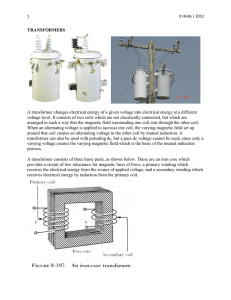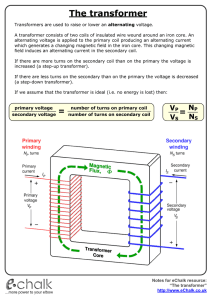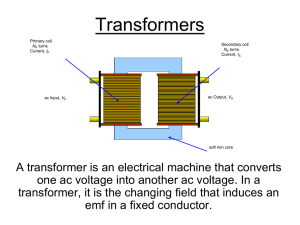
A new type electromagnet controller for isotope ratio mass
... coefficient of dissipation energy due to high inductance and low resistance, the power needed for the periodic supply of the coil current is small. A precise adjustment of the coil current is can be made in a continuous manner by setting of the width of the current pulses. That width can be adjusted ...
... coefficient of dissipation energy due to high inductance and low resistance, the power needed for the periodic supply of the coil current is small. A precise adjustment of the coil current is can be made in a continuous manner by setting of the width of the current pulses. That width can be adjusted ...
A 100-turn coil of area 0.1 m 2 rotates at half a revolution per second
... Q.18. Two point charges,q1 = 10 x 10-8 C and q2 = -2 x 10-8 C are separated by a distance of 60 cm in air. (i) Find at what distance from the 1st charge, q1, would the electric potential be zero. (ii) Also calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the system. ...
... Q.18. Two point charges,q1 = 10 x 10-8 C and q2 = -2 x 10-8 C are separated by a distance of 60 cm in air. (i) Find at what distance from the 1st charge, q1, would the electric potential be zero. (ii) Also calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the system. ...
Ignition system

An ignition system is a system for igniting a fuel-air mixture. Ignition systems are well known in the field of internal combustion engines such as those used in petrol (gasoline) engines used to power the majority of motor vehicles, but they are also used in many other applications such as in oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc.The first ignition system to use an electric spark was probably Alessandro Volta's toy electric pistol from the 1780s. Virtually all petrol engines today use an electric spark for ignition.Diesel engines rely on air compression for ignition, but usually also have glowplugs that preheat the combustion chamber to allow starting of the engine in cold weather. Other engines may use a flame, or a heated tube, for ignition.