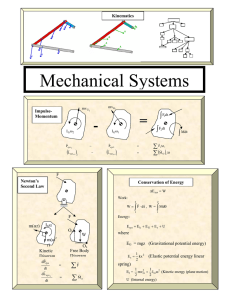
Biomechanical Principles and Applications
... It is important to distinguish between two types of motion: Linear (or Translational) Motion Movement in particular direction (and would include the resultant of more than one linear force acting on an object). Example: a sprinter accelerating down the track. Rotational Motion Movement about an ...
... It is important to distinguish between two types of motion: Linear (or Translational) Motion Movement in particular direction (and would include the resultant of more than one linear force acting on an object). Example: a sprinter accelerating down the track. Rotational Motion Movement about an ...
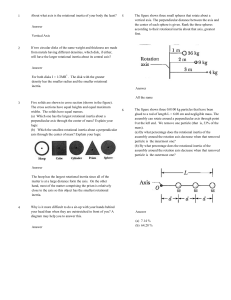
About what axis is the rotational inertia of your body the least? 1
... The four bodies shown in the figure have equal masses m. Body A is a solid cylinder of radius R. Body B is a hollow thin cylinder of radius R. Body C is a solid square with length of side 2R. Body D is the same size as C, but hollow (i.e.) made up of four thin sticks). The bodies have axes of rotati ...
... The four bodies shown in the figure have equal masses m. Body A is a solid cylinder of radius R. Body B is a hollow thin cylinder of radius R. Body C is a solid square with length of side 2R. Body D is the same size as C, but hollow (i.e.) made up of four thin sticks). The bodies have axes of rotati ...
pdf file
... sufficiently strong conditions of smoothness, this is usually defined as a limit: v(t) = limt0 →t (x(t’) - x(t)) / (t’ - t) Note that this limit is defined in terms of the whole family or sequence of states around t, i.e., in terms of the state properties x(t’) for all t’ in a neighbourhood of t. In ...
... sufficiently strong conditions of smoothness, this is usually defined as a limit: v(t) = limt0 →t (x(t’) - x(t)) / (t’ - t) Note that this limit is defined in terms of the whole family or sequence of states around t, i.e., in terms of the state properties x(t’) for all t’ in a neighbourhood of t. In ...
CE-PHY I - MECHANICS
... Suppose the angle of inclination of the smooth plane is increased. (See Figure 2.) Then the boy sitting on the sledge slides down from rest at a point P on this runway, where P is at the same height as point A in the original runway. Would there be any change in the stopping distance along BC when c ...
... Suppose the angle of inclination of the smooth plane is increased. (See Figure 2.) Then the boy sitting on the sledge slides down from rest at a point P on this runway, where P is at the same height as point A in the original runway. Would there be any change in the stopping distance along BC when c ...
Planetary Motion and Gravitation
... Gravity acts over a distance. It acts between objects that are not touching or that are not close together, unlike other forces that are contact forces. For example, friction. In the 19th century, Michael Faraday developed the concept of a field to explain how a magnet attracts objects. Later, the f ...
... Gravity acts over a distance. It acts between objects that are not touching or that are not close together, unlike other forces that are contact forces. For example, friction. In the 19th century, Michael Faraday developed the concept of a field to explain how a magnet attracts objects. Later, the f ...
Chapter 6 - AstroStop
... Your danger is of the order of twenty times greater than that of the truck driver. ...
... Your danger is of the order of twenty times greater than that of the truck driver. ...
here.
... • One may wonder how this formula for energy arose from Newton’s equation. Let us consider one degree of freedom. We wish to integrate m ẍ = − dV dx with respect to time in order to solve the equation of motion. To do so we notice that ẋ is an integrating factor. For, multiplying the equation by x ...
... • One may wonder how this formula for energy arose from Newton’s equation. Let us consider one degree of freedom. We wish to integrate m ẍ = − dV dx with respect to time in order to solve the equation of motion. To do so we notice that ẋ is an integrating factor. For, multiplying the equation by x ...