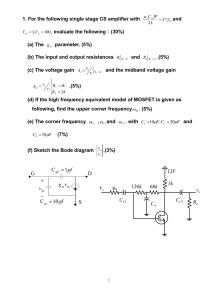
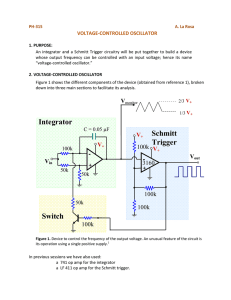
Modelling Electricity
... Current is measured in amps (amperes), A Current is measured with an ammeter ...
... Current is measured in amps (amperes), A Current is measured with an ammeter ...
Example 21-4 Inductor Voltage
... From Equation 21-16, the voltage across the inductor is i = - 10.500 * 10-3 H2 12.67 * 103 A>s2 V = -L t = -1.33 H # A>s = -1.33 V The magnitude of the voltage is 1.33 V. The value of V is negative, which means that there is a voltage drop of 1.33 V across the inductor. Thus, the voltage opposes t ...
... From Equation 21-16, the voltage across the inductor is i = - 10.500 * 10-3 H2 12.67 * 103 A>s2 V = -L t = -1.33 H # A>s = -1.33 V The magnitude of the voltage is 1.33 V. The value of V is negative, which means that there is a voltage drop of 1.33 V across the inductor. Thus, the voltage opposes t ...
KL Series 3000 Watt Regulated High Voltage DC Power Supplies
... Rapid responding control circuits provide a typical response of less than 500 µs to load transients. Single-phase Input. Full 3kW output from a single-phase, 198-264 V, 48-63 Hz input, 3500 VA maximum. Pulse-Width Modulation. Off-the-line pulse-width modulation provides high efficiency, a fixed swit ...
... Rapid responding control circuits provide a typical response of less than 500 µs to load transients. Single-phase Input. Full 3kW output from a single-phase, 198-264 V, 48-63 Hz input, 3500 VA maximum. Pulse-Width Modulation. Off-the-line pulse-width modulation provides high efficiency, a fixed swit ...
AC CIRCUITS : RC CIRCUIT 1. Aim 1. To study current voltage
... series combination of a resistor R and capacitor C if connected to AC source of angular frequency and RMS voltage V, the RMS current flowing in the circuit is given by I = VR /R, where VR is the voltage across the resistor. If VC is the RMS voltage across the capacitor, then VC = ZC I also C = 1/(2π ...
... series combination of a resistor R and capacitor C if connected to AC source of angular frequency and RMS voltage V, the RMS current flowing in the circuit is given by I = VR /R, where VR is the voltage across the resistor. If VC is the RMS voltage across the capacitor, then VC = ZC I also C = 1/(2π ...
AP_Physics_B_-_Planck_s_Constant_lab
... Purpose: To use an LED to measure the threshold voltage in efforts to graphically determine the value for Planck’s Constant. Materials: Pasco Circuit board, voltmeter, ammeter, various LEDS In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also kno ...
... Purpose: To use an LED to measure the threshold voltage in efforts to graphically determine the value for Planck’s Constant. Materials: Pasco Circuit board, voltmeter, ammeter, various LEDS In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also kno ...
Electric Power
... low beam and 65 W for the high beam. How much is the current in the headlight filament of a headlight bulb for both of these settings when 12 V is provided by the car battery? 2. The heating coils of an electric stove are made of a high-resistance material so that the electricity that passes through ...
... low beam and 65 W for the high beam. How much is the current in the headlight filament of a headlight bulb for both of these settings when 12 V is provided by the car battery? 2. The heating coils of an electric stove are made of a high-resistance material so that the electricity that passes through ...
Electricity powerpoint
... The simplest type of circuit involves electricity going around with no “choices” (electrons don’t really choose). This is called a Series circuit. Draw the path the electrons travel. The other main type of circuit has two or more branches. This is called a Parallel circuit. Draw on the electron flow ...
... The simplest type of circuit involves electricity going around with no “choices” (electrons don’t really choose). This is called a Series circuit. Draw the path the electrons travel. The other main type of circuit has two or more branches. This is called a Parallel circuit. Draw on the electron flow ...
