Physics of Music PHY103 Worksheet #4 Setup for fretted monochord
... Pitches are commonly measured with respect to the frequencies of the tempered scale with a concert A of 440Hz. These frequencies are listed in the table below. Tuners usually give the nearest note on the tempered scale and the difference between this not and the one you played. This difference is gi ...
... Pitches are commonly measured with respect to the frequencies of the tempered scale with a concert A of 440Hz. These frequencies are listed in the table below. Tuners usually give the nearest note on the tempered scale and the difference between this not and the one you played. This difference is gi ...
Document
... TARSOSAPI Scripting API: Search for pitch intervals Tone scale (makam, raga) recognition Audio fingerprinting [4] Scripting possible with any JVM language: Scala Groovy Jython ...
... TARSOSAPI Scripting API: Search for pitch intervals Tone scale (makam, raga) recognition Audio fingerprinting [4] Scripting possible with any JVM language: Scala Groovy Jython ...
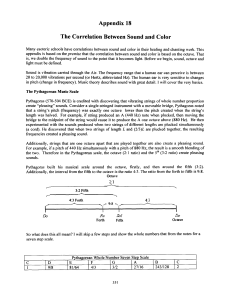
Appendix 18 The Correlation Between Sound and Color
... There were several tempered (meantone, just tone, well tempered, etc) scales that were developed over the centuries as a compromise between harmonic balance and ease of play. The true equal temperament scale was not available to musicians had to wait until the 1870's until the development of scienti ...
... There were several tempered (meantone, just tone, well tempered, etc) scales that were developed over the centuries as a compromise between harmonic balance and ease of play. The true equal temperament scale was not available to musicians had to wait until the 1870's until the development of scienti ...
Why is Music Healing?
... "The main differences between bird songs and their whale counterparts is that the former usually last only a few seconds while humpback songs last from about ten minutes to half an hour. Moreover birds typically rest between songs. Whales on the other hand may sing and re-sing their songs for many h ...
... "The main differences between bird songs and their whale counterparts is that the former usually last only a few seconds while humpback songs last from about ten minutes to half an hour. Moreover birds typically rest between songs. Whales on the other hand may sing and re-sing their songs for many h ...
Timpani
... Ample time should be considered for pitch changes. Can add color, depth, and articulation to bass notes. Lower pitch fudge factor. ...
... Ample time should be considered for pitch changes. Can add color, depth, and articulation to bass notes. Lower pitch fudge factor. ...
Music, Cognition, and Computerized Sound: Chap14
... Beats are the chief means for tuning musical instruments precisely. Through a sense of pitch and a memory of intervals, those with musical ability can tune one note of a piano keyboard to approximately the right interval from another note. But it is by beats that the final tuning is made. In tuning ...
... Beats are the chief means for tuning musical instruments precisely. Through a sense of pitch and a memory of intervals, those with musical ability can tune one note of a piano keyboard to approximately the right interval from another note. But it is by beats that the final tuning is made. In tuning ...
1 Terms and Definitions Characteristics of Modern and Postmodern
... Characteristics of Modern and Postmodern Music Chromatic harmony: harmony utilizing chords built on the five chromatic notes of the scale in addition to the 7 diatonic ones; producing rich harmonies Impressionism and Impressionist Music (See textbook and lecture notes) Modernism and Modernist Music ...
... Characteristics of Modern and Postmodern Music Chromatic harmony: harmony utilizing chords built on the five chromatic notes of the scale in addition to the 7 diatonic ones; producing rich harmonies Impressionism and Impressionist Music (See textbook and lecture notes) Modernism and Modernist Music ...
The Structure of Plato`s Dialogues and Greek Music Theory: A
... of notes) are also equally valid ways of writing the same ratio, since they all are multiples of each other. And second, ratios have different properties and require different algorithms for operations than ordinary numbers. To “add” two ratios is to use an algorithm that looks more like multiplying ...
... of notes) are also equally valid ways of writing the same ratio, since they all are multiples of each other. And second, ratios have different properties and require different algorithms for operations than ordinary numbers. To “add” two ratios is to use an algorithm that looks more like multiplying ...
