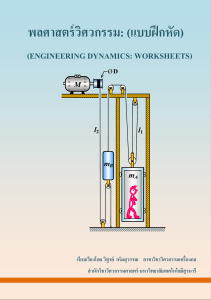
Document
... In the body the skeleton forms a system of levers that allows us to move. The bones act as the levers, the joints are the fulcrums and the effort is provided by the muscle. A lever has two main functions: 1. To increase the speed at which a body can move. 2. To increase the amount of resistance that ...
... In the body the skeleton forms a system of levers that allows us to move. The bones act as the levers, the joints are the fulcrums and the effort is provided by the muscle. A lever has two main functions: 1. To increase the speed at which a body can move. 2. To increase the amount of resistance that ...
Which way does the normal force on the block point?
... objects moving at constant velocity tend to continue at this velocity UNLESS acted on by a net force and ...
... objects moving at constant velocity tend to continue at this velocity UNLESS acted on by a net force and ...
On the Lamb Vector and the Hydrodynamic Charge
... The setup consists of a single stirring rod of 40mm diameter, 110mm in length, rotating at the bottom of a water cell. The cell is cylindrical with 290mm inside diameter and 350mm height, and closed from above by a transparent Perspex plate in complete contact with the water. The tip of the rod is t ...
... The setup consists of a single stirring rod of 40mm diameter, 110mm in length, rotating at the bottom of a water cell. The cell is cylindrical with 290mm inside diameter and 350mm height, and closed from above by a transparent Perspex plate in complete contact with the water. The tip of the rod is t ...
Lab M5: Hooke`s Law
... k is called the spring constant and is a measure of the stiffness of the spring. By inspection of Eq. 1, we see that in the mks system the units of k must be N/m. The minus sign indicates that the direction of the force is opposite to the direction of the displacement. The diagram shows a mass to th ...
... k is called the spring constant and is a measure of the stiffness of the spring. By inspection of Eq. 1, we see that in the mks system the units of k must be N/m. The minus sign indicates that the direction of the force is opposite to the direction of the displacement. The diagram shows a mass to th ...
Seesaws 9 Balanced Seesaw
... Why does the seesaw need a pivot? Why does a lone rider plummet to the ground? Why do the riders’ weights and positions matter? Why does distance from the pivot affect speed? ...
... Why does the seesaw need a pivot? Why does a lone rider plummet to the ground? Why do the riders’ weights and positions matter? Why does distance from the pivot affect speed? ...
How Safe?
... analyzing this interaction is to define “before,” “during,” and “after” and to sketch them as shown in Figure 9–1. You can simplify the collision between the ball and the racket by assuming that all motion is in the horizontal direction. Before the hit, the ball is moving slowly. During the hit, the ...
... analyzing this interaction is to define “before,” “during,” and “after” and to sketch them as shown in Figure 9–1. You can simplify the collision between the ball and the racket by assuming that all motion is in the horizontal direction. Before the hit, the ball is moving slowly. During the hit, the ...
2011 Iredell-Statesville Schools
... • Explain the property of inertia as related to mass ‐ the motion of an object will remain the same (either at rest or moving at a constant speed in a straight line) in the absence of unbalanced forces; if a change in motion of an object is observed, there must have been a net force on the object. ...
... • Explain the property of inertia as related to mass ‐ the motion of an object will remain the same (either at rest or moving at a constant speed in a straight line) in the absence of unbalanced forces; if a change in motion of an object is observed, there must have been a net force on the object. ...
05_02
... the fixed centrode. If body i is part of a mechanism with mobility of one, curvature of the centrode at each location will be invariant to speed of the mechanism. ...
... the fixed centrode. If body i is part of a mechanism with mobility of one, curvature of the centrode at each location will be invariant to speed of the mechanism. ...
the pdf of this lesson!
... When you fire an object from the trebuchet, it travels in a curved path called a trajectory. The distance the object travels is called its range. The range of the object and how high it goes depends on its speed and the angle from which it is launched. Changes in the force (weight of the downward mo ...
... When you fire an object from the trebuchet, it travels in a curved path called a trajectory. The distance the object travels is called its range. The range of the object and how high it goes depends on its speed and the angle from which it is launched. Changes in the force (weight of the downward mo ...