Motion - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Buildings, rocks, utility poles, and trees rarely, if ever, move from one place to another. Even things that do move from time to time sit still for a great deal of time. This includes you, automobiles, and bicycles (Figure 2.1). On the other hand, the sun, the moon, and starry heavens seem to alway ...
... Buildings, rocks, utility poles, and trees rarely, if ever, move from one place to another. Even things that do move from time to time sit still for a great deal of time. This includes you, automobiles, and bicycles (Figure 2.1). On the other hand, the sun, the moon, and starry heavens seem to alway ...
chapter (iii) fluid flow
... If the fluid is considered frictionless with zero viscosity it is called ideal. In real fluids the viscosity is considered and shear stresses occur causing conversion of mechanical energy into thermal energy ...
... If the fluid is considered frictionless with zero viscosity it is called ideal. In real fluids the viscosity is considered and shear stresses occur causing conversion of mechanical energy into thermal energy ...
Chapter4.1 - Department of Physics & Astronomy
... • Realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens one universe • Discovered laws of motion and gravity • Much more: experiments with light, first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
... • Realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens one universe • Discovered laws of motion and gravity • Much more: experiments with light, first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
No Slide Title
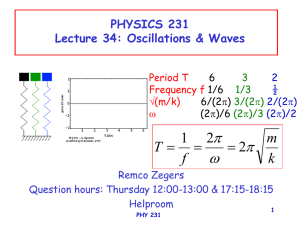
... An anchored fishing boat is going up and down with the waves. It reaches a maximum height every 5 seconds and a person on the boat sees that while reaching a maximum, the previous waves has moves about 40 m away from the boat. What is the speed of the traveling waves? ...
... An anchored fishing boat is going up and down with the waves. It reaches a maximum height every 5 seconds and a person on the boat sees that while reaching a maximum, the previous waves has moves about 40 m away from the boat. What is the speed of the traveling waves? ...
AP Energy Conservation Notes
... road runner -when will he learn? As part of this new ACME trap he throws a ball down on a spring as shown to the right. ...
... road runner -when will he learn? As part of this new ACME trap he throws a ball down on a spring as shown to the right. ...
LEC. 7: Stress I – Introduction to Dynamic Analysis
... LEC. 7: Stress I – Introduction to Dynamic Analysis The four categories of deformation are a rock’s response to stresses that are generated by ...
... LEC. 7: Stress I – Introduction to Dynamic Analysis The four categories of deformation are a rock’s response to stresses that are generated by ...
POWERPOINT JEOPARDY
... • The amount of change in the speed of an object divided by the amount of time it took to change the speed. ...
... • The amount of change in the speed of an object divided by the amount of time it took to change the speed. ...
Proposal-Use
... and found that they were different from physicist views. Results of students’ views taken from individual interview and responses to the Force and Motion Conceptual Evaluation 2 were explicit. In the first case, an object is moving with a constant velocity, most students viewed that there was a non- ...
... and found that they were different from physicist views. Results of students’ views taken from individual interview and responses to the Force and Motion Conceptual Evaluation 2 were explicit. In the first case, an object is moving with a constant velocity, most students viewed that there was a non- ...
MOMENTUM!
... In the first two sample problems, we dealt with a frictionless surface. We couldn’t simply conserve momentum if friction had been present because, as the proof on the last slide shows, there would be another force (friction) in addition to the contact forces. Friction wouldn’t cancel out, and it wou ...
... In the first two sample problems, we dealt with a frictionless surface. We couldn’t simply conserve momentum if friction had been present because, as the proof on the last slide shows, there would be another force (friction) in addition to the contact forces. Friction wouldn’t cancel out, and it wou ...
Document
... Angular Force: force of a muscle contributing to bone's movement around a joint axis; greatest when muscles angle of pull is perpendicular to bone (i.e. 90 degrees). Stabilizing force: degree of parallel forces generated on the lever (bone and joint) when the muscles angle of pull is less than 90 de ...
... Angular Force: force of a muscle contributing to bone's movement around a joint axis; greatest when muscles angle of pull is perpendicular to bone (i.e. 90 degrees). Stabilizing force: degree of parallel forces generated on the lever (bone and joint) when the muscles angle of pull is less than 90 de ...
Marble Tower Analysis
... Calculate the work in units of Joules (1 Joule = 1 N·m) done by your marble from the force of gravity. (Remember: Work = Force ● distance. Since gravity is a force that is applied only in a vertical, down, direction then the distance in this equation is actually the tower’s height.) (SHOW SET UP! Ro ...
... Calculate the work in units of Joules (1 Joule = 1 N·m) done by your marble from the force of gravity. (Remember: Work = Force ● distance. Since gravity is a force that is applied only in a vertical, down, direction then the distance in this equation is actually the tower’s height.) (SHOW SET UP! Ro ...