Physics Lesson Plan #06 - Forces
... A general term for the forces that In the same direction as the move objects such as rockets, acceleration of the object planes, cars and people barring any resistive forces A long-range force due to Straight down towards the gravitational attraction between center of Earth two objects, generally th ...
... A general term for the forces that In the same direction as the move objects such as rockets, acceleration of the object planes, cars and people barring any resistive forces A long-range force due to Straight down towards the gravitational attraction between center of Earth two objects, generally th ...
Momentum and Impulse (updated)
... A railroad car of mass 3000 kg, moving at 20 m/s eastward, strikes head-on a railroad car of mass 1000 kg that is moving at 20 m/s westward. The railroad cars stick together after the impact. a) What is the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the combined trains after the collision? b) What i ...
... A railroad car of mass 3000 kg, moving at 20 m/s eastward, strikes head-on a railroad car of mass 1000 kg that is moving at 20 m/s westward. The railroad cars stick together after the impact. a) What is the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the combined trains after the collision? b) What i ...
AP free response for last week
... horizontally with a velocity of 10 meters per second, as shown above, when it makes a glancing collision with the lower end of a bar that was hanging vertically at rest before the collision. For the system consisting of the object and bar, linear momentum is not conserved in this collision, but kine ...
... horizontally with a velocity of 10 meters per second, as shown above, when it makes a glancing collision with the lower end of a bar that was hanging vertically at rest before the collision. For the system consisting of the object and bar, linear momentum is not conserved in this collision, but kine ...
posted
... EVALUATE: The total momentum can be calculated either as the vector sum of the momenta of the individual objects in the system, or as the total mass of the system times the velocity of the center of mass. IDENTIFY: Use Eq. 8.28 to find the x and y coordinates of the center of mass of the machine par ...
... EVALUATE: The total momentum can be calculated either as the vector sum of the momenta of the individual objects in the system, or as the total mass of the system times the velocity of the center of mass. IDENTIFY: Use Eq. 8.28 to find the x and y coordinates of the center of mass of the machine par ...
FORCE
... a string, rope, cable or wire when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends. Spring Force Fspring the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it. Mass the amount of matter that is contained by the object. (how much stuff is there) Wei ...
... a string, rope, cable or wire when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends. Spring Force Fspring the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it. Mass the amount of matter that is contained by the object. (how much stuff is there) Wei ...
Physics 2511 Laboratory Manual
... Laboratory. Of this list, ten to twelve will be selected by the instructor to be performed this semester. Many of these labs involve use of the Macintoshes in NSCI 307 and the DELL PCs in 301. In general, the computerized version of a particular lab is presented along with the traditional version, g ...
... Laboratory. Of this list, ten to twelve will be selected by the instructor to be performed this semester. Many of these labs involve use of the Macintoshes in NSCI 307 and the DELL PCs in 301. In general, the computerized version of a particular lab is presented along with the traditional version, g ...
Document
... independent of the path taken are called conservative forces. Eg: gravity, elastic force, electric force. 1. Work done by a conservative force depends only on the initial and final position and not on the path taken to get there. 2. Potential energy only goes with conservative forces. There is poten ...
... independent of the path taken are called conservative forces. Eg: gravity, elastic force, electric force. 1. Work done by a conservative force depends only on the initial and final position and not on the path taken to get there. 2. Potential energy only goes with conservative forces. There is poten ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
... Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Newton’s Second Law of Motion • Newton’s second law (acceleration ): • If the resultant force acting on a particle is not zero, the particle will have an acceleration proportional to the magnitude of resultant and in the direction of the resultant. r • When a ...
... Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Newton’s Second Law of Motion • Newton’s second law (acceleration ): • If the resultant force acting on a particle is not zero, the particle will have an acceleration proportional to the magnitude of resultant and in the direction of the resultant. r • When a ...
Lesson 15 notes – Newton 1 and 3 - science
... (a) Newton’s first law states that an object will remain stationary or continue at a constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force. (1) If it is acted on by a resultant force it will either accelerate, decelerate or change direction (1) depending on the direction of the force.(1) … (3) (b)… ...
... (a) Newton’s first law states that an object will remain stationary or continue at a constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force. (1) If it is acted on by a resultant force it will either accelerate, decelerate or change direction (1) depending on the direction of the force.(1) … (3) (b)… ...
Chapter 12 Section 2 Notes - School District of La Crosse
... Newton’s Laws of Motion I. Newton’s first law of motion, the state of motion of an object does not change as long as the net force acting on the object is zero. A Unless an unbalanced force acts, an object at rest remains at rest. B.Unless an unbalanced force acts, an object in motion remains in mot ...
... Newton’s Laws of Motion I. Newton’s first law of motion, the state of motion of an object does not change as long as the net force acting on the object is zero. A Unless an unbalanced force acts, an object at rest remains at rest. B.Unless an unbalanced force acts, an object in motion remains in mot ...
Newton`s Third Law and Momentum
... 1. An object will remain at rest or in motion at constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. 2. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to the mass ...
... 1. An object will remain at rest or in motion at constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. 2. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to the mass ...
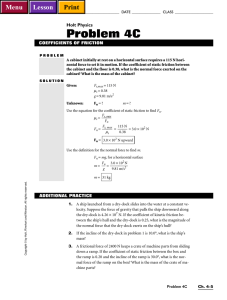
Holt Physics Problem 4C
... 4. A passenger with a mass of 60.0 kg is standing in a subway car that is accelerating at 3.70 m/s2. If the coefficient of static friction between the passenger’s shoes and the car floor is 0.455, will the passenger be able to stand without sliding? 5. A 90.0 kg skier glides down a slope with an inc ...
... 4. A passenger with a mass of 60.0 kg is standing in a subway car that is accelerating at 3.70 m/s2. If the coefficient of static friction between the passenger’s shoes and the car floor is 0.455, will the passenger be able to stand without sliding? 5. A 90.0 kg skier glides down a slope with an inc ...
mapping fields
... Newton’s 2nd Law: The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law: The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of ...