the patents officer - Institute of Physics
... What is the root mean square (rms) speed of a molecule of gas? What is the equipartition theorem? What do we mean by ‘mean free path’ and how can you calculate it in an ideal gas? What is the difference between heat and temperature? When we consider heat flow what is the difference between C, c’ and ...
... What is the root mean square (rms) speed of a molecule of gas? What is the equipartition theorem? What do we mean by ‘mean free path’ and how can you calculate it in an ideal gas? What is the difference between heat and temperature? When we consider heat flow what is the difference between C, c’ and ...
Thermodynamics Notes
... On the microscopic level, the atoms of the gas collide from time to time with the walls of the container. Let us consider a single atom, as shown in the figure above. It collides elastically with the wall of the container and experiences a change in momentum mvx m2vx . That is, the wall exerts a ...
... On the microscopic level, the atoms of the gas collide from time to time with the walls of the container. Let us consider a single atom, as shown in the figure above. It collides elastically with the wall of the container and experiences a change in momentum mvx m2vx . That is, the wall exerts a ...
I. Development of the Virial Theorem
... theorem finds its widest application. However, in astrophysics few if any investigators live long enough to perform the time-averages for which the theorem calls. Thus, one more step is needed. It is this step which occasionally leads to difficulty and erroneous results. In order to replace the time ...
... theorem finds its widest application. However, in astrophysics few if any investigators live long enough to perform the time-averages for which the theorem calls. Thus, one more step is needed. It is this step which occasionally leads to difficulty and erroneous results. In order to replace the time ...
Diffusion: Microscopic Theory
... 2) The probability of going to the right at each step is 1/2, and the probability of going to the left at each step is 1/2. The particles, by interacting with the molecules of ...
... 2) The probability of going to the right at each step is 1/2, and the probability of going to the left at each step is 1/2. The particles, by interacting with the molecules of ...
A Generalized Statement of Highest
... ble equilibrium for a given value of energy content, compatible with a given composition of constituents and compatible with a given set of parameters of any system A. This statement implies that each subsystem of a whole system has to be individually in stable equilibrium and that the composite of ...
... ble equilibrium for a given value of energy content, compatible with a given composition of constituents and compatible with a given set of parameters of any system A. This statement implies that each subsystem of a whole system has to be individually in stable equilibrium and that the composite of ...
First Law of Thermodynamics - Derry Area School District
... When you look at large systems like the ideal gas with 1023 particles, the most likely macrostate – described by p, V, and T and obeying the ideal gas law – has so many microstates associated with it that it’s the only one you have any chance of observing. • When you allow two systems at different t ...
... When you look at large systems like the ideal gas with 1023 particles, the most likely macrostate – described by p, V, and T and obeying the ideal gas law – has so many microstates associated with it that it’s the only one you have any chance of observing. • When you allow two systems at different t ...
temperature 2015 10 13
... The Kelvin scale of hotness, T, is proportional to the ideal-gas scale of temperature. Write kT = PV/N. The unit of the Kelvin scale, K, is defined such that the triple point of pure water is T = 273.16 K exactly. Experimental value: k = 1.38x10-23 J/K. k is the conversion factor between the two sca ...
... The Kelvin scale of hotness, T, is proportional to the ideal-gas scale of temperature. Write kT = PV/N. The unit of the Kelvin scale, K, is defined such that the triple point of pure water is T = 273.16 K exactly. Experimental value: k = 1.38x10-23 J/K. k is the conversion factor between the two sca ...
CHAPTER 4: PHASE TRANSITIONS
... example, solid ice, liquid water, and gaseous water vapor are separate phases of the same chemical species ( H 2O ) . Each phase can be distinguished with the density ρ of the constituent. For example, a portion of the Arctic Ocean in vicinity of the North Pole is frozen and consists of ice in a top ...
... example, solid ice, liquid water, and gaseous water vapor are separate phases of the same chemical species ( H 2O ) . Each phase can be distinguished with the density ρ of the constituent. For example, a portion of the Arctic Ocean in vicinity of the North Pole is frozen and consists of ice in a top ...
Stability of Plasma in Static Equilibrium
... in velocity space. We assume for simplicity that any boundaries present are such as to present no complications, e.g., rigid and perfectly conducting walls with В entirely tangential. The properties of the small tn/e limit we employ are: (a) v is constant following a particle motion. (b) f is rotati ...
... in velocity space. We assume for simplicity that any boundaries present are such as to present no complications, e.g., rigid and perfectly conducting walls with В entirely tangential. The properties of the small tn/e limit we employ are: (a) v is constant following a particle motion. (b) f is rotati ...
Part IV
... At T=0, the system is in the state of lowest energy, so that the N lowest single-particle states are filled, giving a sharp cut-off in n() at T = TF. At low non-zero temperatures, the occupancies are less than unity, and states with energies greater than μ are partially occupied. Electrons with e ...
