The Measurement of Mass
... Another device which may be used to determine mass is Atwood's machine. This device uses Newton's second law, which relates the net force, F, acting on a body of mass, m, to the acceleration, a, the force produces. Specifically, ...
... Another device which may be used to determine mass is Atwood's machine. This device uses Newton's second law, which relates the net force, F, acting on a body of mass, m, to the acceleration, a, the force produces. Specifically, ...
- GEOCITIES.ws
... Mr. Moe Mentum • We’ve talked about forces, but how do they affect and relate to motion? • If we remember Newton’s 2nd Law, the net force = time rate change of momentum • momentum () – defined as mass of an object times its velocity • compare the momentum of a baby carriage and bus ...
... Mr. Moe Mentum • We’ve talked about forces, but how do they affect and relate to motion? • If we remember Newton’s 2nd Law, the net force = time rate change of momentum • momentum () – defined as mass of an object times its velocity • compare the momentum of a baby carriage and bus ...
B (2) - TSG@MIT Physics
... Chrome Inertia Wheel: This aparatus is made from four horizontal rods wrapped around the vertical axel of the bearing. The weight exerts a constant torque on the system. The demonstration shows that when the four masses are close to the axel the angular acceleration is greater than when the four mas ...
... Chrome Inertia Wheel: This aparatus is made from four horizontal rods wrapped around the vertical axel of the bearing. The weight exerts a constant torque on the system. The demonstration shows that when the four masses are close to the axel the angular acceleration is greater than when the four mas ...
Document
... A car with a mass of 950 kg and an initial speed of v1 = 17.8 m/s approaches an intersection, as shown in the figure. A 1300 kg minivan traveling northward is heading for the same intersection. The car and minivan collide and stick together. If the direction of the wreckage after the collision is 37 ...
... A car with a mass of 950 kg and an initial speed of v1 = 17.8 m/s approaches an intersection, as shown in the figure. A 1300 kg minivan traveling northward is heading for the same intersection. The car and minivan collide and stick together. If the direction of the wreckage after the collision is 37 ...
Physics 121. Review Exam 3.
... Two views of rolling motion: 1) Pure rotation around the instantaneous axis or 2) rotation and translation. Frank L. H. Wolfs ...
... Two views of rolling motion: 1) Pure rotation around the instantaneous axis or 2) rotation and translation. Frank L. H. Wolfs ...
Document
... Visualize: Please refer to Figure 26.7. The figure shows a dipole aligned on the y-axis, so the x-axis is the bisecting axis. The field at a point on the x-axis is E dipole = E + + E − . Solve: From the symmetry of the situation we can see that the x-components of the two contributions to the ...
... Visualize: Please refer to Figure 26.7. The figure shows a dipole aligned on the y-axis, so the x-axis is the bisecting axis. The field at a point on the x-axis is E dipole = E + + E − . Solve: From the symmetry of the situation we can see that the x-components of the two contributions to the ...
Elastic Potential Energy
... (1) A spring scale is calibrated from zero to 20. N. The calibrations extend over a length of 0.10 m. (a) What is the elastic potential energy of the spring in the scale when a weight of 5.0 N hangs from it? (b) What is the elastic potential energy when the spring is fully stretched? (2) The force c ...
... (1) A spring scale is calibrated from zero to 20. N. The calibrations extend over a length of 0.10 m. (a) What is the elastic potential energy of the spring in the scale when a weight of 5.0 N hangs from it? (b) What is the elastic potential energy when the spring is fully stretched? (2) The force c ...
Rotational Motion
... the pulley used be Rp . A rigid body whose moment of inertia about the pulley axis is I is mounted on the pulley. A string is wound around the pulley, goes horizontally to a “super” pulley, and then goes straight down to a hanging mass m. Let the tension in the string be T . The equations of motion ...
... the pulley used be Rp . A rigid body whose moment of inertia about the pulley axis is I is mounted on the pulley. A string is wound around the pulley, goes horizontally to a “super” pulley, and then goes straight down to a hanging mass m. Let the tension in the string be T . The equations of motion ...
Chapter 1 - asmasaid
... Wire, briar, limber, lock, three geese in a flock. One flew east, one flew west, and one flew over the cuckoo's nest. If they all flew at the same speed and the cuckoo's nest is to the northwest, which graph represents their total momentum? A) B) C) ...
... Wire, briar, limber, lock, three geese in a flock. One flew east, one flew west, and one flew over the cuckoo's nest. If they all flew at the same speed and the cuckoo's nest is to the northwest, which graph represents their total momentum? A) B) C) ...
Producing RHS of Acceleration Eq.
... The three stages of Kinematics Analysis: position analysis, velocity analysis, and acceleration analysis they each follow *very* similar recipes for finding for each body of the mechanism its position, velocity and acceleration, respectively ...
... The three stages of Kinematics Analysis: position analysis, velocity analysis, and acceleration analysis they each follow *very* similar recipes for finding for each body of the mechanism its position, velocity and acceleration, respectively ...
AH (SHM) - mrmackenzie
... (a) Determine the value for the amplitude (A), period (T), frequency (f) and angular frequency (ω ω) of the motion. (b) Use values from part (a) to obtain an expression in the form y = A cos ωt for the displacement y from the equilibrium position of the object undergoing simple harmonic motion. (c) ...
... (a) Determine the value for the amplitude (A), period (T), frequency (f) and angular frequency (ω ω) of the motion. (b) Use values from part (a) to obtain an expression in the form y = A cos ωt for the displacement y from the equilibrium position of the object undergoing simple harmonic motion. (c) ...
here
... things cancel. r = RE (1.759) = RE (1 +0.759). The altitude is the extra part. Answer: 4.8 Mm. 2) All two-body systems orbit about their mutual centre of mass. Usually one of the two objects is much bigger and that point is almost the same as the centre of the large mass. In this case each star orbi ...
... things cancel. r = RE (1.759) = RE (1 +0.759). The altitude is the extra part. Answer: 4.8 Mm. 2) All two-body systems orbit about their mutual centre of mass. Usually one of the two objects is much bigger and that point is almost the same as the centre of the large mass. In this case each star orbi ...
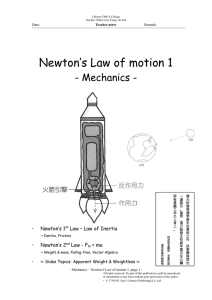
Newton`s Law of motion 1
... If an object with mass, m, is placed about the surface of the Earth. A downward force (towards the centre of the Earth) acted on it. This is called weight of the object. This force comes from the Earth, and is called gravity. [Def.] Weight is the force of gravity on an object and is equal to the pro ...
... If an object with mass, m, is placed about the surface of the Earth. A downward force (towards the centre of the Earth) acted on it. This is called weight of the object. This force comes from the Earth, and is called gravity. [Def.] Weight is the force of gravity on an object and is equal to the pro ...