Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The acceleration on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net external force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object ...
... The acceleration on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net external force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object ...
Forces & Newton`s Laws
... feather rests on a strong, solid oak table. Does the table exert any forces on the feather? I lean on a solid cement wall. Does it exert forces on me? What force causes a ball to bounce? ...
... feather rests on a strong, solid oak table. Does the table exert any forces on the feather? I lean on a solid cement wall. Does it exert forces on me? What force causes a ball to bounce? ...
Notes in pdf format
... Over the entrance to a restaurant is mounted a strip of equally spaced light bulbs. Starting at the left end, each bulb turns on in sequence for one-half second. Thus, a lighted bulb appears to move from left to right. Once the apparent motion of the lighted bulb reaches the right side of the sign, ...
... Over the entrance to a restaurant is mounted a strip of equally spaced light bulbs. Starting at the left end, each bulb turns on in sequence for one-half second. Thus, a lighted bulb appears to move from left to right. Once the apparent motion of the lighted bulb reaches the right side of the sign, ...
Review - prettygoodphysics
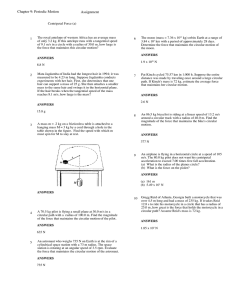
... Larry pushes a 200 kg block on a frictionless floor at a 45o angle below the horizontal with a force of 150 N while Moe pulls the same block horizontally with a force of 120 N. a) Draw a free body diagram. b) What is the acceleration of the block? c) What is the normal force exerted on the block? ...
... Larry pushes a 200 kg block on a frictionless floor at a 45o angle below the horizontal with a force of 150 N while Moe pulls the same block horizontally with a force of 120 N. a) Draw a free body diagram. b) What is the acceleration of the block? c) What is the normal force exerted on the block? ...
FORCES:
... going downhill (Inclined plane) . When the axis is chosen for vector resolution it is slanted to a normal Cartesian system. This means that the vertical and horizontal components in the vector ...
... going downhill (Inclined plane) . When the axis is chosen for vector resolution it is slanted to a normal Cartesian system. This means that the vertical and horizontal components in the vector ...
Chapter 3 Problem Set
... to (370 m) and we know that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/sec2. We are also give the amount of time required to do the amount of work the athlete did (25 min). First, solving for the force involved: F = mg = 70 kg X 9.8 m/sec2 = 686 kg*m/sec2 = 686 N (newtons) Now solving for the work don ...
... to (370 m) and we know that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/sec2. We are also give the amount of time required to do the amount of work the athlete did (25 min). First, solving for the force involved: F = mg = 70 kg X 9.8 m/sec2 = 686 kg*m/sec2 = 686 N (newtons) Now solving for the work don ...
A Guide to “Physics-ing”
... Notice that the picture in Fig. 1 is large enough so that all of these items are included and are clearly discernible. Note that even though some of the aforementioned quantities are vectors, we did not draw them on the FDB–an FDB should include only forces. Instead, we drew them just next to the o ...
... Notice that the picture in Fig. 1 is large enough so that all of these items are included and are clearly discernible. Note that even though some of the aforementioned quantities are vectors, we did not draw them on the FDB–an FDB should include only forces. Instead, we drew them just next to the o ...