... At T=0, the system is in the state of lowest energy, so that the N lowest single-particle states are filled, giving a sharp cut-off in n() at T = TF. At low non-zero temperatures, the occupancies are less than unity, and states with energies greater than μ are partially occupied. Electrons with e ...
chapter 4 general relationships between state variables of
... The last equation is usually refered to as the combined first and second law equation, and serves as the starting point for discussing any problem in thermodynamics. The ability to write the first law in terms only of state variables allows us to calculate many useful relationships between the therm ...
... The last equation is usually refered to as the combined first and second law equation, and serves as the starting point for discussing any problem in thermodynamics. The ability to write the first law in terms only of state variables allows us to calculate many useful relationships between the therm ...
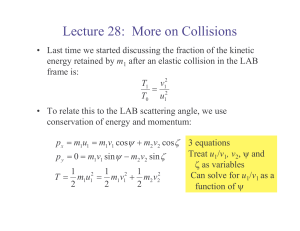
Lecture 28: More on Collisions
... • The quantity b is called the “impact parameter”, and we usually don’t know its value for a collision – We typically do control the initial energies accurately, and can measure the scattering angle and final energies – We also know the intensity (number of particles per unit area) of the incoming b ...
... • The quantity b is called the “impact parameter”, and we usually don’t know its value for a collision – We typically do control the initial energies accurately, and can measure the scattering angle and final energies – We also know the intensity (number of particles per unit area) of the incoming b ...
Lecture Notes for Statistical Mechanics of Soft Matter
... parents both died from eating poisonous mushrooms. The city council put the four younger Fahrenheit children in foster homes. But they apprenticed Daniel to a merchant, who taught him bookkeeping and took him off to Amsterdam. He settled in Amsterdam in 1701 looking for a trade. He became interested ...
... parents both died from eating poisonous mushrooms. The city council put the four younger Fahrenheit children in foster homes. But they apprenticed Daniel to a merchant, who taught him bookkeeping and took him off to Amsterdam. He settled in Amsterdam in 1701 looking for a trade. He became interested ...
2. Local equilibrium thermodynamics.
... applicable concept, the reciprocal of the thermodynamic temperature, spatial inhomogeneities, with the time courses and rates of, can be found through the assumption, this approximation assumes, the instantaneous global entropy of a non-equilibrium system, the simultaneous instantaneous entropies, d ...
... applicable concept, the reciprocal of the thermodynamic temperature, spatial inhomogeneities, with the time courses and rates of, can be found through the assumption, this approximation assumes, the instantaneous global entropy of a non-equilibrium system, the simultaneous instantaneous entropies, d ...
lecture notes on statistical mechanics - MSU Physics
... to understand why all states are equally populated from the perspective of dynamics. The Ergodic theorem is built on the symmetry of time-reversal, i.e., the rate at which one changes from state i to state j is the same as the rate at which one changes from state j to state i. Here, we can consider ...
... to understand why all states are equally populated from the perspective of dynamics. The Ergodic theorem is built on the symmetry of time-reversal, i.e., the rate at which one changes from state i to state j is the same as the rate at which one changes from state j to state i. Here, we can consider ...
PDF File - Tulane University
... disorganized at high temperature, increasing the entropy and molecules vibrate more at high temperature, increasing the volume). Similarly, both S and V tend to decrease with increasing pressure (less room to vibrate means better organization and lower volume). In addition, the change in volume and ...
... disorganized at high temperature, increasing the entropy and molecules vibrate more at high temperature, increasing the volume). Similarly, both S and V tend to decrease with increasing pressure (less room to vibrate means better organization and lower volume). In addition, the change in volume and ...
Lecture12
... initial temperature of 293 K slowly expands at constant pressure from a volume of 1.00 L to 2.50 L. (a) Find the work done on the environment. ...
... initial temperature of 293 K slowly expands at constant pressure from a volume of 1.00 L to 2.50 L. (a) Find the work done on the environment. ...
H-theorem

In classical statistical mechanics, the H-theorem, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872, describes the tendency to increase in the quantity H (defined below) in a nearly-ideal gas of molecules. As this quantity H was meant to represent the entropy of thermodynamics, the H-theorem was an early demonstration of the power of statistical mechanics as it claimed to derive the second law of thermodynamics—a statement about fundamentally irreversible processes—from reversible microscopic mechanics.The H-theorem is a natural consequence of the kinetic equation derived by Boltzmann that has come to be known as Boltzmann's equation. The H-theorem has led to considerable discussion about its actual implications, with major themes being: What is entropy? In what sense does Boltzmann's quantity H correspond to the thermodynamic entropy? Are the assumptions (such as the Stosszahlansatz described below) behind Boltzmann's equation too strong? When are these assumptions violated?↑