D. Gravitational, Electric, and Magnetic Fields
... • use appropriate terminology related to fields, including, but not limited to: forces, potential energies, potential, and exchange particles • analyse, and solve problems relating to, Newton’s law of universal gravitation and circular motion (e.g., with respect to satellite orbits, black holes, d ...
... • use appropriate terminology related to fields, including, but not limited to: forces, potential energies, potential, and exchange particles • analyse, and solve problems relating to, Newton’s law of universal gravitation and circular motion (e.g., with respect to satellite orbits, black holes, d ...
Exercise 4 (Electromagnetism)
... (b) Assume the magnetic field is perpendicular to the current in the wire. By Fleming’s left hand rule, the magnetic force on the coil points to left. ...
... (b) Assume the magnetic field is perpendicular to the current in the wire. By Fleming’s left hand rule, the magnetic force on the coil points to left. ...
Electrostatics HW 2 HW 4.2 1e- = -1.6x10
... 8) A small glass ball rubbed with silk gains a charge of +2.00 µC (2.0x10-6 C). The glass ball is placed 12 cm from a small charged rubber ball that carries a charge of -3.5 µC (3.5x10-6 C). What is the magnitude of the electric force between the two spheres? Is the force attractive or repulsive? ...
... 8) A small glass ball rubbed with silk gains a charge of +2.00 µC (2.0x10-6 C). The glass ball is placed 12 cm from a small charged rubber ball that carries a charge of -3.5 µC (3.5x10-6 C). What is the magnitude of the electric force between the two spheres? Is the force attractive or repulsive? ...
class10
... So, does my proton exert a force if no one is around to feel it? • Force, no. But we can define an electric field which describes the force a charge would feel if it came near the proton ...
... So, does my proton exert a force if no one is around to feel it? • Force, no. But we can define an electric field which describes the force a charge would feel if it came near the proton ...
... plates. B in between the plates goes into the plane of the picture and is zero outside the plates. I calculate E from Gauss’ law. I use the fact that superposition tells me there is no field above the top plate and no field below the bottom plate. Furthermore I know for preceding chapters that the e ...
Solutions7
... motion of the crossbar using a right-hand rule or, equivalently, by applying F I B . We can find the minimum field B necessary to start the bar moving by applying a condition for static equilibrium to it. (a) Using a constant-acceleration ...
... motion of the crossbar using a right-hand rule or, equivalently, by applying F I B . We can find the minimum field B necessary to start the bar moving by applying a condition for static equilibrium to it. (a) Using a constant-acceleration ...
Key Homework 5.3.
... 1. a. A direct current I flows in a straight wire of length 2L situated along the z-axis (stretching from –L to L). Find the magnetic vector potential in a field point P that is situated in the bisecting plane (see figure below). ...
... 1. a. A direct current I flows in a straight wire of length 2L situated along the z-axis (stretching from –L to L). Find the magnetic vector potential in a field point P that is situated in the bisecting plane (see figure below). ...
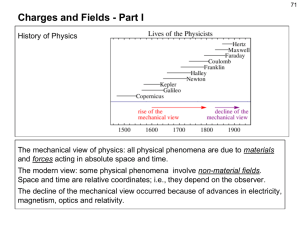
Charges and Fields - Part I
... theory that “electricity” was a kind of fluid - a material substance - that would flow from one object to another; then the objects would be electrified, with either positive charge (excess fluid) or negative charge (deficit of fluid). You learned in grade school: “like charges repel and unlike char ...
... theory that “electricity” was a kind of fluid - a material substance - that would flow from one object to another; then the objects would be electrified, with either positive charge (excess fluid) or negative charge (deficit of fluid). You learned in grade school: “like charges repel and unlike char ...
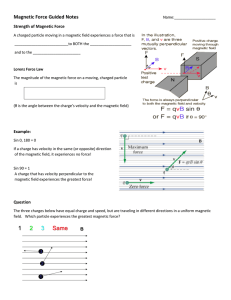
Magnetic Force Guided Notes
... What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on a proton moving at 2.5 X 105 m/s in a magnetic field of 0.5 T … (a) …if the velocity and magnetic field are at right angles? (b) … if the velocity and magnetic field are at 30°? (c) … if the velocity is parallel to a magnetic field? ...
... What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on a proton moving at 2.5 X 105 m/s in a magnetic field of 0.5 T … (a) …if the velocity and magnetic field are at right angles? (b) … if the velocity and magnetic field are at 30°? (c) … if the velocity is parallel to a magnetic field? ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 09. Write down the boundary conditions when an electromagnetic wave passes from one medium to another 10. Write down Ampere’s law in differential form, with Maxwell’s modification PART B Answer any four ...
... 09. Write down the boundary conditions when an electromagnetic wave passes from one medium to another 10. Write down Ampere’s law in differential form, with Maxwell’s modification PART B Answer any four ...
Solutions from Yosumism website Problem 61 Problem 62:
... . Since there is a force contribution from each charge, and since, by the where right-hand-rule, their cross-products with the moment-arm point in the same direction, one finds the torque to be ...
... . Since there is a force contribution from each charge, and since, by the where right-hand-rule, their cross-products with the moment-arm point in the same direction, one finds the torque to be ...