The Structure of Plato`s Dialogues and Greek Music Theory: A
... of notes) are also equally valid ways of writing the same ratio, since they all are multiples of each other. And second, ratios have different properties and require different algorithms for operations than ordinary numbers. To “add” two ratios is to use an algorithm that looks more like multiplying ...
... of notes) are also equally valid ways of writing the same ratio, since they all are multiples of each other. And second, ratios have different properties and require different algorithms for operations than ordinary numbers. To “add” two ratios is to use an algorithm that looks more like multiplying ...
RATIOS AND MUSICAL INTERVALS We like to think of an interval
... set of downward intervals = {x ∈ R | 0 < x < 1} = (0, 1) set of upward intervals = {x ∈ R | 1 < x} = (0, ∞) The interval created when f1 = f2 will here be called the unison interval. It is given by the ratio f : f (for any f ∈ R+ ), whcich corresponds via ϕ to the number 1. Each interval f1 : f2 has ...
... set of downward intervals = {x ∈ R | 0 < x < 1} = (0, 1) set of upward intervals = {x ∈ R | 1 < x} = (0, ∞) The interval created when f1 = f2 will here be called the unison interval. It is given by the ratio f : f (for any f ∈ R+ ), whcich corresponds via ϕ to the number 1. Each interval f1 : f2 has ...
Elements of Music
... Intervals - The distance between the pitches of the melody may be steps from one note to an adjacent note, or skips where pitches leap from one to another skipping a tone or tones. Conjunct – notes in melody change by small intervals. Notes move in stepwise motion or are very close to each other o ...
... Intervals - The distance between the pitches of the melody may be steps from one note to an adjacent note, or skips where pitches leap from one to another skipping a tone or tones. Conjunct – notes in melody change by small intervals. Notes move in stepwise motion or are very close to each other o ...
Minor Scales
... lower it. These last two can apply to any scale degree, but least commonly with the perfect intervals. ...
... lower it. These last two can apply to any scale degree, but least commonly with the perfect intervals. ...
Elements of Music - Harmony
... Harmony is often thought of as the art of combining pitches into chords (several notes played simultaneously as a “block”). In this way we think of harmony as vertical. *Chords are usually arranged into sentence-like patterns called chord progressions. Harmony also occurs in counterpoint when the no ...
... Harmony is often thought of as the art of combining pitches into chords (several notes played simultaneously as a “block”). In this way we think of harmony as vertical. *Chords are usually arranged into sentence-like patterns called chord progressions. Harmony also occurs in counterpoint when the no ...
Pythagoras and His Vibrating Strings
... ¾Often times, when two notes are sounded their upper partials, or harmonics, do not agree mathematically. When this is undetectable because of the higher pitches being the ones that disagree, this is called ...
... ¾Often times, when two notes are sounded their upper partials, or harmonics, do not agree mathematically. When this is undetectable because of the higher pitches being the ones that disagree, this is called ...
notes and equations
... If they add up to a periodic tone, the fundamental is the first component, whose frequency is that of the combined tone. Some people use the word overtone to mean a component other than the fundamental. An interval is a ratio between two frequencies. The interval between two musical tones is the rat ...
... If they add up to a periodic tone, the fundamental is the first component, whose frequency is that of the combined tone. Some people use the word overtone to mean a component other than the fundamental. An interval is a ratio between two frequencies. The interval between two musical tones is the rat ...
Document
... • Contain seven pitches • The eighth note of the scale (octave) repeats the starting pitch • Examples: major scales, minor scales, church modes ...
... • Contain seven pitches • The eighth note of the scale (octave) repeats the starting pitch • Examples: major scales, minor scales, church modes ...
AP Music Theory - Somerset Academy
... 6th – Submediant 7th – Subtonic or leading tone – depends on whether it is raised ...
... 6th – Submediant 7th – Subtonic or leading tone – depends on whether it is raised ...