Lecture 9: Limiting and Clamping Diode Circuits. Voltage Doubler
... Hence, this is called a clamped capacitor circuit. Without the diode present in this circuit, the capacitor would not retain any net charge per period so it would never “charge up” to 6 V. Note that here we are looking at the steady state response. It may take a few periods for the capacitor to comp ...
... Hence, this is called a clamped capacitor circuit. Without the diode present in this circuit, the capacitor would not retain any net charge per period so it would never “charge up” to 6 V. Note that here we are looking at the steady state response. It may take a few periods for the capacitor to comp ...
952 EE Quiz 01 ID#: Name:
... (h) Virtual short or ground is a concept based on the open-loop gain of an OPA tends to infinite. ...
... (h) Virtual short or ground is a concept based on the open-loop gain of an OPA tends to infinite. ...
CONSTRUCTING A VARIABLE POWER SUPPLY UNIT
... volts is in the center of the secondary coil of wire. This causes the transformer output to have both positive and negative outputs. The center tap is 0 volts, the top one is + 12 volts, and the bottom one is – 12 volts. The schematic symbol for that is: ...
... volts is in the center of the secondary coil of wire. This causes the transformer output to have both positive and negative outputs. The center tap is 0 volts, the top one is + 12 volts, and the bottom one is – 12 volts. The schematic symbol for that is: ...
Chapter3: Signal conditioning
... • Filtering is the process of removing a certain band of frequencies from a signal and permitting others to be transmitted. • The Pass Band: the range of frequencies passed by the filter • The Stop Band: the range not passed by the filter. • CUT OFF frequency: the boundary between stopping and passi ...
... • Filtering is the process of removing a certain band of frequencies from a signal and permitting others to be transmitted. • The Pass Band: the range of frequencies passed by the filter • The Stop Band: the range not passed by the filter. • CUT OFF frequency: the boundary between stopping and passi ...
FET AS A VOLTAGE –VARIABLE RESISTOR (VVR):
... The variation of the rd with vgs can be closely approximated by rd = ro / 1- KVgs ro – drain resistance at zero gate bias and K constant dependent upon FET type. Small signal FET drain resistance rd varies with applied gate voltage Vgs and FET act like a VARIABLE PASSIVE RESISTOR. ...
... The variation of the rd with vgs can be closely approximated by rd = ro / 1- KVgs ro – drain resistance at zero gate bias and K constant dependent upon FET type. Small signal FET drain resistance rd varies with applied gate voltage Vgs and FET act like a VARIABLE PASSIVE RESISTOR. ...
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD TL084
... Notes: 1. Absolute maximum ratings are those values beyond which the device could be permanently damaged. Absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only and functional device operation is not implied. 2. All voltage values, except differential voltage, are with respect to the zero reference level ...
... Notes: 1. Absolute maximum ratings are those values beyond which the device could be permanently damaged. Absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only and functional device operation is not implied. 2. All voltage values, except differential voltage, are with respect to the zero reference level ...
مواصفات_العطاء
... Online Smart UPS 120 KVA 3 Phase in – 3 Phase out 380V line to line 10% 50Hz 5% 220V Line-to-Neutral, 380V Line-to-Line 3% 50Hz 0.5% Pure Sine-Wave 105% ~ 150% for 30 seconds Auto cut off output no transferring to bypass Zero-cross transfer, <4ms. UPS to bypass or reverse 10 minutes Less than 4 hour ...
... Online Smart UPS 120 KVA 3 Phase in – 3 Phase out 380V line to line 10% 50Hz 5% 220V Line-to-Neutral, 380V Line-to-Line 3% 50Hz 0.5% Pure Sine-Wave 105% ~ 150% for 30 seconds Auto cut off output no transferring to bypass Zero-cross transfer, <4ms. UPS to bypass or reverse 10 minutes Less than 4 hour ...
Voltage regulator

A voltage regulator is designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may be a simple ""feed-forward"" design or may include negative feedback control loops. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components. Depending on the design, it may be used to regulate one or more AC or DC voltages.Electronic voltage regulators are found in devices such as computer power supplies where they stabilize the DC voltages used by the processor and other elements. In automobile alternators and central power station generator plants, voltage regulators control the output of the plant. In an electric power distribution system, voltage regulators may be installed at a substation or along distribution lines so that all customers receive steady voltage independent of how much power is drawn from the line.