SPRING 2016 PHYS 1211 (as of Jan. 11/2016)
... As a University of Georgia student, you have agreed to abide by the University’s academic honesty policy, “A Culture of Honesty,” and the Student Honor Code. All academic work must meet the standards described in “A Culture of Honesty” found at: www.uga.edu/honesty. Lack of knowledge of the academic ...
... As a University of Georgia student, you have agreed to abide by the University’s academic honesty policy, “A Culture of Honesty,” and the Student Honor Code. All academic work must meet the standards described in “A Culture of Honesty” found at: www.uga.edu/honesty. Lack of knowledge of the academic ...
sy18_nov02_f11
... Now the pulleys are uniform disks of 4.00 kg mass and 0.50 m radius. The rope does not slip. T1 m1 ...
... Now the pulleys are uniform disks of 4.00 kg mass and 0.50 m radius. The rope does not slip. T1 m1 ...
Unit 4 Packet (Labs)
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
Gr. 11 Physics Forces
... We will use a spring scale to measure the size of forces. First you need to calibrate the spring scale. Hold the scale horizontally or vertically just as you will use it when measuring, but without pulling on the hook. Adjust the scale (a sliding cover or nut at the top) so it reads zero. The scale ...
... We will use a spring scale to measure the size of forces. First you need to calibrate the spring scale. Hold the scale horizontally or vertically just as you will use it when measuring, but without pulling on the hook. Adjust the scale (a sliding cover or nut at the top) so it reads zero. The scale ...
On the relation between the Bicircular model and the Coupled
... Circular restricted Three-Body problem The CR3BP is a simplified case of the general Three-Body Problem and models the motion of a massless particle under the gravitational influence of two bodies, with masses M1 < M2 , that are revolving with constant angular velocity in circular orbit around their ...
... Circular restricted Three-Body problem The CR3BP is a simplified case of the general Three-Body Problem and models the motion of a massless particle under the gravitational influence of two bodies, with masses M1 < M2 , that are revolving with constant angular velocity in circular orbit around their ...
Notes with Impulse
... If you run into a brick wall with momentum x, the contact time is short and the force large (ouch!) If you run into a wall of pillows with momentum x, the contact time is long and force small (pain is minimized) ...
... If you run into a brick wall with momentum x, the contact time is short and the force large (ouch!) If you run into a wall of pillows with momentum x, the contact time is long and force small (pain is minimized) ...
Honors Review for Midterm
... ____ 10. A 6.0-kg wooden block is pulled across a carpet with a force of F = 36 N. The block begins at rest and accelerates to a velocity of 0.25 m/s in 0.50 s. What is the force of friction acting on the block? a. 3.0 N c. 36 N b. 33 N d. 39 N ____ 11. Which graph most accurately describes the rela ...
... ____ 10. A 6.0-kg wooden block is pulled across a carpet with a force of F = 36 N. The block begins at rest and accelerates to a velocity of 0.25 m/s in 0.50 s. What is the force of friction acting on the block? a. 3.0 N c. 36 N b. 33 N d. 39 N ____ 11. Which graph most accurately describes the rela ...
physics - Board of Studies
... • Part A 15 multiple-choice questions, each worth 1 mark. Mark your answers in pencil on the Answer Sheet provided. • Part B 10 questions, each worth 3 marks. Answer this Part in the Part B Answer Book. • Part C 6 questions, each worth 5 marks. Answer this Part in the Part C Answer Book. • Write you ...
... • Part A 15 multiple-choice questions, each worth 1 mark. Mark your answers in pencil on the Answer Sheet provided. • Part B 10 questions, each worth 3 marks. Answer this Part in the Part B Answer Book. • Part C 6 questions, each worth 5 marks. Answer this Part in the Part C Answer Book. • Write you ...
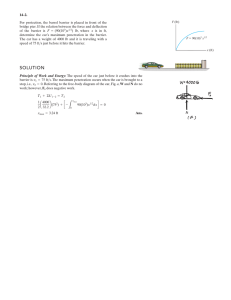
SOLUTION
... Free-Body Diagram:The free-body diagram of the passenger at positions B and C are shown in Figs. a and b, respectively. Equations of Motion: Here, an = NB = 4mg. By referring to Fig. a, + c ©Fn = man; ...
... Free-Body Diagram:The free-body diagram of the passenger at positions B and C are shown in Figs. a and b, respectively. Equations of Motion: Here, an = NB = 4mg. By referring to Fig. a, + c ©Fn = man; ...
V p
... It may be that kinetic energy is conserved in a collision. In that case, the collision is “elastic.” You can use Kf = Ki any time you know a collision is elastic. ...
... It may be that kinetic energy is conserved in a collision. In that case, the collision is “elastic.” You can use Kf = Ki any time you know a collision is elastic. ...
MATH 312 Section 5.1: Linear Models: IVPs
... We end with another example involving driven motion. Example A mass of 1 slug is attached to a spring with constant 5 = lb/ft. The mass is released 1 foot below equilibrium, with downward velocity of 5 ft/sec. A viscus medium dampens with a force numerically equivalent to 2 times the instantaneous v ...
... We end with another example involving driven motion. Example A mass of 1 slug is attached to a spring with constant 5 = lb/ft. The mass is released 1 foot below equilibrium, with downward velocity of 5 ft/sec. A viscus medium dampens with a force numerically equivalent to 2 times the instantaneous v ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued
... External forces – Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity (and momentum) of a mass. ...
... External forces – Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity (and momentum) of a mass. ...