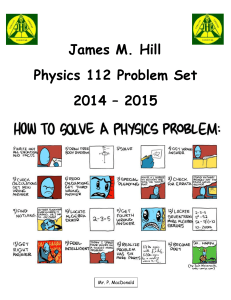
$doc.title
... • Suppose we are moving along a line, but the force we are interested in in pointed in another direction? (How can this happen?) • Only the part of the force in the direction of the motion counts to change the speed (energy). ...
... • Suppose we are moving along a line, but the force we are interested in in pointed in another direction? (How can this happen?) • Only the part of the force in the direction of the motion counts to change the speed (energy). ...
File - Physics Made Easy
... conservation of momentum ,centre of mass of the two fragments. Remain at rest. ...
... conservation of momentum ,centre of mass of the two fragments. Remain at rest. ...
Gravity and Motion
... • Acceleration = change in velocity over time • Review: velocity = change in speed and/or direction weight = gravitational force (unbalanced) ...
... • Acceleration = change in velocity over time • Review: velocity = change in speed and/or direction weight = gravitational force (unbalanced) ...
Document
... • What are the defining characteristics of inertia? • How can forces be quantified and measured? • How can you use the summation of forces to calculate the acceleration of an object? • How can you infer the forces on an object from information about its motion? • What affects the strength of the con ...
... • What are the defining characteristics of inertia? • How can forces be quantified and measured? • How can you use the summation of forces to calculate the acceleration of an object? • How can you infer the forces on an object from information about its motion? • What affects the strength of the con ...
Chapter 6
... Yes. Impulse is the product of the average force times the time the force acts. The first force is the larger force because impulse is equal to the product of force and time. If the second time is twice that of the first, then the first force must be twice that of the second force. Momentum is mass ...
... Yes. Impulse is the product of the average force times the time the force acts. The first force is the larger force because impulse is equal to the product of force and time. If the second time is twice that of the first, then the first force must be twice that of the second force. Momentum is mass ...
momentum - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... interacting objects remains the same in the absence of external forces Applications: Collisions, analyzing action/reaction interactions ...
... interacting objects remains the same in the absence of external forces Applications: Collisions, analyzing action/reaction interactions ...
Physics 106b/196b – Problem Set 9 – Due Jan 19,... Version 3: January 18, 2007
... small oscillations. 7. (196b) Consider a charged sphere whose mass m and charge q are both distributed in a spherically symmetric way. That is, the mass and charge densities are each functions of the radius r (but not necessarily the same function). Do the following: ~ then the torque on (a) (3 pts) ...
... small oscillations. 7. (196b) Consider a charged sphere whose mass m and charge q are both distributed in a spherically symmetric way. That is, the mass and charge densities are each functions of the radius r (but not necessarily the same function). Do the following: ~ then the torque on (a) (3 pts) ...
Sixth Grade Physics - Math/Science Nucleus
... answer to these questions are all "no". Motion including spinning, velocity, acceleration, momentum and other terms, reflect this movement that all substances, large and small, are experiencing all the time. It is this motion that physicists must understand in order to explain physical phenomena. Mo ...
... answer to these questions are all "no". Motion including spinning, velocity, acceleration, momentum and other terms, reflect this movement that all substances, large and small, are experiencing all the time. It is this motion that physicists must understand in order to explain physical phenomena. Mo ...
This worksheet uses the concepts of rotational
... L is called the angular momentum, and it is conserved in the absence of external torques. For systems which are rotating about one principle (symmetry) axis, the direction of the angular momentum is in the same direction as the angular velocity. The direction of the angular velocity is found by what ...
... L is called the angular momentum, and it is conserved in the absence of external torques. For systems which are rotating about one principle (symmetry) axis, the direction of the angular momentum is in the same direction as the angular velocity. The direction of the angular velocity is found by what ...
Questions - TTU Physics
... 1. See figure. Two masses, m1 & m2, are connected by a massless, inextensible string of length ℓ, which is put over the massless, frictionless pulley at the top of a wedge, as shown. m1 & m2, are allowed to slide under the influence of gravity on the 2 frictionless inclined planes. As suggested in t ...
... 1. See figure. Two masses, m1 & m2, are connected by a massless, inextensible string of length ℓ, which is put over the massless, frictionless pulley at the top of a wedge, as shown. m1 & m2, are allowed to slide under the influence of gravity on the 2 frictionless inclined planes. As suggested in t ...