Chapter 10 - galileo.harvard.edu
... and rotation quantity, then L(qt1,qt2,…) is a translational dynamics formula or law, if and only if L(qr1,qr2,…) is a rotational dynamics formula or law. (To the extent this is not true, the analogy is said to be limited. Most analogies are ...
... and rotation quantity, then L(qt1,qt2,…) is a translational dynamics formula or law, if and only if L(qr1,qr2,…) is a rotational dynamics formula or law. (To the extent this is not true, the analogy is said to be limited. Most analogies are ...
F - AdvancedPlacementPhysicsC
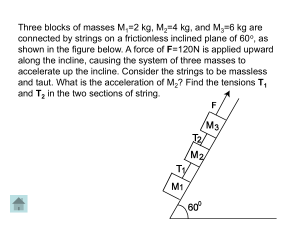
... 1) Three blocks of masses M1=2 kg, M2=4 kg, and M3=6 kg are connected by strings on a frictionless inclined plane of 60 o, as shown in the figure below. A force of F=120N is applied upward along the incline, causing the system of three masses to accelerate up the incline. Consider the strings to be ...
... 1) Three blocks of masses M1=2 kg, M2=4 kg, and M3=6 kg are connected by strings on a frictionless inclined plane of 60 o, as shown in the figure below. A force of F=120N is applied upward along the incline, causing the system of three masses to accelerate up the incline. Consider the strings to be ...
Inertia
... Note that inertia is a property of matter, not a reason for the behavior of matter. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Note that inertia is a property of matter, not a reason for the behavior of matter. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
PH 201-4A spring 2007 PH 201 4A spring 2007
... The work-energy theorem deals with the work done by the net external force. The workenergy theorem does not apply to the work done by an individual force. If W>0 then KE increases; if W<0 then KE decreases; if W=0 then KE remains constant. Downhill Skiing: A 58kg skier is coasting down a 25° slope. ...
... The work-energy theorem deals with the work done by the net external force. The workenergy theorem does not apply to the work done by an individual force. If W>0 then KE increases; if W<0 then KE decreases; if W=0 then KE remains constant. Downhill Skiing: A 58kg skier is coasting down a 25° slope. ...
How is friction useful?
... Sample Problem A 10-kg wooden box rests on a ramp that is lying flat. The coefficient of static friction is 0.50, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30. What is the friction force between the box and ramp if a) no force horizontal force is applied to the box? ...
... Sample Problem A 10-kg wooden box rests on a ramp that is lying flat. The coefficient of static friction is 0.50, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30. What is the friction force between the box and ramp if a) no force horizontal force is applied to the box? ...
1 - vnhsteachers
... 1. Gravity is an action-at-a-distance force that always exists between two particles regardless of the medium that separates them. 2. The force varies as the inverse square of the distance between the particles. 3. The force is proportional to the product of their masses. UNIVERSAL LAW OF GRAVITATIO ...
... 1. Gravity is an action-at-a-distance force that always exists between two particles regardless of the medium that separates them. 2. The force varies as the inverse square of the distance between the particles. 3. The force is proportional to the product of their masses. UNIVERSAL LAW OF GRAVITATIO ...
Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics - Beck-Shop
... speed. Average speed is calculated over a period of time. Displacement / cm ...
... speed. Average speed is calculated over a period of time. Displacement / cm ...
12.2 Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... you throw it…a baseball or a bowling ball? A baseball – less mass ...
... you throw it…a baseball or a bowling ball? A baseball – less mass ...
VOLCANOES AND PLATE TECTONICS
... Vocabulary: Define the following terms from Chapter 2.4. a. Momentum-characteristic of a moving object that is related to mass and the velocity of the object. ...
... Vocabulary: Define the following terms from Chapter 2.4. a. Momentum-characteristic of a moving object that is related to mass and the velocity of the object. ...
Chap. 16 Conceptual Modules Giancoli
... 2) closer to the electron’s side 3) closer to the proton’s side ...
... 2) closer to the electron’s side 3) closer to the proton’s side ...
Fundamentals
of
Physics
in
Engineering
I
Unit 3.- WORK AND ENERGY
... vertically downward. Find the work done during a time interval of t = 10 s, against the air resistance force, if at the end of this time interval the object’s velocity is v = 50 m / s. Consider that the air resistance force is constant. 3.-A 5 kg block is thrown upward along a ramp that is inclined ...
... vertically downward. Find the work done during a time interval of t = 10 s, against the air resistance force, if at the end of this time interval the object’s velocity is v = 50 m / s. Consider that the air resistance force is constant. 3.-A 5 kg block is thrown upward along a ramp that is inclined ...
Newton`s first law of motion
... net force: the combination of all the forces acting on an object gravity: an attractive force that exists between all objects that have force velocity: the change in an object’s position over time; includes both speed and direction acceleration: the change in an object’s velocity over time inertia: ...
... net force: the combination of all the forces acting on an object gravity: an attractive force that exists between all objects that have force velocity: the change in an object’s position over time; includes both speed and direction acceleration: the change in an object’s velocity over time inertia: ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... Example for Spring Block System A car with a mass of 1300kg is constructed so that its frame is supported by four springs. Each spring has a force constant of 20,000N/m. If two people riding in the car have a combined mass of 160kg, find the frequency of vibration of the car after it is driven over ...
... Example for Spring Block System A car with a mass of 1300kg is constructed so that its frame is supported by four springs. Each spring has a force constant of 20,000N/m. If two people riding in the car have a combined mass of 160kg, find the frequency of vibration of the car after it is driven over ...
Mechanics - Modeling Instruction Program
... 3rd law – prove that for circular orbits it is the result of gravity as an inward force Solving for orbital speed of an elliptical orbit using conservation of angular momentum and conservation of energy Total energy for an object in a circular orbit Lab This is a lab done by writing a computer ...
... 3rd law – prove that for circular orbits it is the result of gravity as an inward force Solving for orbital speed of an elliptical orbit using conservation of angular momentum and conservation of energy Total energy for an object in a circular orbit Lab This is a lab done by writing a computer ...