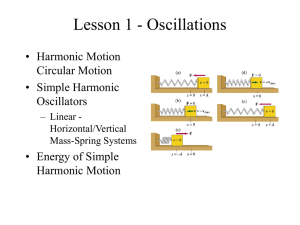
Kinematics of simple harmonic motion (SHM)
... equilibrium position x = 0) When the spring is compressed and displacement is to the left, the spring exert a force to the right. ...
... equilibrium position x = 0) When the spring is compressed and displacement is to the left, the spring exert a force to the right. ...
Chapter 2 - Motion in One Dimension
... • Check to see if your solution works. • Determine if there are any restrictions (required conditions). • If the guess works, your guess is a solution, but it might not be the only one. • Look at your constants and evaluate them using initial conditions or boundary conditions. ...
... • Check to see if your solution works. • Determine if there are any restrictions (required conditions). • If the guess works, your guess is a solution, but it might not be the only one. • Look at your constants and evaluate them using initial conditions or boundary conditions. ...
The Lagrangian Method
... At this point it seems to be personal preference, and all academic, whether you use the Lagrangian method or the F = ma method. The two methods produce the same equations. However, in problems involving more than one variable, it usually turns out to be much easier to write down T and V , as opposed ...
... At this point it seems to be personal preference, and all academic, whether you use the Lagrangian method or the F = ma method. The two methods produce the same equations. However, in problems involving more than one variable, it usually turns out to be much easier to write down T and V , as opposed ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... In this article, we first look at zeroes of the virtual work functional for more general variations of the kinematical state of the system that also include variations of the parameters in O, as well. In order to be dealing with the usual machinery of Noether’s theorem, one then considers the parame ...
... In this article, we first look at zeroes of the virtual work functional for more general variations of the kinematical state of the system that also include variations of the parameters in O, as well. In order to be dealing with the usual machinery of Noether’s theorem, one then considers the parame ...
Topic 9: Electric Forces
... How to do this??? (Method given below) Observe the displaced ball from the plate and the force vectors at work: ...
... How to do this??? (Method given below) Observe the displaced ball from the plate and the force vectors at work: ...
canim-11 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Gravity • The law describes an equal and opposite force exchanged between two bodies, where the force is proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to their distance squared. The force acts in a direction e along a line from one particle to the other (in an attractive d ...
... Gravity • The law describes an equal and opposite force exchanged between two bodies, where the force is proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to their distance squared. The force acts in a direction e along a line from one particle to the other (in an attractive d ...
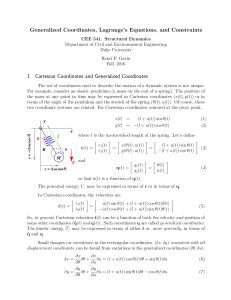
Generalized Coordinates, Lagrange`s Equations, and Constraints 1
... 1 Cartesian Coordinates and Generalized Coordinates The set of coordinates used to describe the motion of a dynamic system is not unique. For example, consider an elastic pendulum (a mass on the end of a spring). The position of the mass at any point in time may be expressed in Cartesian coordinates ...
... 1 Cartesian Coordinates and Generalized Coordinates The set of coordinates used to describe the motion of a dynamic system is not unique. For example, consider an elastic pendulum (a mass on the end of a spring). The position of the mass at any point in time may be expressed in Cartesian coordinates ...
Machines
... Through the process of doing work, energy can move between the external world and the system. The direction of energy transfer can go both ways. If the external world does work on a system, then W is positive and the energy of the system increases. If, however, a system does work on the external wor ...
... Through the process of doing work, energy can move between the external world and the system. The direction of energy transfer can go both ways. If the external world does work on a system, then W is positive and the energy of the system increases. If, however, a system does work on the external wor ...
Moment of Inertia
... 1. Measure the diameter of the disk and record this value, along with the mass of the disk, in Table 2. 2. Using the dimensions you determined in Step 1, calculate and record the theoretical moment of inertia for the disk. 3. Switch to a 100g hooked mass. As in Procedure 1, time the descent of this ...
... 1. Measure the diameter of the disk and record this value, along with the mass of the disk, in Table 2. 2. Using the dimensions you determined in Step 1, calculate and record the theoretical moment of inertia for the disk. 3. Switch to a 100g hooked mass. As in Procedure 1, time the descent of this ...
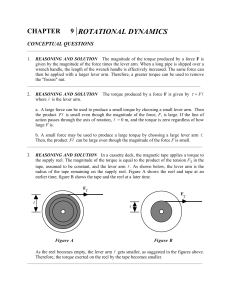
solution - HCC Learning Web
... 15. REASONING AND SOLUTION The translational kinetic energy of a rigid body depends only on the mass and the speed of the body. It does not depend on how the mass is distributed. Therefore, for purposes of computing the body's translational kinetic energy, the mass of a rigid body can be considered ...
... 15. REASONING AND SOLUTION The translational kinetic energy of a rigid body depends only on the mass and the speed of the body. It does not depend on how the mass is distributed. Therefore, for purposes of computing the body's translational kinetic energy, the mass of a rigid body can be considered ...
Force Vectors
... Since any vector in 3-D can be expressed as components in x,y,z directions, we just need to add the corresponding components since the components are scalars. A Axiˆ Ay ˆj Az kˆ B Bxiˆ By ˆj Bz kˆ ...
... Since any vector in 3-D can be expressed as components in x,y,z directions, we just need to add the corresponding components since the components are scalars. A Axiˆ Ay ˆj Az kˆ B Bxiˆ By ˆj Bz kˆ ...
Physicsskiing3
... human force to push yourself along the snow, still wearing skies. There are many types of skiing, different ways to ski, conditions which suite different people, and different types of ski equipment but in general many different variables but everything comes down do to one sure thing: without physi ...
... human force to push yourself along the snow, still wearing skies. There are many types of skiing, different ways to ski, conditions which suite different people, and different types of ski equipment but in general many different variables but everything comes down do to one sure thing: without physi ...
Lab Roundup Summary
... 2. How do you determine the speed of light in the glass block? 3. How would you determine the wavelength of light inside the block? 4. Sketch the path of the incident light ray hitting the glass block at theta > 0 degrees. Lab 44 Critical Angle 1. Write the equation for critical angle; define critic ...
... 2. How do you determine the speed of light in the glass block? 3. How would you determine the wavelength of light inside the block? 4. Sketch the path of the incident light ray hitting the glass block at theta > 0 degrees. Lab 44 Critical Angle 1. Write the equation for critical angle; define critic ...
chap. 9
... Since water is denser than the air-filled ball, the buoyant force acting on the ball exceeds the weight of the fully submerged ball. This means that choice (b) is true and choice (d) is false. Neglecting a very small variation in the density of water with depth, the weight of the displaced water (i. ...
... Since water is denser than the air-filled ball, the buoyant force acting on the ball exceeds the weight of the fully submerged ball. This means that choice (b) is true and choice (d) is false. Neglecting a very small variation in the density of water with depth, the weight of the displaced water (i. ...
Drag!
... the faster lane, eventually slowing down the faster lane. Local decisions of the drivers reduce the velocity gradient. Similarly, molecular motion (in a gas) or collisions (in a fluid) transports speed (really, momentum) from fast- to slow-flowing regions. This transport reduces the velocity differe ...
... the faster lane, eventually slowing down the faster lane. Local decisions of the drivers reduce the velocity gradient. Similarly, molecular motion (in a gas) or collisions (in a fluid) transports speed (really, momentum) from fast- to slow-flowing regions. This transport reduces the velocity differe ...