統計力學 1. Consider a binary mixture that consists of n1 moles of
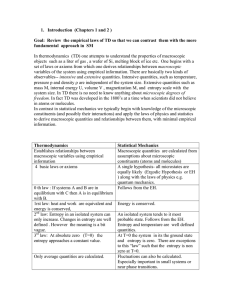
... 2. A container contains N non- interacting, distinguishable, two level atoms. Each atom can exist in one of two energy levels, ε 0 =0 and ε1 =ε. The number of atoms in energy level ε 0 is n0 and in energy level ε 1 is n1 . The total energy E of the system is E = n0 ε 0 + n1 ε 1 a) Compute the entro ...
... 2. A container contains N non- interacting, distinguishable, two level atoms. Each atom can exist in one of two energy levels, ε 0 =0 and ε1 =ε. The number of atoms in energy level ε 0 is n0 and in energy level ε 1 is n1 . The total energy E of the system is E = n0 ε 0 + n1 ε 1 a) Compute the entro ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... Thermal Energy: The kinetic energy of molecular motion and is measured by finding the temperature of an object Heat: The amount of thermal energy transferred from one object to another as the result of a temperature difference between the two Units: ...
... Thermal Energy: The kinetic energy of molecular motion and is measured by finding the temperature of an object Heat: The amount of thermal energy transferred from one object to another as the result of a temperature difference between the two Units: ...
PHYS 1220, Engineering Physics, Chapter 19 – The First Law of
... • A system is any collection of objects that is convenient to regard as a unit, and that may have the potential to exchange energy with its surroundings. - What is a “status” of a system? • A status is to describe the states of a system. It does not depend on the history of the system, rather it onl ...
... • A system is any collection of objects that is convenient to regard as a unit, and that may have the potential to exchange energy with its surroundings. - What is a “status” of a system? • A status is to describe the states of a system. It does not depend on the history of the system, rather it onl ...
Radiation
... Today's fore-cast calls for a mix of hazy sun and clouds . . ." Whhhhhew. It's hot! Your radio is blaring while you lounge on the beach, catching some rays from the Sun. When you squint and look down the beach you see waves of heat floating above the hot sand. You can practically feel the earth sizz ...
... Today's fore-cast calls for a mix of hazy sun and clouds . . ." Whhhhhew. It's hot! Your radio is blaring while you lounge on the beach, catching some rays from the Sun. When you squint and look down the beach you see waves of heat floating above the hot sand. You can practically feel the earth sizz ...
Thermodynamics
... When a system gains heat, the internal energy of the system increases. Q is positive when a system gains heat and negative when a system loses heat. Internal energy of a system can decrease if the system does work on its surroundings. Work is positive when it is done by the system and negative when ...
... When a system gains heat, the internal energy of the system increases. Q is positive when a system gains heat and negative when a system loses heat. Internal energy of a system can decrease if the system does work on its surroundings. Work is positive when it is done by the system and negative when ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... Standard Heats of Formation Standard Heat of Formation (DHof ): The enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their ...
... Standard Heats of Formation Standard Heat of Formation (DHof ): The enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... Standard Heats of Formation Standard Heat of Formation (DHof ): The enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their ...
... Standard Heats of Formation Standard Heat of Formation (DHof ): The enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their ...
Thermodynamic functions - Phase Transformations Group
... The Helmholtz free energy F is the corresponding term at constant volume, when H is replaced by U in equation 9. A process can occur spontaneously if it leads to a reduction in the free energy. Quantities such as H, G and S are path independent and therefore are called functions of state. More About ...
... The Helmholtz free energy F is the corresponding term at constant volume, when H is replaced by U in equation 9. A process can occur spontaneously if it leads to a reduction in the free energy. Quantities such as H, G and S are path independent and therefore are called functions of state. More About ...
241 Lecture 11
... temperature differences tend to cause the flow of heat. Gradients in chemical potential tend to cause substance to be transfer from one phase to another. ...
... temperature differences tend to cause the flow of heat. Gradients in chemical potential tend to cause substance to be transfer from one phase to another. ...