Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for Rotational Motion
... Imagine an object that moves in a complete circle. The object rotates through the angle of ...
... Imagine an object that moves in a complete circle. The object rotates through the angle of ...
mi08sol
... which means that the force is the rate of change of the momentum with time. If the mass is constant then this reduces to Fnet = ma, because the change in velocity with time is the acceleration. But sometimes the mass changes, for example a vehicle which burns fuel changes mass as it uses the fuel. I ...
... which means that the force is the rate of change of the momentum with time. If the mass is constant then this reduces to Fnet = ma, because the change in velocity with time is the acceleration. But sometimes the mass changes, for example a vehicle which burns fuel changes mass as it uses the fuel. I ...
JP`s Physics 101 Test Bank 1
... ____ 68. To report the ____ of an object, we must specify both its speed and its direction . A. acceleration B. position C. mass D. velocity E. length ____ 69. Assuming level ground and no air resistance, a projectile fired at an angle of 30° will have the same range as another projectile fired with ...
... ____ 68. To report the ____ of an object, we must specify both its speed and its direction . A. acceleration B. position C. mass D. velocity E. length ____ 69. Assuming level ground and no air resistance, a projectile fired at an angle of 30° will have the same range as another projectile fired with ...
Review the study notes and homework for the hour tests and
... Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Summary is on p.154. Know what is meant by the term period for uniform circular motion and how the speed v 2r of an object in uniform motion around a circle of radius r is related to the period: v . Know that an object T in uniform circular motion has ...
... Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Summary is on p.154. Know what is meant by the term period for uniform circular motion and how the speed v 2r of an object in uniform motion around a circle of radius r is related to the period: v . Know that an object T in uniform circular motion has ...
Experiment 5U: Kinetic Friction
... surface will exert a force of friction fs (force of static friction) which exactly balances F until F reaches a critical value Fcrit. Fcrit is the maximum value of the static force of friction fmax. Until this point, the net force is zero and the object remains at rest. Above this point the net forc ...
... surface will exert a force of friction fs (force of static friction) which exactly balances F until F reaches a critical value Fcrit. Fcrit is the maximum value of the static force of friction fmax. Until this point, the net force is zero and the object remains at rest. Above this point the net forc ...
apPhysics_lec_06
... other end, whirls the stone in a vertical circle of radius 0.91 m, slowly increasing the speed until the string breaks. a) Where is the stone on its path when the string break? b) What is the speed of the stone as the string breaks? a) In order to keep the same speed, and therefore the same centripe ...
... other end, whirls the stone in a vertical circle of radius 0.91 m, slowly increasing the speed until the string breaks. a) Where is the stone on its path when the string break? b) What is the speed of the stone as the string breaks? a) In order to keep the same speed, and therefore the same centripe ...
TheRotorRideLab
... 10. Gently reattach the Rotor to the turntable. You can use the blue masking tape to secure the bottom if it slips. Start Data Studio and select “Create Experiment”. Select “Smart Pulley (Rotational)” from the list. Delete the Graph 1 window. Drag the Graph icon from the Displays Window to the Veloc ...
... 10. Gently reattach the Rotor to the turntable. You can use the blue masking tape to secure the bottom if it slips. Start Data Studio and select “Create Experiment”. Select “Smart Pulley (Rotational)” from the list. Delete the Graph 1 window. Drag the Graph icon from the Displays Window to the Veloc ...
Class 10 Newton’s third law | Friction PHY 231 Fall 2004
... equal and opposite force (somewhere in the universe) balancing it out. This means that the net force of these two forces must be zero. F=ma => there can be no acceleration; nothing accelerates. 1. True, but Newton’s 3rd law only works part of the time 2. False, Newton’s 3rd law is wrong 3. False, Ne ...
... equal and opposite force (somewhere in the universe) balancing it out. This means that the net force of these two forces must be zero. F=ma => there can be no acceleration; nothing accelerates. 1. True, but Newton’s 3rd law only works part of the time 2. False, Newton’s 3rd law is wrong 3. False, Ne ...
Forces_and_Newtons_Laws_powerpoint
... when it has UNBALANCED forces acting on it. A net force acting on an object will cause the object to accelerate (speed up, slow down, or change direction). The greater the net force acting on an object, the larger the acceleration of the object will be. The larger the object’s mass, the greater the ...
... when it has UNBALANCED forces acting on it. A net force acting on an object will cause the object to accelerate (speed up, slow down, or change direction). The greater the net force acting on an object, the larger the acceleration of the object will be. The larger the object’s mass, the greater the ...
Momentum and Collisions
... Most of us know intuitively that in a head-on collision between a large dump truck and a subcompact car, you are better off being in the truck than in the car. Why is this? Many people imagine that the collision force exerted on the car is much greater than that experienced by the truck. To substan ...
... Most of us know intuitively that in a head-on collision between a large dump truck and a subcompact car, you are better off being in the truck than in the car. Why is this? Many people imagine that the collision force exerted on the car is much greater than that experienced by the truck. To substan ...
GRAVITATION - Testlabz.com
... Q. 1. State the Universal law of Gravitation. Ans. Newton’s Universal law of Gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which is proportional to the square of the distance between them. This force acts along the line joining the centre of the two ob ...
... Q. 1. State the Universal law of Gravitation. Ans. Newton’s Universal law of Gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which is proportional to the square of the distance between them. This force acts along the line joining the centre of the two ob ...
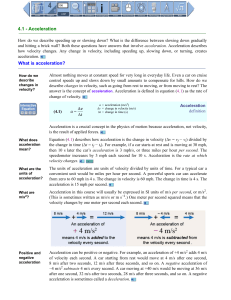
4.1 - Acceleration What is acceleration?
... c. “I underwent zero acceleration during the three-second interval shown.” 3. Nikita and Rachel are driving their new cars westward on the highway. At the very same instant, they cross the Weston town line (call it t = 0). Nikita’s velocity is 20 m/s westward at that moment, while Rachel is going fa ...
... c. “I underwent zero acceleration during the three-second interval shown.” 3. Nikita and Rachel are driving their new cars westward on the highway. At the very same instant, they cross the Weston town line (call it t = 0). Nikita’s velocity is 20 m/s westward at that moment, while Rachel is going fa ...