Chapter 4: Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
... Before the first law of thermodynamics can be applied to systems, ways to calculate the change in internal energy of the substance enclosed by the system boundary must be determined. For real substances like water, the property tables are used to find the internal energy change. For ideal gases the ...
... Before the first law of thermodynamics can be applied to systems, ways to calculate the change in internal energy of the substance enclosed by the system boundary must be determined. For real substances like water, the property tables are used to find the internal energy change. For ideal gases the ...
NOTES on THERMODYNAMICS - University of Utah Physics
... is the behavior of its internal energy. Observations indicate that if such a gas expands adiabatically (but not necessarily quasi-statically), from a volume Vi to Vf , the initial and final temperatures are the same. Since the transformation is adiabatic (ΔQ = 0) and there is no external work done on ...
... is the behavior of its internal energy. Observations indicate that if such a gas expands adiabatically (but not necessarily quasi-statically), from a volume Vi to Vf , the initial and final temperatures are the same. Since the transformation is adiabatic (ΔQ = 0) and there is no external work done on ...
Calorimetry - NC State University
... pressure or 1 molar concentration. The standard state can have any temperature, but the temperature should be specified. For example, the standard enthalpy of vaporization of water Is the enthalpy of vaporization at 373 K (the boiling point) and 1 bar of pressure. If we lower the temperature below 3 ...
... pressure or 1 molar concentration. The standard state can have any temperature, but the temperature should be specified. For example, the standard enthalpy of vaporization of water Is the enthalpy of vaporization at 373 K (the boiling point) and 1 bar of pressure. If we lower the temperature below 3 ...
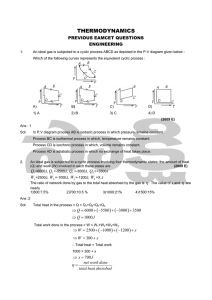
UNIT I PART B 1). (i). A spherical balloon of diameter
... phase (including polymorphs); igneous melts, liquids (aqueous solutions), and vapor are also considered unique phases. It is possible to have two or more phases in the same state of matter (e.g. solid mineral assemblages, immiscible silicate and sulfide melts, immiscible liquids such as water and hy ...
... phase (including polymorphs); igneous melts, liquids (aqueous solutions), and vapor are also considered unique phases. It is possible to have two or more phases in the same state of matter (e.g. solid mineral assemblages, immiscible silicate and sulfide melts, immiscible liquids such as water and hy ...
JIF 314 Thermodynamics - comsics
... Two kinds of work done on a system can be distinguished: work done due to external forces, and work done due to internal forces Unless specified, when the word work is referred, it shall refer to external work Internal work is due to forces acting among the particles within a system As the internal ...
... Two kinds of work done on a system can be distinguished: work done due to external forces, and work done due to internal forces Unless specified, when the word work is referred, it shall refer to external work Internal work is due to forces acting among the particles within a system As the internal ...
Equations of State Ideal Gas
... ∗ the gas particles take up negligible volume ∗ the intermolecular potential energy between particles is small ∗ particles act independent of one another – Under what conditions can it be used? ∗ low density ∗ high temperatures - considerably in excess of the saturation region ∗ at very low pressure ...
... ∗ the gas particles take up negligible volume ∗ the intermolecular potential energy between particles is small ∗ particles act independent of one another – Under what conditions can it be used? ∗ low density ∗ high temperatures - considerably in excess of the saturation region ∗ at very low pressure ...
15. Thermodynamics
... 24. A lead bullet, of initial temperature 270C and speed ‘v’ kmph penetrates into a solid object and melts. If 50% of the kinetic energy is used to heat it, the value of v in kmph is (for lead melting point = 600K, latent heat of fusion = 2.5 × 10 4 Jkg−1 specific heat 125Jkg−1 K −1 ). ...
... 24. A lead bullet, of initial temperature 270C and speed ‘v’ kmph penetrates into a solid object and melts. If 50% of the kinetic energy is used to heat it, the value of v in kmph is (for lead melting point = 600K, latent heat of fusion = 2.5 × 10 4 Jkg−1 specific heat 125Jkg−1 K −1 ). ...
Review of fundamental principles ? Thermodynamics : Part I
... Thermodynamics is the study of energy interactions between systems and the effect of these interactions on the system properties. Energy transfer between systems takes place in the form of heat and/or work. Thermodynamics deals with systems in equilibrium. A thermodynamic system is defined as a quan ...
