Thermal Physics Tutorial
... is the sum of random distribution of KE and PE of all the molecules in the system. The substance contains internal energy, not heat. The word “heat” is used only when referring to the thermal energy actually in transit from hot to cold. 11. A flask containing boiling water is removed from the burner ...
... is the sum of random distribution of KE and PE of all the molecules in the system. The substance contains internal energy, not heat. The word “heat” is used only when referring to the thermal energy actually in transit from hot to cold. 11. A flask containing boiling water is removed from the burner ...
Chemistry and the material world
... definition of heat because we can measure ΔU for a process that takes s system from an initial to a final state by measuring wad for the adiabatic path and w for the non-adiabatic path. q = wad – w Finally, from the first law of thermodynamics also follows that the internal energy of an isolated sys ...
... definition of heat because we can measure ΔU for a process that takes s system from an initial to a final state by measuring wad for the adiabatic path and w for the non-adiabatic path. q = wad – w Finally, from the first law of thermodynamics also follows that the internal energy of an isolated sys ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
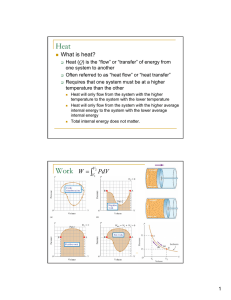
... Irreversible process is one in which thermal system’s changes cannot be retraced, such as gas expanding to fill a vacuum through an open stopcock. A thermodynamic system can transfer its internal energy by changing the temperature (or phase) of another system of it can use its internal energy to do ...
... Irreversible process is one in which thermal system’s changes cannot be retraced, such as gas expanding to fill a vacuum through an open stopcock. A thermodynamic system can transfer its internal energy by changing the temperature (or phase) of another system of it can use its internal energy to do ...
Document
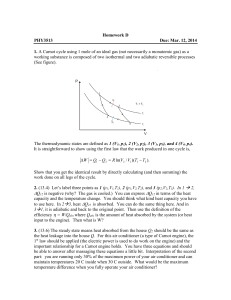
... Work done by expansion of a 1 liter of a gas to 2 liters against a constant pressure at 10 atm is: wP= -Pex (V2-V1)= -10 atm *1 liter ...
... Work done by expansion of a 1 liter of a gas to 2 liters against a constant pressure at 10 atm is: wP= -Pex (V2-V1)= -10 atm *1 liter ...
Unit 6 Review
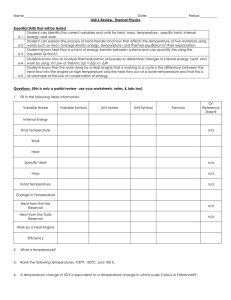
... Student can identify the correct variables and units for heat, mass, temperature, specific heat, internal 6-1 energy, and work. Student can explain the process of heat transfer and how that affects the temperature of two materials using 6-2 words such as heat, average kinetic energy, temperature, an ...
... Student can identify the correct variables and units for heat, mass, temperature, specific heat, internal 6-1 energy, and work. Student can explain the process of heat transfer and how that affects the temperature of two materials using 6-2 words such as heat, average kinetic energy, temperature, an ...
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTORY REMARKS 1.1 Introduction
... expressed in J kg−1 Co −1. This is what is commonly (though loosely) called “the specific heat”, but we shall use the correct term: specific heat capacity. Incidentally, we would all find it much easier to understand each other if we all used the word “specific” in contexts such as these to mean “pe ...
... expressed in J kg−1 Co −1. This is what is commonly (though loosely) called “the specific heat”, but we shall use the correct term: specific heat capacity. Incidentally, we would all find it much easier to understand each other if we all used the word “specific” in contexts such as these to mean “pe ...
Mr Alasdair Ross at Southpointe Academy: Math and Chemistry Pages
... The standard state of a gas is the pure gas behaving as an ideal gas at 1 atm pressure and the temperature of interest (usually 25ºC). The standard enthalpy of reaction ( H ) is the enthalpy change for a reaction in which the reactants in their standard states yield products in their standard sta ...
... The standard state of a gas is the pure gas behaving as an ideal gas at 1 atm pressure and the temperature of interest (usually 25ºC). The standard enthalpy of reaction ( H ) is the enthalpy change for a reaction in which the reactants in their standard states yield products in their standard sta ...
Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion and Stress
... From the Greek thermos meaning heat and dynamis meaning power is a branch of physics that studies the effects of changes in temperature, pressure, and volume on physical systems at the macroscopic scale by analyzing the collective motion of their particles using statistics. ...
... From the Greek thermos meaning heat and dynamis meaning power is a branch of physics that studies the effects of changes in temperature, pressure, and volume on physical systems at the macroscopic scale by analyzing the collective motion of their particles using statistics. ...
Lecture_1_ Heat and - Arizona State University
... in the equation W pdV . The unusual convention was established to fit the behavior of heat engines whose normal operation involves the input of heat and the output of work. So according to this unfortunate convention work is positive if the engine is doing its job. Note that some textbooks e.g., ...
... in the equation W pdV . The unusual convention was established to fit the behavior of heat engines whose normal operation involves the input of heat and the output of work. So according to this unfortunate convention work is positive if the engine is doing its job. Note that some textbooks e.g., ...