NCEA Level 1 Science (90940) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... • Air resistance = 0N at the instant the parachutist leaves the plane. Acceleration at that instant will be 10ms-2 AND • When falling her air resistance < weight / gravity, therefore unbalanced forces apply (net downward force) which causes acceleration (increase in speed). ...
... • Air resistance = 0N at the instant the parachutist leaves the plane. Acceleration at that instant will be 10ms-2 AND • When falling her air resistance < weight / gravity, therefore unbalanced forces apply (net downward force) which causes acceleration (increase in speed). ...
Answer, Key – Homework 8 – David McIntyre 1 This print
... with r14 the distance between Q4 and Q1 , r24 = r34 the distance between Q4 and either Q2 or Q3 , and θ indicated in the sketch above. Remember that this force FQ4 will be set equal to zero since the problem tells us the forces are in equilibrium. Because Q1 , Q2 , and Q3 form an equilateral triangl ...
... with r14 the distance between Q4 and Q1 , r24 = r34 the distance between Q4 and either Q2 or Q3 , and θ indicated in the sketch above. Remember that this force FQ4 will be set equal to zero since the problem tells us the forces are in equilibrium. Because Q1 , Q2 , and Q3 form an equilateral triangl ...
ppt - MrMaloney.com
... with Newton’s 2nd Law. Dynamic problems are problems in which the net force is not ZERO. In this case the sum of the forces in the X-direction and/or the Y-direction are not always zero, and may result in some acceleration. BACK © 2002 Mike Maloney ...
... with Newton’s 2nd Law. Dynamic problems are problems in which the net force is not ZERO. In this case the sum of the forces in the X-direction and/or the Y-direction are not always zero, and may result in some acceleration. BACK © 2002 Mike Maloney ...
laws of motion
... tendency (sanskara) to move in a straight line(vega) or restoration of shape in an elastic body; transmitted force by a string, rod, etc. The notion of (vega) in the Vaisesika theory of motion perhaps comes closest to the concept of inertia. Vega, the tendency to move in a straight line, was thought ...
... tendency (sanskara) to move in a straight line(vega) or restoration of shape in an elastic body; transmitted force by a string, rod, etc. The notion of (vega) in the Vaisesika theory of motion perhaps comes closest to the concept of inertia. Vega, the tendency to move in a straight line, was thought ...
laws of motion
... tendency (sanskara) to move in a straight line(vega) or restoration of shape in an elastic body; transmitted force by a string, rod, etc. The notion of (vega) in the Vaisesika theory of motion perhaps comes closest to the concept of inertia. Vega, the tendency to move in a straight line, was thought ...
... tendency (sanskara) to move in a straight line(vega) or restoration of shape in an elastic body; transmitted force by a string, rod, etc. The notion of (vega) in the Vaisesika theory of motion perhaps comes closest to the concept of inertia. Vega, the tendency to move in a straight line, was thought ...
Physics 11 - BigEngine
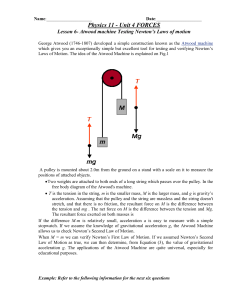
... A pulley is mounted about 2.0m from the ground on a stand with a scale on it to measure the positions of attached objects. Two weights are attached to both ends of a long string which passes over the pulley. In the free body diagram of the Atwood's machine. T is the tension in the string, m is t ...
... A pulley is mounted about 2.0m from the ground on a stand with a scale on it to measure the positions of attached objects. Two weights are attached to both ends of a long string which passes over the pulley. In the free body diagram of the Atwood's machine. T is the tension in the string, m is t ...
Engineering Physics 1 Studio Manual - KSU Physics
... track. Set the metronome pulsing. Coincident with a given pulse, the starter releases the glider. At the next pulse of the metronome, the first observer notes the position of the glider as it passes. The second observer does the same at the second pulse. Record positions and times and repeat a few t ...
... track. Set the metronome pulsing. Coincident with a given pulse, the starter releases the glider. At the next pulse of the metronome, the first observer notes the position of the glider as it passes. The second observer does the same at the second pulse. Record positions and times and repeat a few t ...
Objective Assignment - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... In projectile motion, horizontal component of velocity (u cos), acceleration (g) and mechanical energy remains constant while, speed, velocity, vertical component of velocity (u sin ), momentum, kinetic energy and potential energy all changes. Velocity, and KE are maximum at the point of projectio ...
... In projectile motion, horizontal component of velocity (u cos), acceleration (g) and mechanical energy remains constant while, speed, velocity, vertical component of velocity (u sin ), momentum, kinetic energy and potential energy all changes. Velocity, and KE are maximum at the point of projectio ...
Fluid Mechanics
... should you worry about the units) It can be thought of as the effect of friction in a fluid Friction (sometimes called skin friction) is a resistance to motion created by two objects rubbing against one another When a fluid travels over an object, The amount of friction is determined by: ...
... should you worry about the units) It can be thought of as the effect of friction in a fluid Friction (sometimes called skin friction) is a resistance to motion created by two objects rubbing against one another When a fluid travels over an object, The amount of friction is determined by: ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy conclusion
... only be converted from one form to another. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat energy. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of molecules. Examples of heat generation: sliding friction, muscle forces. ...
... only be converted from one form to another. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat energy. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of molecules. Examples of heat generation: sliding friction, muscle forces. ...
Fluid Mechanics Intro Slides.
... evaluate the shear stress (and ultimately the shear force) exerted by a moving fluid onto the fluid’s boundaries. ...
... evaluate the shear stress (and ultimately the shear force) exerted by a moving fluid onto the fluid’s boundaries. ...
Safety OF CAR AND PHYSICS
... The driver may hits the dashboard or windshield w hich also acts as a force stopping the driver but it i njures them at the same time By the way. Airbag gives a force over time (Impulse ). The more the the force acts on the driver to slow him down, the less damage caused to the driver ...
... The driver may hits the dashboard or windshield w hich also acts as a force stopping the driver but it i njures them at the same time By the way. Airbag gives a force over time (Impulse ). The more the the force acts on the driver to slow him down, the less damage caused to the driver ...