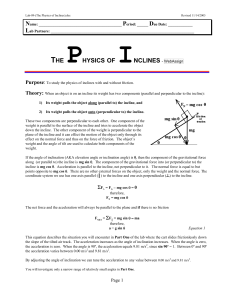
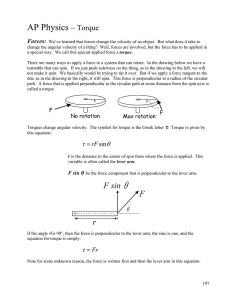
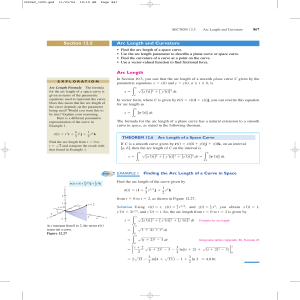
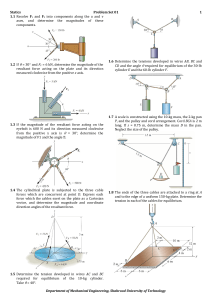
term-exam2-keys - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... 1. What force is needed to make an object move in a circle? a) kinetic friction b) static friction c) centripetal force d) weight 2. How many revolutions per minute must a circular, rotating spacestation of radius 1000 m rotate to produce an artificial gravity of 9.80 m/s2? a) 0.65 rpm b) 0.75 rpm c ...
... 1. What force is needed to make an object move in a circle? a) kinetic friction b) static friction c) centripetal force d) weight 2. How many revolutions per minute must a circular, rotating spacestation of radius 1000 m rotate to produce an artificial gravity of 9.80 m/s2? a) 0.65 rpm b) 0.75 rpm c ...
Document
... 1) In the absence of forces, an object ("body") at rest will stay at rest, and a body moving at a constant velocity in straight line continues doing so indefinitely. ...
... 1) In the absence of forces, an object ("body") at rest will stay at rest, and a body moving at a constant velocity in straight line continues doing so indefinitely. ...
MS Word
... was present (GE 1: 8) but what happens if we increase the force that was used in GE 1: 1? Let's try to double the force used in that case. Push the cart/person with twice the force that it took to move the cart at a constant velocity. You may have to try several times to get it right. Try to keep th ...
... was present (GE 1: 8) but what happens if we increase the force that was used in GE 1: 1? Let's try to double the force used in that case. Push the cart/person with twice the force that it took to move the cart at a constant velocity. You may have to try several times to get it right. Try to keep th ...
Physics 601 – Momentum VO Why does a gun kick when it`s fired
... So we have three variables that can change. Since we’re concentrating on time’s effect on velocity, let’s not consider force for now. We’ll keep it constant, too. That leaves two variables to look at: time and change in velocity. We want to see how time and velocity affect each other. In this case, ...
... So we have three variables that can change. Since we’re concentrating on time’s effect on velocity, let’s not consider force for now. We’ll keep it constant, too. That leaves two variables to look at: time and change in velocity. We want to see how time and velocity affect each other. In this case, ...
Lab M08: A Study of Sliding Friction PH306 24/01/08
... Whenever one object is dragged across another, sliding (kinetic) friction acts on the surface of each object. The size of the sliding frictional force is determined by the characteristics of the two surfaces and the normal force each surface exerts on the other. The sliding frictional force on each ...
... Whenever one object is dragged across another, sliding (kinetic) friction acts on the surface of each object. The size of the sliding frictional force is determined by the characteristics of the two surfaces and the normal force each surface exerts on the other. The sliding frictional force on each ...
Ch 12.5 Arc Length and Curvature
... Arc length and curvature are closely related to the tangential and normal components of acceleration. The tangential component of acceleration is the rate of change of the speed, which in turn is the rate of change of the arc length. This component is negative as a moving object slows down and posit ...
... Arc length and curvature are closely related to the tangential and normal components of acceleration. The tangential component of acceleration is the rate of change of the speed, which in turn is the rate of change of the arc length. This component is negative as a moving object slows down and posit ...
2565 Opt B Part 1
... • these are all terms which describe the turning effect produced by a force • when it acts eccentrically (to one side of) to an axis of rotation • moment = F x d ...
... • these are all terms which describe the turning effect produced by a force • when it acts eccentrically (to one side of) to an axis of rotation • moment = F x d ...
4. Motion, Energy, and Gravity
... • Realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens one universe • Discovered laws of motion and gravity • Much more: experiments with light, first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
... • Realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens one universe • Discovered laws of motion and gravity • Much more: experiments with light, first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
Ch 6 ppt
... ground at the same rate because the acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects. • Acceleration Due to Gravity As shown on the next slide, for every second that an object falls, the object’s downward velocity increases by 9.8 m/s. ...
... ground at the same rate because the acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects. • Acceleration Due to Gravity As shown on the next slide, for every second that an object falls, the object’s downward velocity increases by 9.8 m/s. ...
Conservation of Momentum AIM To determine the momentum of a
... Momentum of an object is defined as the product of its mass and velocity. momentum = mass x velocity The symbol for momentum is (logically!?) 'p'. We can therefore write the above definition in symbolic form as p = mv Since the units for m are ........, and the units for v are ........., it is logic ...
... Momentum of an object is defined as the product of its mass and velocity. momentum = mass x velocity The symbol for momentum is (logically!?) 'p'. We can therefore write the above definition in symbolic form as p = mv Since the units for m are ........, and the units for v are ........., it is logic ...