Gravity
... + What is a force? In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. Force can also be described as a push or pull that can cause an object with mass to change its velocity – something moving from where it started f ...
... + What is a force? In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. Force can also be described as a push or pull that can cause an object with mass to change its velocity – something moving from where it started f ...
4. Dynamics
... spring. Instead, if the mass is released suddenly from the same initial position, the maximum extension of the spring now is: (g – acceleration due to gravity) [EAMCET 2009 M] mg mg 2) 2d ...
... spring. Instead, if the mass is released suddenly from the same initial position, the maximum extension of the spring now is: (g – acceleration due to gravity) [EAMCET 2009 M] mg mg 2) 2d ...
A x
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i.e. zero displac ...
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i.e. zero displac ...
Objective 2 Examine the force exerted on objects by gravity
... 10. Explain an example of Newton’s second law: To move a train takes a lot of energy. To stop a train takes a lot of energy. A train wreck would have a lot of force. 11. Newton’s 3rd law states: that for every _Action_ there is an equal and opposite _Reaction__. 12. Explain an example of Newton’s th ...
... 10. Explain an example of Newton’s second law: To move a train takes a lot of energy. To stop a train takes a lot of energy. A train wreck would have a lot of force. 11. Newton’s 3rd law states: that for every _Action_ there is an equal and opposite _Reaction__. 12. Explain an example of Newton’s th ...
Classical Dynamics for a System of Particles (Chapter 9)
... life, we normally think of a collision as an event in which two objects hit each other. In physics the word is used in a more general way. A collision is an event in which: Two objects move together, experience equal but opposite f forces, and d accelerate l in response to those h forces. f When ...
... life, we normally think of a collision as an event in which two objects hit each other. In physics the word is used in a more general way. A collision is an event in which: Two objects move together, experience equal but opposite f forces, and d accelerate l in response to those h forces. f When ...
Document
... When the ball is displaced from its equilibrium position and released, it moves in simple harmonic motion. Consider the relationship between the angular frequency, the mass, and the spring constant given in the text. Which one of the following statements concerning that relationship is true? a) Incr ...
... When the ball is displaced from its equilibrium position and released, it moves in simple harmonic motion. Consider the relationship between the angular frequency, the mass, and the spring constant given in the text. Which one of the following statements concerning that relationship is true? a) Incr ...
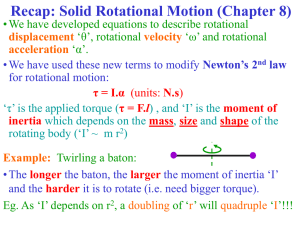
Angular Momentum - USU Department of Physics
... • This causes the moment of inertia of the star to decrease drastically and results in a tremendous increase in its angular velocity. Example: A star of similar size & mass to the Sun would shrink down to form a very dense object of diameter ~25 km! Called a ‘neutron’ star! • A neutron star is at th ...
... • This causes the moment of inertia of the star to decrease drastically and results in a tremendous increase in its angular velocity. Example: A star of similar size & mass to the Sun would shrink down to form a very dense object of diameter ~25 km! Called a ‘neutron’ star! • A neutron star is at th ...
p - Chris Hecker
... • this is why “v’=vM” makes no sense for column vectors – either you’re using row vectors, or you’re confused – either way, you’re in for some pain when trying to do real math • because all math books use columns for vectors and rows are special • early computer graphics books got this backwards, an ...
... • this is why “v’=vM” makes no sense for column vectors – either you’re using row vectors, or you’re confused – either way, you’re in for some pain when trying to do real math • because all math books use columns for vectors and rows are special • early computer graphics books got this backwards, an ...
AP PHYSICS 2 E01
... problems with motion qualitatively and quantitatively, and can explain forces based on internal structure. [LO 3.B.2.1, SP 1.1, SP 1.4, SP 2.2] 4. TSW predict the motion of an object subject to forces exerted by several objects using an application of Newton’s second law in a variety of physical sit ...
... problems with motion qualitatively and quantitatively, and can explain forces based on internal structure. [LO 3.B.2.1, SP 1.1, SP 1.4, SP 2.2] 4. TSW predict the motion of an object subject to forces exerted by several objects using an application of Newton’s second law in a variety of physical sit ...