Thermochemistry
... to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
... to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
Verdana 30 pt
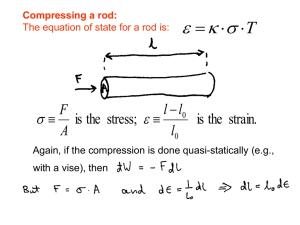
... which we can describe the behavior with relatively simple and accurate laws, based on measures of volume, pressure and temperature, said state quantities; these, we add the internal energy U of an ideal gas, which is all kinetic and depends only on the temperature. ...
... which we can describe the behavior with relatively simple and accurate laws, based on measures of volume, pressure and temperature, said state quantities; these, we add the internal energy U of an ideal gas, which is all kinetic and depends only on the temperature. ...
HEAT- Chapter 9
... In general, the volume of a liquid will decrease as temperature decreases; the exception is water Solids tend to have the smallest coefficient of volume Coefficient of Volume Expansion- a number assigned to different material to show the thermal expansion characteristic of the material Gases ...
... In general, the volume of a liquid will decrease as temperature decreases; the exception is water Solids tend to have the smallest coefficient of volume Coefficient of Volume Expansion- a number assigned to different material to show the thermal expansion characteristic of the material Gases ...
Thermodynamics lesson 1 Tempersture
... • Be able to explain thermal equilibrium • Describe the absolute scale of temperature (i.e. the thermodynamic scale) that does not depend on property of any particular substance and explain why the triple point is used. • To be able to use and convert temperature measurements both in degrees Celsius ...
... • Be able to explain thermal equilibrium • Describe the absolute scale of temperature (i.e. the thermodynamic scale) that does not depend on property of any particular substance and explain why the triple point is used. • To be able to use and convert temperature measurements both in degrees Celsius ...
Energy - Winona State University
... Energy can be converted from one form to another but can neither be created nor destroyed. (Euniverse is constant) ...
... Energy can be converted from one form to another but can neither be created nor destroyed. (Euniverse is constant) ...
Lecture 5
... cv (lower case) = specific heat at constant volume cp = specific heat at constant pressure Specific heat is the heat energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree. ...
... cv (lower case) = specific heat at constant volume cp = specific heat at constant pressure Specific heat is the heat energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree. ...
Calorimetry Key - Iowa State University
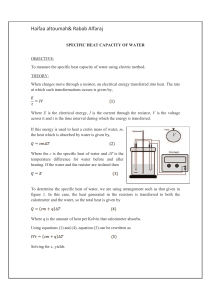
... 1. Heat Capacity (C) represents the amount of heat required to raise a given amount of a substance 1 K. 2. (a) In your own words, what is the difference between Molar Heat Capacity and Specific Heat? (b) Write out the equation for each. Cm = q/ΔT = Joules/mole Cs = q/ΔT = Joules/gram 3. When H2 (g) ...
... 1. Heat Capacity (C) represents the amount of heat required to raise a given amount of a substance 1 K. 2. (a) In your own words, what is the difference between Molar Heat Capacity and Specific Heat? (b) Write out the equation for each. Cm = q/ΔT = Joules/mole Cs = q/ΔT = Joules/gram 3. When H2 (g) ...
Document
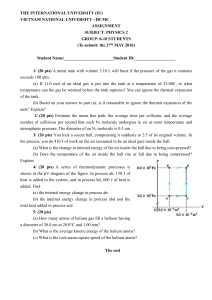
... Pour a liter of water at 40 degrees C into a liter of water at 20 degrees C and the final temperature of the two becomes A) less than 30 degrees C. B) at or about 30 degrees C. C) more than 30 degrees C. ...
... Pour a liter of water at 40 degrees C into a liter of water at 20 degrees C and the final temperature of the two becomes A) less than 30 degrees C. B) at or about 30 degrees C. C) more than 30 degrees C. ...