Impact and Momentum - definition and units
... Momentum has both magnitude and direction and thus is a vector quantity. The units of momentum are kg m s−1 or newton seconds, N s. This is often referred to as linear momentum in order to distinguish it from angular momentum. Worked Example 1. A cyclist and his bike have a combined mass of 100 kg a ...
... Momentum has both magnitude and direction and thus is a vector quantity. The units of momentum are kg m s−1 or newton seconds, N s. This is often referred to as linear momentum in order to distinguish it from angular momentum. Worked Example 1. A cyclist and his bike have a combined mass of 100 kg a ...
Projectile Motion
... used. The other two equations are seldom (if ever) used. An application of projectile concepts to each of these equations would also lead one to conclude that any term with ax in it would cancel out of the equation since ax = 0 m/s/s. ...
... used. The other two equations are seldom (if ever) used. An application of projectile concepts to each of these equations would also lead one to conclude that any term with ax in it would cancel out of the equation since ax = 0 m/s/s. ...
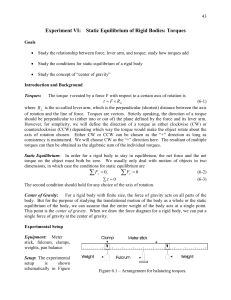
Torque
... 1. So far the fulcrum has been placed only at the center of gravity. Now move the fulcrum to a point between the 10 cm and 25 cm marks. Balance the meter stick by applying a single mass between 100 to 500 g to the shorter side. Record the mass, its position, and the fulcrum position. Weigh the stick ...
... 1. So far the fulcrum has been placed only at the center of gravity. Now move the fulcrum to a point between the 10 cm and 25 cm marks. Balance the meter stick by applying a single mass between 100 to 500 g to the shorter side. Record the mass, its position, and the fulcrum position. Weigh the stick ...
conservation of momentum in two dimensions
... they must be undergoing compression and elongation, in other words they are acting as springs. Let’s see where this understanding leads. A 3 kg ball moving 5 m/s [R] collides elastically with a stationary 2 kg ball. The balls have a radius of 10 cm. The balls have a spring constant of 1250 N/m. a) W ...
... they must be undergoing compression and elongation, in other words they are acting as springs. Let’s see where this understanding leads. A 3 kg ball moving 5 m/s [R] collides elastically with a stationary 2 kg ball. The balls have a radius of 10 cm. The balls have a spring constant of 1250 N/m. a) W ...
Chap. 8 Friction
... + ↑ ∑ Fy = 0; − 80 sin 30o N + N C − 196.2 N = 0 ∑ M O = 0; 80 sin 30o N (0.4m) − 80 cos 30o N (0.2m) + N C ( x) = 0 F = 69.3 N , N C = 236 N ...
... + ↑ ∑ Fy = 0; − 80 sin 30o N + N C − 196.2 N = 0 ∑ M O = 0; 80 sin 30o N (0.4m) − 80 cos 30o N (0.2m) + N C ( x) = 0 F = 69.3 N , N C = 236 N ...
Sample problem
... Practice Problem: You are driving through town at 12.0 m/s when suddenly a ball rolls out in front of you. You apply the brakes and decelerate at 3.5 m/s2. a) How far do you travel before stopping? ...
... Practice Problem: You are driving through town at 12.0 m/s when suddenly a ball rolls out in front of you. You apply the brakes and decelerate at 3.5 m/s2. a) How far do you travel before stopping? ...
Electricity
... 1) A white snooker ball moving at 5m/s strikes a red ball and pots it. Both balls have a mass of 1kg. If the white ball continued in the same direction at 2m/s what was the velocity of the red ball? 2) A car of mass 1000kg heading up the M1 at 50m/s collides with a stationary truck of mass 8000kg an ...
... 1) A white snooker ball moving at 5m/s strikes a red ball and pots it. Both balls have a mass of 1kg. If the white ball continued in the same direction at 2m/s what was the velocity of the red ball? 2) A car of mass 1000kg heading up the M1 at 50m/s collides with a stationary truck of mass 8000kg an ...
CEENbot Pull - Mechatronics
... the individual (or components of forces) that are acting on the object. Newton’s first law states that an object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. The net force on an object is the sum of all the forces (both contact ...
... the individual (or components of forces) that are acting on the object. Newton’s first law states that an object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. The net force on an object is the sum of all the forces (both contact ...
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1
... bottom of the slope was ‘taken’ (dissipated) by friction. So if we determine the kinetic energy at the bottom of the slope, we know the answer to the problem. To find the KE at the bottom of the slope we use conservation of energy: KEi+PEi=KEf+PEf KEi : kinetic energy at top = 0 (starts from rest) P ...
... bottom of the slope was ‘taken’ (dissipated) by friction. So if we determine the kinetic energy at the bottom of the slope, we know the answer to the problem. To find the KE at the bottom of the slope we use conservation of energy: KEi+PEi=KEf+PEf KEi : kinetic energy at top = 0 (starts from rest) P ...
Gravitation
... 1. Each planet moves in an ellipse which has the sun at one focus. 2. The line joining the sun to the moving planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time. 3. The squares of the times of revolution of the planets about the sun are proportional to the cubes of their mean orbit distance r from it. i.e. ...
... 1. Each planet moves in an ellipse which has the sun at one focus. 2. The line joining the sun to the moving planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time. 3. The squares of the times of revolution of the planets about the sun are proportional to the cubes of their mean orbit distance r from it. i.e. ...
Stacey Carpenter
... Do a mini-activity. Pair the students. Have one student hold up a hand and the other push on it with their hand without touching. Impossible, of course. You can't have a force without a counter-force. Another mini-activity. Give each pair of students a spring scale. Instruct one student to hold one ...
... Do a mini-activity. Pair the students. Have one student hold up a hand and the other push on it with their hand without touching. Impossible, of course. You can't have a force without a counter-force. Another mini-activity. Give each pair of students a spring scale. Instruct one student to hold one ...
Document
... the point with distance a away from the pivot, rendering a 30o . Deflection angle of the rod with respect to the vertical axis, what is the initial speed of the? ...
... the point with distance a away from the pivot, rendering a 30o . Deflection angle of the rod with respect to the vertical axis, what is the initial speed of the? ...