* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download secondary coil
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
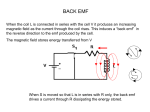
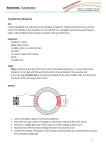
Transformer • Transformer is used to increase or decrease AC Voltage (potential difference). • Transformer is consisted of a soft iron core, a primary coil, and a secondary coil. • Primary coil is connected to AC supply, while the secondary coil is connected to the electrical component (lamp, computer, TV, etc) Soft iron Primary coil secondary coil Symbol of transformer Principle of Transformers • A transformer works only with alternating current supply (AC supply). • Mutual induction: When the primary coil is connected to a source of AC voltage, the changing current creates a changing magnetic field, which is carried through the core to the secondary coil. In the secondary coil the changing field induces a varying voltage. • The voltage induced in the secondary coil is called the secondary voltage and voltage induced in the primary coil is called the primary voltage. • In a transformer, the ratio of input voltage to output voltage depends on the ratio of the number of turn on the primary coil and secondary coil, as shown by formula: • • • • VS= secondary voltage or output voltage (Volt) VP= primary voltage or input voltage (Volt) NS= number of turns on secondary coil NP= number of turns on primary coil • In the above photograph the school’s transformer was used. 10.05V (rounded by the meter to 10.1V) across the primary coil of 2,000 turns resulted in an output of 100.5V across the secondary coil of 20,000 turns. Step-up and step-down transformer • Step-up transformer -used to increase the AC voltage (VP < VS ) -secondary voltage is larger than the primary voltage (VP < VS ) -number of turn on secondary coil is larger than on primary coil (NP < NS ) -Output current is smaller than input current (IP > IS ) Step-down transformer -used to decrease the AC voltage (VP > VS ) -secondary voltage is smaller than the primary voltage (VP > VS ) -number of turn on secondary coil is smaller than on primary coil (NP > NS) -Output current is the larger than input current (IP < IS ) • In an ideal transformer (100% efficient), the electric power delivered to the secondary coil equals the power supplied to the primary coil. It can be represented by the following equations: PP = PS VP .IP = VS .IS PP = Power in primary coil or power input (Watt) PS = Power in secondary coil or power output (Watt) IP = Current in primary coil or current input (Ampere) IS = Current in secondary coil or current output (Ampere) Energy Losses in a Transformer are caused by: 1) Resistance of winding The windings of copper wire – have some resistance heat is produced 2) Eddy Currents. Iron core – changing magnetic field of the primary – induced – current (eddy currents)- caused heating. Reduced by laminating core made of sheets 3) Leakage of field lines Field lines produced – primary may not cut the secondary – has air gap or badly designed Application of Eddy Currents: Speedometer Application of Eddy Currents: Metal Detector Diagram of Power Transmission Power station Houses Offices Hotels Substation