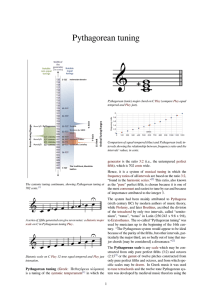
Pythagorean tuning
... In the formulas, the ratios 3:2 or 2:3 represent an ascending or descending perfect fifth (i.e. an increase or decrease in frequency by a perfect fifth), while 2:1 or 1:2 represent an ascending or descending octave. The major scale based on C, obtained from this tuning is:[5] In equal temperament, pai ...
... In the formulas, the ratios 3:2 or 2:3 represent an ascending or descending perfect fifth (i.e. an increase or decrease in frequency by a perfect fifth), while 2:1 or 1:2 represent an ascending or descending octave. The major scale based on C, obtained from this tuning is:[5] In equal temperament, pai ...
RESEARCH ARTICLE Metrics for Scales and Tunings
... same number of notes (and hence the same number of intervals), any reasonable metric can be used to describe the distance between them. For example, Chalmers [2] measures the distances between tetrachords using a variety of metrics such as the Euclidean `2 , the taxicab metric `1 , and the max-value ...
... same number of notes (and hence the same number of intervals), any reasonable metric can be used to describe the distance between them. For example, Chalmers [2] measures the distances between tetrachords using a variety of metrics such as the Euclidean `2 , the taxicab metric `1 , and the max-value ...
Sample History Placement Exam 2013
... Choose one of the following passages, and write an essay that situates the passage in its historical context. 1. Giovanni Maria Artusi on harmonic developments in the music of Claudio Monteverdi: Such composers, in my opinion, have nothing but smoke in their heads if they are so impressed with thems ...
... Choose one of the following passages, and write an essay that situates the passage in its historical context. 1. Giovanni Maria Artusi on harmonic developments in the music of Claudio Monteverdi: Such composers, in my opinion, have nothing but smoke in their heads if they are so impressed with thems ...
A Non-Pythagorean Musical Scale Based on Logarithms
... scale to compose with not only the tones themselves, but with the beat frequencies within chords. Specifically, if whole-numbered tones X* and Y* are chosen such that is an integer, the beat frequency created by sounding the two pitches together will itself be a tone * of the logarithmic scale, allo ...
... scale to compose with not only the tones themselves, but with the beat frequencies within chords. Specifically, if whole-numbered tones X* and Y* are chosen such that is an integer, the beat frequency created by sounding the two pitches together will itself be a tone * of the logarithmic scale, allo ...
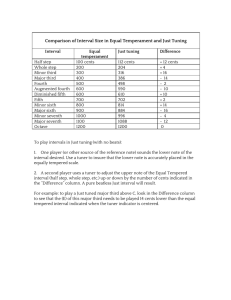
Comparison of Interval Size in Equal Temperament and Just Tuning
... the “Difference” column. A pure beatless Just interval will result. For example: to play a Just tuned major third above C, look in the Difference column to see that the (E) of this major third needs to be played 14 cents lower than the equal tempered interval indicated when the tuner indicator is ce ...
... the “Difference” column. A pure beatless Just interval will result. For example: to play a Just tuned major third above C, look in the Difference column to see that the (E) of this major third needs to be played 14 cents lower than the equal tempered interval indicated when the tuner indicator is ce ...
PERSIAN TRADITIONAL MUSIC - Foundation for Iranian Studies
... a scale of 17 tones. The tones, as given in mathematical numbers, are extremely precise. Safiaddin’s 17-tone scale was a synthesis of various scale patterns, described by different scholars, which were at minor variance with one another. Equally well defined, as outlined in the works of medieval sch ...
... a scale of 17 tones. The tones, as given in mathematical numbers, are extremely precise. Safiaddin’s 17-tone scale was a synthesis of various scale patterns, described by different scholars, which were at minor variance with one another. Equally well defined, as outlined in the works of medieval sch ...
Microtonal music

Microtonal music or microtonality is the use in music of microtones—intervals smaller than a semitone, which are also called ""microintervals"". It may also be extended to include any music using intervals not found in the customary Western tuning of twelve equal intervals per octave.