The Four Laws of Thermodynamics
... ”The laws of thermodynamics drive everything that happens in the universe. From the sudden expansion of a cloud of gas to the cooling of hot metal, and from the unfurling of a leaf to the course of life itself–everything is moved or restrained by four simple laws. They establish fundamental concepts ...
... ”The laws of thermodynamics drive everything that happens in the universe. From the sudden expansion of a cloud of gas to the cooling of hot metal, and from the unfurling of a leaf to the course of life itself–everything is moved or restrained by four simple laws. They establish fundamental concepts ...
CHEM 240 Who am I?
... • Can we predict the transition temperature, i.e., the melting temperature Tm and the boiling temperature Tb, or the macroscopic properties of the different phases, e.g., the molar volumes, or the dependence of the transition temperatures on pressure on impurities (e.g. ...
... • Can we predict the transition temperature, i.e., the melting temperature Tm and the boiling temperature Tb, or the macroscopic properties of the different phases, e.g., the molar volumes, or the dependence of the transition temperatures on pressure on impurities (e.g. ...
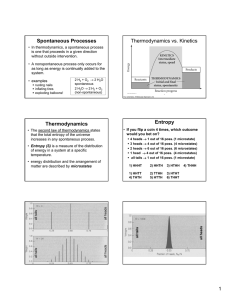
Entropy
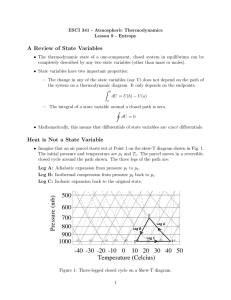
... 2. What are the units for entropy? For specific entropy? 3. Two moles of helium (M = 4 g/mol) are at 15 degrees C and 1000 mb. (a) If 6240 Joules of heat are added while keeping volume constant, what is the final temperature and pressure? (b) The helium is now allowed to expand isothermally to twice ...
... 2. What are the units for entropy? For specific entropy? 3. Two moles of helium (M = 4 g/mol) are at 15 degrees C and 1000 mb. (a) If 6240 Joules of heat are added while keeping volume constant, what is the final temperature and pressure? (b) The helium is now allowed to expand isothermally to twice ...
Lecture 4
... evolution to equilibrium will lead to an increase of the entropy S. If the relaxation process passes through macroscopically defined configurations we can define an S(t) that increases monotonically. Note: Thermodynamics is only concerned with macroscopic states, i.e. ones that are essentially in eq ...
... evolution to equilibrium will lead to an increase of the entropy S. If the relaxation process passes through macroscopically defined configurations we can define an S(t) that increases monotonically. Note: Thermodynamics is only concerned with macroscopic states, i.e. ones that are essentially in eq ...