Chapter 3 Summary
... • Set up the problem as usual, including the force of friction • For example, as seen in fig. 3.11: • ΣF = Ffriction = -μk N = m a • From the y-direction, Fgrav = N = m g • Therefore, -μk m g = m a and a = - μk g • Once you have found the acceleration, other quantities involved with motion can also ...
... • Set up the problem as usual, including the force of friction • For example, as seen in fig. 3.11: • ΣF = Ffriction = -μk N = m a • From the y-direction, Fgrav = N = m g • Therefore, -μk m g = m a and a = - μk g • Once you have found the acceleration, other quantities involved with motion can also ...
CE2
... Assuming that friction is negligible. Which of the following statements are correct? (1) The potential energy lost by block A is the same as that of block B when they reach the end of the track. (2) The speed of block A is the same as that of block B when they reach the end of the track. (3) Block A ...
... Assuming that friction is negligible. Which of the following statements are correct? (1) The potential energy lost by block A is the same as that of block B when they reach the end of the track. (2) The speed of block A is the same as that of block B when they reach the end of the track. (3) Block A ...
Vectors and Scalars * Learning Outcomes
... Draw a diagram showing the horse’s path. What is the overall displacement of the horse from its starting point? e.g. A ship moves parallel to a straight river bank at 4 m∙s-1. Bronagh walks across the ship at right angles to the direction of forward motion of the ship at 3 m∙s-1. Find Bronagh’ ...
... Draw a diagram showing the horse’s path. What is the overall displacement of the horse from its starting point? e.g. A ship moves parallel to a straight river bank at 4 m∙s-1. Bronagh walks across the ship at right angles to the direction of forward motion of the ship at 3 m∙s-1. Find Bronagh’ ...
Newton`s Second Law NTG (Hewitt) PPT
... Newton’s 2nd Law is known as the Law of Acceleration: The effect of an applied force is to cause the body to move in the direction of the force. Net FORCE produces acceleration! Force tends to accelerate things, mass tends to resist acceleration. ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law is known as the Law of Acceleration: The effect of an applied force is to cause the body to move in the direction of the force. Net FORCE produces acceleration! Force tends to accelerate things, mass tends to resist acceleration. ...
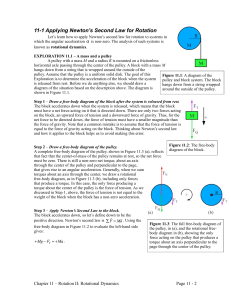
11-1 Applying Newton`s Second Law for Rotation
... Thus, the tangential acceleration of a point on the outer edge of the pulley is equal in magnitude to the acceleration of the string, which equals the magnitude of the block’s acceleration. Finally, we connect the magnitude of the tangential acceleration of the outer edge of the pulley to the magnit ...
... Thus, the tangential acceleration of a point on the outer edge of the pulley is equal in magnitude to the acceleration of the string, which equals the magnitude of the block’s acceleration. Finally, we connect the magnitude of the tangential acceleration of the outer edge of the pulley to the magnit ...
Unit 1 - Teacher Notes
... Unit 3 begins the study of the causes of motion (dynamics). An unbalanced force is one cause of motion. “Normal-sized objects moving at normal speeds,” keep our atudies in the realm of Newtonian physics. Newton's three laws are quite powerful and elegant and explain how an object moves when acted on ...
... Unit 3 begins the study of the causes of motion (dynamics). An unbalanced force is one cause of motion. “Normal-sized objects moving at normal speeds,” keep our atudies in the realm of Newtonian physics. Newton's three laws are quite powerful and elegant and explain how an object moves when acted on ...
NOTES - Air Resistance
... Which encounters the greater force of air resistance? 1. A falling elephant 2. A falling feather Math: The elephant has a much larger cross-sectional area (approximated as a circle) than a feather. Therefore it will experience a larger force of drag. Concept: The elephant will “run into” more air th ...
... Which encounters the greater force of air resistance? 1. A falling elephant 2. A falling feather Math: The elephant has a much larger cross-sectional area (approximated as a circle) than a feather. Therefore it will experience a larger force of drag. Concept: The elephant will “run into” more air th ...
grade 9 physics notes
... Momentum Momentum is a measure of the tendency of an object to keep moving and is determined as a product of its mass and velocity. Momentum ( p) = mass x velocity . The unit of momentum is kg m/s. Momentum is a vecter quantity so if two objects are moving in opposite direction, we give the momentum ...
... Momentum Momentum is a measure of the tendency of an object to keep moving and is determined as a product of its mass and velocity. Momentum ( p) = mass x velocity . The unit of momentum is kg m/s. Momentum is a vecter quantity so if two objects are moving in opposite direction, we give the momentum ...
Physics S1 ideas overview
... 24. Understand the 2 components of a projectile and how they are related (and how component vectors relate to other measurements as well). 25. Understand the relationship between component vectors and Ɵ (also used for many other measurements). 26. At the very top of the trajectory, describe an objec ...
... 24. Understand the 2 components of a projectile and how they are related (and how component vectors relate to other measurements as well). 25. Understand the relationship between component vectors and Ɵ (also used for many other measurements). 26. At the very top of the trajectory, describe an objec ...
p211c07
... across a room by two paths: a direct 2.5m path, and dogleg path of 2.00m on the first leg and 1.50m along the second leg. How much work is done dragging the object across each path? ...
... across a room by two paths: a direct 2.5m path, and dogleg path of 2.00m on the first leg and 1.50m along the second leg. How much work is done dragging the object across each path? ...