* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Days 11-12 (Work/Energy Review)
Survey
Document related concepts
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
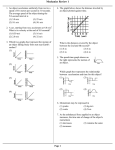
Days #11-12 Work and Energy Review Packet 1. How much work is required to slow a 45 kg snowboarder down from 30 m/s to 15 m/s? How much power was exerted (in Watts) if the snowboarder was slowed down by this amount in 2.5 seconds. 2. A 1200 kg car is traveling at 6.67 m/s (about 15 mph) in a school zone. If its brakes can supply a force of 6674 Newtons, determine the stopping distance. 3. If the same car in (from the previous question above) with the same brakes was traveling at 13.3 m/s (twice as fast), determine the stopping distance. 4. A horse pulls a 20 kg carriage by pulling with a horizontal force of 500 Newtons over a distance of 200 meters. How much work is done? 5. A motorcycle engine supplies a force of 1000 Newtons to a 100 kg bike. Determine the final velocity of the motorcycle if it starts at 15 m/s for 20 meters. a. b. c. d. Determine the final velocity of the bike. What is the work done by the engine? What force is required to make the bike come to a stop in 20 meters? What is the change in kinetic energy of the motorcycle while coming to rest? 6. What variables affect the period of a mass-spring system that is oscillating up and down? What 2 things (surprisingly) don’t affect the period? 7. A pendulum has a period of 2 seconds on the Earth. What is its length? 8. A 2 kg mass is hung on a 15 cm long spring. It lowers and comes to a rest (stays at rest) when the spring has reached a length of 32 cm. (a) find the spring constant and (b) determine the period of the same spring is a 4 kg mass is placed on it and allowed to oscillate (remove the 2 kg mass). 9. A 40 kg boy riding on a 60 kg go-kart has a kinetic energy of 3125 Joules. Determine the velocity of the go-kart and boy. 10. A bike experiences a force as shown by the graph below. The bike and its rider have a mass of 110 kg and an initial velocity of 6 m/s. Determine the final velocity of the bike and rider at 120 meters. F 100 (N) 100 40 70 120 d (m) - 60 11. A 20 kg box is lifted up a set of steps to a vertical height of 12 meters. How much work is done? How much gravitational potential energy did the box gain? 12. A ball is thrown up at 6 m/s from the top of a 20 meter cliff. It passes by the edge of the cliff on the way down and hits the ground. With what speed did the ball hit the ground? (Do not use the equations of motion to solve this problem. Do it another way, more suitable to this chapter ) 13. A 20 gram pellet is placed up against a spring with force constant 6000 N/m. The spring is initially compressed 2 cm. The pellet is fired from rest from the compressed spring and an initial height of 2 meters from the ground. At what speed will the pellet hit the ground? 14. A ball is rolling along level ground at 10 m/s. It begins to climb a hill with an angle of 30 o. How far up the incline will the ball roll? 15. A 6 kg block is pressed against a spring with force constant 600 N/m at the top of a hill 4 meters high. The spring is initially compressed 40 cm. (a) What is the speed of the block at the bottom of the hill after sliding down the frictionless surface? (b) How far will the block slide if it encounters a rough level surface with coefficient of friction 0.4 at the bottom of the hill? 16. A 40 kg little girl slides down a 10 meter slide from rest at an angle of 40 o. She reaches the bottom with a speed of 4 m/s. What was the force of friction along the incline? 17. A 6 kg block moving to the right at 10 m/s collides head on with a 4 kg block moving to the left at 8 m/s. After they hit, the 4 kg block is moving to the right at 10 m/s. Determine the final velocity of the 6 kg block after the collision (using the conservation of momentum). 18. Was the collision in the previous problem above elastic or not? How much energy was lost if any? 19. A 40 gram bullet is fired into a 4 kg block with a speed of 350 m/s. The 4 kg block is hanging from a 3 meter string. How high will the block rise (vertically) after the bullet embeds itself into the block (sticks). What will the angle be between the string and the vertical at its highest height? 20. A 30 gram bullet is fired into a 2 kg block with a speed of 380 m/s. It passes through the block and exits with a speed of 120 m/s. The block slides along a level frictionless surface and collides with a spring of force constant of 760 N/m. How much will the spring compress? 21. A student performs the spring lab in class. She measures the distance from the floor to the bottom of the unloaded spring to be 60 cm. She hangs the 1 kg mass on the spring and allows it to come to a rest. The bottom of the spring is now 23.5 cm above the floor. (This is the time to determine the “k” value of the spring). She then pulls the mass down so that the bottom of the spring is 8 cm above the floor. She releases the mass from rest and it rises to a height of 40 cm. Determine the change in potential energy of the spring and the change in the gravitational potential energy. What is the percentage of error if you use PEsp as the theoretical value? 22. A boy pulls on a 100 kg crate with a force of 800 N at an angle of 60 o above the horizontal. A frictional force of 200 N acts on the crate at the same time. If he pulls the crate through a distance of 15 m, determine (a) the work done by the boy, (b) determine the work done by the frictional force, (c) determine the net work done on the box. 23. A 6 kg cat is hoisted up into the air a distance of 20 meters. How much work is done on the cat? How much power is exerted (in W, kW, and hp) if the work is done in 3 seconds? 24. A 200 kg jet ski experiences a force as shown on the Force vs. position graph below. Its initial velocity at x = 0 is 15 m/s. (a) How much work is done from 0 to 8 sec? (b) How fast is the car moving at 8 sec? (c) How much work is done from 15 to 18 m? (d) How fast is the ski moving at 18 m? (e) What is the ski’s change in kinetic energy from 0 to 15 meters? F (N) F 1000 d (m) 0 6 8 15 18 -600 25. An 800 kg block is pushed up a 5 m long ramp with an incline angle of 20 o. Find: a) the work needed to push the box up if the ramp is frictionless. b) the work needed to push the box up if the coefficient of friction is 0.20. c) the horsepower needed to do the work in part b above, assuming that the block is pushed up the ramp in 10 seconds. 26) TOUGH!!! A HORIZONTAL force of “F” (not parallel to the incline, but truly horizontal) pushes a 200 kg block up a 20o incline that has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.2. Find the force necessary to give the block a speed of 4 m/s after moving 3 meters (starting from rest). Then, find the work done by the horizontal force “F”.