... Thermodynamics is the study of energy interactions between systems and the effect of these interactions on the system properties. Energy transfer between systems takes place in the form of heat and/or work. Thermodynamics deals with systems in equilibrium. A thermodynamic system is defined as a quan ...
Spring Book Problems - Blue Valley Schools
... (I) If a particle undergoes SHM with amplitude 0.18 m, what is the total distance it travels in one period? [T, f, A] (I) The springs of a 1500-kg car compress 5.0 mm when its 68-kg driver gets into the driver’s seat. If the car goes over a bump, what will be the frequency of vibrations? [k, T, A, m ...
... (I) If a particle undergoes SHM with amplitude 0.18 m, what is the total distance it travels in one period? [T, f, A] (I) The springs of a 1500-kg car compress 5.0 mm when its 68-kg driver gets into the driver’s seat. If the car goes over a bump, what will be the frequency of vibrations? [k, T, A, m ...
PSS 17.1: The Bermuda Triangle
... Two Conventions, One Law Description: Several conceptual and computational questions focusing on relationships between U, Q and W. Questions emphasize that W, depending on the convention used by the problem authors, may mean either work done on or by the system. Learning Goal: To understand the firs ...
... Two Conventions, One Law Description: Several conceptual and computational questions focusing on relationships between U, Q and W. Questions emphasize that W, depending on the convention used by the problem authors, may mean either work done on or by the system. Learning Goal: To understand the firs ...
The basic concepts and Thermochemistry
... The internal energy of a substance increases when its temperature is raised. Let’s suppose that the sample is confined to a constant volume. If the internal energy is plotted against temperature, the slope of the tangent to the curve at any temperature is called the heat capacity of the system at th ...
... The internal energy of a substance increases when its temperature is raised. Let’s suppose that the sample is confined to a constant volume. If the internal energy is plotted against temperature, the slope of the tangent to the curve at any temperature is called the heat capacity of the system at th ...
Maxwell Relations
... •Four relations are obtained by starting either from T or S Clockwise or anticlockwise direction. A negative Sign must appear in the resulting equation ...
... •Four relations are obtained by starting either from T or S Clockwise or anticlockwise direction. A negative Sign must appear in the resulting equation ...
The First Law of Thermodynamics
... A few hundred years ago when people were investigating heat and temperature phenomena, the idea was that heat was some kind of invisible caloric fluid which could flow from one material to another. This is the origin of the word calorie, which we now know as a form of energy. A calorie can be define ...
... A few hundred years ago when people were investigating heat and temperature phenomena, the idea was that heat was some kind of invisible caloric fluid which could flow from one material to another. This is the origin of the word calorie, which we now know as a form of energy. A calorie can be define ...
Basic Thermodynamics - CERN Accelerator School
... (volume, for example) and the intensive parameters are equal (pressure, temperature). At equilibrium, a functional relationship between the parameters (state variables) of a system can be expressed as an equation of state. As an example, a gas is completely described at equilibrium by the parameters ...
... (volume, for example) and the intensive parameters are equal (pressure, temperature). At equilibrium, a functional relationship between the parameters (state variables) of a system can be expressed as an equation of state. As an example, a gas is completely described at equilibrium by the parameters ...
kinetic theory
... chemically to yield another gas, their volumes are in the ratios of small integers. Avogadro’s law (or hypothesis) says: Equal volumes of all gases at equal temperature and pressure have the same number of molecules. Avogadro’s law, when combined with Dalton’s theory explains Gay Lussac’s law. Since ...
... chemically to yield another gas, their volumes are in the ratios of small integers. Avogadro’s law (or hypothesis) says: Equal volumes of all gases at equal temperature and pressure have the same number of molecules. Avogadro’s law, when combined with Dalton’s theory explains Gay Lussac’s law. Since ...
Lectures 21 and 22 - NUS Physics Department
... Effect of High Specific Heat of Water The high specific heat of water is responsible, in part, for the moderate temperatures found near large bodies of water. As the temperature of a body of water decreases during the winter, energy is transferred from the cooling water to the air by heat, increasin ...
... Effect of High Specific Heat of Water The high specific heat of water is responsible, in part, for the moderate temperatures found near large bodies of water. As the temperature of a body of water decreases during the winter, energy is transferred from the cooling water to the air by heat, increasin ...