y, Z are its coordinates. A new system of reference with 01 as the origin is drawn as shown where, for convenience, 01 is taken along the X axis of the first system. Let 01X, 01Y1 and 01Z1 be the corresponding axes of the new system. 01Y1 and 01Z1 are evidently parallel to 0Y and 0Z. The point, P ...
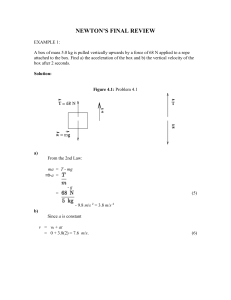
Final Newtons Review
... d. The acceleration of an object is directly dependent upon its mass and inversely dependent upon its net force. e. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 2, then the new acceleration would be 10 m/s/s. f. An object has an accel ...
... d. The acceleration of an object is directly dependent upon its mass and inversely dependent upon its net force. e. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 2, then the new acceleration would be 10 m/s/s. f. An object has an accel ...
PHY 121
... III. GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF DATA: Some essentials in plotting a graph. 1. Arrange the numbers to be plotted in tabular form if they are not already so arranged. 2. Decide which of the two quantities is to be plotted along the X-axis and which along the Y-axis. It is customary to plot the indep ...
... III. GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF DATA: Some essentials in plotting a graph. 1. Arrange the numbers to be plotted in tabular form if they are not already so arranged. 2. Decide which of the two quantities is to be plotted along the X-axis and which along the Y-axis. It is customary to plot the indep ...
PHY 116
... III. GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF DATA: Some essentials in plotting a graph. 1. Arrange the numbers to be plotted in tabular form if they are not already so arranged. 2. Decide which of the two quantities is to be plotted along the X-axis and which along the Y-axis. It is customary to plot the indep ...
... III. GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION OF DATA: Some essentials in plotting a graph. 1. Arrange the numbers to be plotted in tabular form if they are not already so arranged. 2. Decide which of the two quantities is to be plotted along the X-axis and which along the Y-axis. It is customary to plot the indep ...
FREE Sample Here
... the same place it would if the bus were at rest? Answer: In accord with Newton's first law, in both cases there is no horizontal force on the dropped pencil, so no change occurs horizontally. The dropped pencil in the moving bus simply keeps up with you as you move, not changing its velocity in the ...
... the same place it would if the bus were at rest? Answer: In accord with Newton's first law, in both cases there is no horizontal force on the dropped pencil, so no change occurs horizontally. The dropped pencil in the moving bus simply keeps up with you as you move, not changing its velocity in the ...
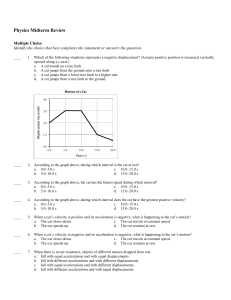
Physics Midterm Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... 70. What is the magnitude of the resultant displacement of a dog looking for its bone in the yard if the dog first heads 57.0 north of west for 10.3 m and then turns and heads west for 4.00 m? 71. A stone is thrown at an angle of 30.0 above the horizontal from the top edge of a cliff with an init ...
... 70. What is the magnitude of the resultant displacement of a dog looking for its bone in the yard if the dog first heads 57.0 north of west for 10.3 m and then turns and heads west for 4.00 m? 71. A stone is thrown at an angle of 30.0 above the horizontal from the top edge of a cliff with an init ...
Preview Sample 2
... the same place it would if the bus were at rest? Answer: In accord with Newton's first law, in both cases there is no horizontal force on the dropped pencil, so no change occurs horizontally. The dropped pencil in the moving bus simply keeps up with you as you move, not changing its velocity in the ...
... the same place it would if the bus were at rest? Answer: In accord with Newton's first law, in both cases there is no horizontal force on the dropped pencil, so no change occurs horizontally. The dropped pencil in the moving bus simply keeps up with you as you move, not changing its velocity in the ...
Document
... Simultaneous solution of the equations leads to v0 0 and a 0.40 m s2 . We now have two ways to finish the problem. One is to compute force from F = ma and then obtain the work from Eq. 7-7. The other is to find K as a way of computing W (in accordance with Eq. 7-10). In this latter approach, we ...
... Simultaneous solution of the equations leads to v0 0 and a 0.40 m s2 . We now have two ways to finish the problem. One is to compute force from F = ma and then obtain the work from Eq. 7-7. The other is to find K as a way of computing W (in accordance with Eq. 7-10). In this latter approach, we ...
Old Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... T062: Q9. An impulsive force Fx as a function of time (in ms) is shown in the Fig. 3 as applied to an object (m = 5.0 kg) at rest. What will be its final speed? A) 2.0 m/s. Q10. Each object in Fig. 4 has a mass of 2.0 kg. The mass m1 is at rest, m2 has a speed of 3.0 m/s in the direction of +ve x-ax ...
... T062: Q9. An impulsive force Fx as a function of time (in ms) is shown in the Fig. 3 as applied to an object (m = 5.0 kg) at rest. What will be its final speed? A) 2.0 m/s. Q10. Each object in Fig. 4 has a mass of 2.0 kg. The mass m1 is at rest, m2 has a speed of 3.0 m/s in the direction of +ve x-ax ...
ampere`s law - Project PHYSNET
... 3a. Magnetic Field Near a Long Thin Wire. The magnetic field ~ at some point in space, associated with a current I in a long straight B wire, can be calculated using Ampere’s law. The integration path we choose is a circle, centered on the wire (see Fig. 3) and going through the ~ By symmetry, we ex ...
... 3a. Magnetic Field Near a Long Thin Wire. The magnetic field ~ at some point in space, associated with a current I in a long straight B wire, can be calculated using Ampere’s law. The integration path we choose is a circle, centered on the wire (see Fig. 3) and going through the ~ By symmetry, we ex ...