Systems of Particles - UCF College of Sciences
... m1 = m2 – the particles exchange velocities – When a very heavy particle collides head-on with a very light one initially at rest, the heavy particle continues in motion unaltered and the light particle rebounds with a speed of about twice the initial speed of the heavy particle – When a very light ...
... m1 = m2 – the particles exchange velocities – When a very heavy particle collides head-on with a very light one initially at rest, the heavy particle continues in motion unaltered and the light particle rebounds with a speed of about twice the initial speed of the heavy particle – When a very light ...
Packet 8: Impulse Momentum
... of two cans to be isolated, the post-explosion momentum of the system ____. A) is dependent upon the mass and velocities of the two cans B) is dependent upon the velocities of the two cans (but not their mass) C) is typically a very large value D) can be a positive, negative or zero value E) is defi ...
... of two cans to be isolated, the post-explosion momentum of the system ____. A) is dependent upon the mass and velocities of the two cans B) is dependent upon the velocities of the two cans (but not their mass) C) is typically a very large value D) can be a positive, negative or zero value E) is defi ...
B. Nuclear Physics
... E. Circular Motion And Rotation Reading/Homework Assignments: Selected items from Chapters 5 and 8 Physlet problem: 3:15 Learning Objectives: At the end of this unit the student should be able to: • Explain the characteristics of uniform circular motion • Derive the equation for centripetal accelera ...
... E. Circular Motion And Rotation Reading/Homework Assignments: Selected items from Chapters 5 and 8 Physlet problem: 3:15 Learning Objectives: At the end of this unit the student should be able to: • Explain the characteristics of uniform circular motion • Derive the equation for centripetal accelera ...
Chapter 5 – Linking Forces to Momentum and Energy
... The negative sign is associated with the restoring nature of the force. When you displace the end of the spring in one direction from its equilibrium position the spring applies a force in the opposite direction, essentially in an attempt to return the system toward the equilibrium position (the pos ...
... The negative sign is associated with the restoring nature of the force. When you displace the end of the spring in one direction from its equilibrium position the spring applies a force in the opposite direction, essentially in an attempt to return the system toward the equilibrium position (the pos ...
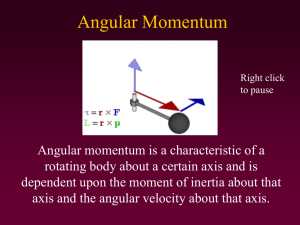
MOMENTUM!
... Ball B deflects much less than ball A when the same force is applied because ball B had a greater initial momentum. ...
... Ball B deflects much less than ball A when the same force is applied because ball B had a greater initial momentum. ...
4 Newton’s Second Law Experiment 4.1
... The standard SI unit for force is kg m/s2 , which is given the name Newton (N). In this lab it will be more convenient to make measurements in grams (g) and centimeters (cm) so you will be using the cgs system of units instead. Note: In the cgs system of units, the unit for force is the dyne: 1 dyne ...
... The standard SI unit for force is kg m/s2 , which is given the name Newton (N). In this lab it will be more convenient to make measurements in grams (g) and centimeters (cm) so you will be using the cgs system of units instead. Note: In the cgs system of units, the unit for force is the dyne: 1 dyne ...
ch13
... and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the relation is the velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown and the maximum deflection of the spring velocity at the final ...
... and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the relation is the velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown and the maximum deflection of the spring velocity at the final ...
chapter 7
... orbit and beyond, a rocket will move simply because there is some gas coming out of its nozzle. But how do you quantify the force necessary to move such a rocket? To do this, we need to introduce the concepts of thrust and impulse. Thrust and impulse quantify the propulsion capabilities of a rocket ...
... orbit and beyond, a rocket will move simply because there is some gas coming out of its nozzle. But how do you quantify the force necessary to move such a rocket? To do this, we need to introduce the concepts of thrust and impulse. Thrust and impulse quantify the propulsion capabilities of a rocket ...
A grindstone with a radius of 0.610 m is being used to sharpen an ax
... position, with zero speed there. (a) How much work is done on the ball by the gravitational force from the initial point to the lowest point? (b) How much work is done on the ball by the gravitational force from the initial point to the highest point? (c) How much work is done on the ball by the gra ...
... position, with zero speed there. (a) How much work is done on the ball by the gravitational force from the initial point to the lowest point? (b) How much work is done on the ball by the gravitational force from the initial point to the highest point? (c) How much work is done on the ball by the gra ...
Physics Pre AP –Scope and Sequence –Year at a Glance
... Waves/Optics. Approximate Time: 3 weeks. 9th 3 weeks Essential Learning Outcomes TEKS Students should understand image formation by plane or spherical mirrors so they can: • Relate the focal point of a spherical mirror to its center of curvature. • Given a diagram of a mirror with the focal point sh ...
... Waves/Optics. Approximate Time: 3 weeks. 9th 3 weeks Essential Learning Outcomes TEKS Students should understand image formation by plane or spherical mirrors so they can: • Relate the focal point of a spherical mirror to its center of curvature. • Given a diagram of a mirror with the focal point sh ...