Chapter 2: Pressure Distribution in a Fluid
... The center of buoyancy (centroid of the displaced volume) shifts laterally to the right for the case shown because part of the original buoyant volume AOB is transferred to a new buoyant volume EOD. The point of intersection of the lines of action of the buoyant force before and after heel is called ...
... The center of buoyancy (centroid of the displaced volume) shifts laterally to the right for the case shown because part of the original buoyant volume AOB is transferred to a new buoyant volume EOD. The point of intersection of the lines of action of the buoyant force before and after heel is called ...
Name………… - science
... requires a greater amount of internal contraction and release of our muscle fibers, and hence internal work in our bodies. But the work done on the box is zero since by moving in a straight line at constant speed, its energy is remaining the same. There are many important examples of forces which do ...
... requires a greater amount of internal contraction and release of our muscle fibers, and hence internal work in our bodies. But the work done on the box is zero since by moving in a straight line at constant speed, its energy is remaining the same. There are many important examples of forces which do ...
Document
... Kinetic energy is related to mass and velocity. In other words, when some object with mass is moving, it has some kinetic energy. This is related to potential energy because those are the two main types of energies that an object has. Potential energy is the relationship between the distance an obje ...
... Kinetic energy is related to mass and velocity. In other words, when some object with mass is moving, it has some kinetic energy. This is related to potential energy because those are the two main types of energies that an object has. Potential energy is the relationship between the distance an obje ...
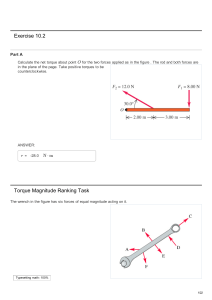
Exercise 10.2 Torque Magnitude Ranking Task
... perpendicular to the length of the rod at one end and is stationary. The rod has an angular velocity of 0.4 rad/s and a moment of inertia about the axis of 2.50×10−3 kg ⋅ m2 . A bug initially standing on the rod at the axis of rotation decides to crawl out to the other end of the rod. When the bug ...
... perpendicular to the length of the rod at one end and is stationary. The rod has an angular velocity of 0.4 rad/s and a moment of inertia about the axis of 2.50×10−3 kg ⋅ m2 . A bug initially standing on the rod at the axis of rotation decides to crawl out to the other end of the rod. When the bug ...
systems of particles
... • Moment resultant about fixed point O of the external forces is equal to the rate of change of angular momentum of the system of particles, ...
... • Moment resultant about fixed point O of the external forces is equal to the rate of change of angular momentum of the system of particles, ...