Section Summary
... In free fall, the force of gravity is an unbalanced force that causes an object to accelerate. Near Earth’s surface, acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s 2. Objects falling through air experience a type of fluid friction called air resistance. Air resistance is not the same for all objects. The gr ...
... In free fall, the force of gravity is an unbalanced force that causes an object to accelerate. Near Earth’s surface, acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s 2. Objects falling through air experience a type of fluid friction called air resistance. Air resistance is not the same for all objects. The gr ...
sept19
... Newton’s law of gravity explained the ocean tides Because the force of gravity falls off rapidly with distance, the pull of the Moon and Sun are stronger on the side of Earth that is closer to, or faces, the Moon or Sun. And it is weakest farthest from the Moon or Sun. ...
... Newton’s law of gravity explained the ocean tides Because the force of gravity falls off rapidly with distance, the pull of the Moon and Sun are stronger on the side of Earth that is closer to, or faces, the Moon or Sun. And it is weakest farthest from the Moon or Sun. ...
1 - nglc
... Sleds A and B are connected by a horizontal rope, with A in front of B. Sled A is pulled forward with a horizontal rope with a tension of magnitude 29.0 N. The masses of sleds A and B are 6.7 kg and 5.6 kg, respectively. The magnitudes of kinetic friction on A and B are 9.0 N and 8.0 N respectively. ...
... Sleds A and B are connected by a horizontal rope, with A in front of B. Sled A is pulled forward with a horizontal rope with a tension of magnitude 29.0 N. The masses of sleds A and B are 6.7 kg and 5.6 kg, respectively. The magnitudes of kinetic friction on A and B are 9.0 N and 8.0 N respectively. ...
Are You suprised
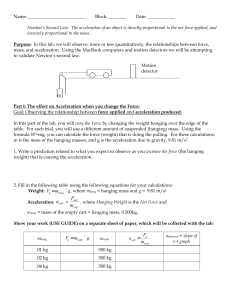
... Purpose: In this lab, we will observe, more or less quantitatively, the relationships between force, mass, and acceleration. Using the MacBook computers and motion detectors we will be attempting to validate Newton’s second law. Motion detector ...
... Purpose: In this lab, we will observe, more or less quantitatively, the relationships between force, mass, and acceleration. Using the MacBook computers and motion detectors we will be attempting to validate Newton’s second law. Motion detector ...
Forces - RIO Commons
... Begin this section by reading Chapter 5, Section 5.1, pp. 145 to 149 in the Newtonian Physics textbook. View the video from Khan Academy on Newton's 3rd Law of Motion. When you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you. This is an example of a Newton's 3rd Law, actionreaction pair of forces. These ...
... Begin this section by reading Chapter 5, Section 5.1, pp. 145 to 149 in the Newtonian Physics textbook. View the video from Khan Academy on Newton's 3rd Law of Motion. When you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you. This is an example of a Newton's 3rd Law, actionreaction pair of forces. These ...
CfE Advanced Higher Physics – Unit 1 – Rotational Motion
... The radian is used when measuring a new quantity known as angular displacement, θ, measured in radians (rad). One radian represents an arc with a length of one radius of that circle. This is the displacement (in angle form) around the arc of a circle, which has an equivalent angle in degrees. There ...
... The radian is used when measuring a new quantity known as angular displacement, θ, measured in radians (rad). One radian represents an arc with a length of one radius of that circle. This is the displacement (in angle form) around the arc of a circle, which has an equivalent angle in degrees. There ...
Freezing Point of Water
... 7. What particle has a mass of 1 amu and has no charge? Neutron 8. What is the nuclear symbol of this particle?1 0 n 9. What particle has a mass of 1 amu and has a 1+ charge? Proton 10. What is the nuclear symbol of this particle? 1 1 p 11. All nuclei with an atomic number above 92 are radioactive 1 ...
... 7. What particle has a mass of 1 amu and has no charge? Neutron 8. What is the nuclear symbol of this particle?1 0 n 9. What particle has a mass of 1 amu and has a 1+ charge? Proton 10. What is the nuclear symbol of this particle? 1 1 p 11. All nuclei with an atomic number above 92 are radioactive 1 ...
Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields
... motion. The acceleration due to the B-field is also perpendicular the particles velocity. The net result of the acceleration is that the particle bends as it moves through the B-field. The magnitude of the velocity does not change, only the direction of the velocity changes. This is exactly the same ...
... motion. The acceleration due to the B-field is also perpendicular the particles velocity. The net result of the acceleration is that the particle bends as it moves through the B-field. The magnitude of the velocity does not change, only the direction of the velocity changes. This is exactly the same ...
equilibrium
... The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic friction The coefficient of friction (µ) depends on the surfaces in contact The direction of the frictional force is opposite the direction of motion The coefficients of friction are nearly independent of the area of contact ...
... The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic friction The coefficient of friction (µ) depends on the surfaces in contact The direction of the frictional force is opposite the direction of motion The coefficients of friction are nearly independent of the area of contact ...
PowerPoint Lesson
... object’s state of motion, that is, changing its velocity. Any particular force may not actually change an object’s state of motion, as there may be other forces that prevent it from doing so. However, if the net force—the vector sum of all forces acting on the object—is not zero, the velocity will i ...
... object’s state of motion, that is, changing its velocity. Any particular force may not actually change an object’s state of motion, as there may be other forces that prevent it from doing so. However, if the net force—the vector sum of all forces acting on the object—is not zero, the velocity will i ...
Lecture_1 - Department of Mathematics
... 5. A 100 kg woman stands with her legs making 45 degree angles with respect to the vertical direction. What is the compressive force in her knees ? 6. How is biomechanics important for orthopaedics ? 7. What is Pascal’s law for fluid statics ? 8. Compute the mass of the object on the side of the blo ...
... 5. A 100 kg woman stands with her legs making 45 degree angles with respect to the vertical direction. What is the compressive force in her knees ? 6. How is biomechanics important for orthopaedics ? 7. What is Pascal’s law for fluid statics ? 8. Compute the mass of the object on the side of the blo ...
Study Guide for Final
... Matter - anything that has mass and takes up space Volume - the amount of space taken up by an object Density of liquids A. In a liquid, the denser layers will sink to the bottom B. If the density of an object is less than the density of water it will float Mass - a measure of the amount of matter i ...
... Matter - anything that has mass and takes up space Volume - the amount of space taken up by an object Density of liquids A. In a liquid, the denser layers will sink to the bottom B. If the density of an object is less than the density of water it will float Mass - a measure of the amount of matter i ...