Chapter 6:
... 6. At constant pressure, to what is the change in enthalpy of a system equal? a. The internal energy of the system. b. The work done on the system. c. The heat supplied to the system. d. The work done by the system. Answer: C 7. Heat capacity is determined by what two measurable factors? ...
... 6. At constant pressure, to what is the change in enthalpy of a system equal? a. The internal energy of the system. b. The work done on the system. c. The heat supplied to the system. d. The work done by the system. Answer: C 7. Heat capacity is determined by what two measurable factors? ...
Document
... A cube of copper of mass mc=75 g is placed in an oven at a temperature of T0=3120C until it comes to thermal equilibrium. The cube is then dropped quickly into an insulated beaker(烧杯) containing a quantity of water of mass mw=220 g. The heat capacity of the beaker alone is Cb=190 J/K. Initially the ...
... A cube of copper of mass mc=75 g is placed in an oven at a temperature of T0=3120C until it comes to thermal equilibrium. The cube is then dropped quickly into an insulated beaker(烧杯) containing a quantity of water of mass mw=220 g. The heat capacity of the beaker alone is Cb=190 J/K. Initially the ...
States of matter - Tennessee State University
... There is such a function state U, called internal energy, that dU = dQ - dW where dQ is the heat delivered to the system and dW is the work performed by the system. Comment: On the microscopic scale, the internal energy of a system is the total mechanical energy of the system. ...
... There is such a function state U, called internal energy, that dU = dQ - dW where dQ is the heat delivered to the system and dW is the work performed by the system. Comment: On the microscopic scale, the internal energy of a system is the total mechanical energy of the system. ...
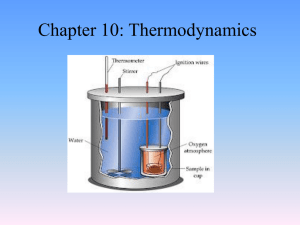
Chapter 10: Thermodynamics
... • A total of 135 J of work is done on a gaseous refrigerant as it undergoes compression. If the internal energy of the gas increases by 114 J during the process, what is the total amount of energy transferred as heat? ...
... • A total of 135 J of work is done on a gaseous refrigerant as it undergoes compression. If the internal energy of the gas increases by 114 J during the process, what is the total amount of energy transferred as heat? ...
3 - CFD - Anna University
... viewed as a sufficiently slow process that allows the system to adjust itself internally so that properties in one part of the system do not change any faster than those at other parts ...
... viewed as a sufficiently slow process that allows the system to adjust itself internally so that properties in one part of the system do not change any faster than those at other parts ...
Thermodynamics: Lecture 2
... temperature. Since we can only measure temperature we can rewrite: q C.dT C (T2 T1 ) Generally C does not vary much with temperature except near phase transition. T2 and T1 are the final and initial temperatures. So if system cools then the sign of q is negative since it looses heat to surro ...
... temperature. Since we can only measure temperature we can rewrite: q C.dT C (T2 T1 ) Generally C does not vary much with temperature except near phase transition. T2 and T1 are the final and initial temperatures. So if system cools then the sign of q is negative since it looses heat to surro ...
More Carnot Cycle March 4, 2010 Efficiency = W/Qin = Qin
... Conduction: for heat to be transferred by conduction, there must be contact between water. Matter or a medium is required. Convection: Convection relies on mass transport of matter. Eg: air thermals. Hot air rises cold air sinks. Radiation: Heat transferred through radiation (electrons - magnetic wa ...
... Conduction: for heat to be transferred by conduction, there must be contact between water. Matter or a medium is required. Convection: Convection relies on mass transport of matter. Eg: air thermals. Hot air rises cold air sinks. Radiation: Heat transferred through radiation (electrons - magnetic wa ...
Thermodynamics - StrikerPhysics
... • Thermo (heat) dynamics (transfer) • Thermodynamic systems describe many many particles (molecules) which obey Newton’s laws for dynamics but which would be difficult to analyze due to their numbers. • We use macroscopic means for analysis of these systems of many particles - involving quantities s ...
... • Thermo (heat) dynamics (transfer) • Thermodynamic systems describe many many particles (molecules) which obey Newton’s laws for dynamics but which would be difficult to analyze due to their numbers. • We use macroscopic means for analysis of these systems of many particles - involving quantities s ...