Group–A Thermodynamics - New Age International
... Reversible process is a process carried out in such a way that at every instant, the system deviation is only infinitesimal from the thermodynamic state, and also which can be reversed in direction and the system retraces the same equilibrium states. Thus in reversible process, the interactions betw ...
... Reversible process is a process carried out in such a way that at every instant, the system deviation is only infinitesimal from the thermodynamic state, and also which can be reversed in direction and the system retraces the same equilibrium states. Thus in reversible process, the interactions betw ...
Thermodynamic Cycles
... Irreversible Process An irreversible process cannot return both the system and the surroundings to their original conditions if reversed. For example, an automobile engine does not give back the fuel it took to drive up a hill as it coasts down the hill to its original position. There are factors th ...
... Irreversible Process An irreversible process cannot return both the system and the surroundings to their original conditions if reversed. For example, an automobile engine does not give back the fuel it took to drive up a hill as it coasts down the hill to its original position. There are factors th ...
Heat Engines, Entropy, and the Second Law of Thermodynamics P
... statement of the second law specifies that the energy removed from the gas to return the temperature to its original value cannot be completely converted to mechanical energy in the form of the work done by the engine in compressing the gas. Thus, we must conclude that the process is irreversible. W ...
... statement of the second law specifies that the energy removed from the gas to return the temperature to its original value cannot be completely converted to mechanical energy in the form of the work done by the engine in compressing the gas. Thus, we must conclude that the process is irreversible. W ...
Chapter 3. The Second Law
... 1. The surroundings consist of a reservoir of constant V. 2. The energy supplied as heat can be identified with the change in internal energy, ΔUsur. 3. U is a state function and independent of the path. 4. So we can drop “rev”. ...
... 1. The surroundings consist of a reservoir of constant V. 2. The energy supplied as heat can be identified with the change in internal energy, ΔUsur. 3. U is a state function and independent of the path. 4. So we can drop “rev”. ...
Chapter 19 Thermodynamics - Farmingdale State College
... cyclic process. Note that pA _ pD is one side of the rectangular path of figure 19.2(a) while VB _ VA is the other side of that rectangle. Hence, their product in equation 19.11 represents the entire area of the rectangle enclosed by the thermodynamic path ABCDA and is shown as the cross-hatched are ...
... cyclic process. Note that pA _ pD is one side of the rectangular path of figure 19.2(a) while VB _ VA is the other side of that rectangle. Hence, their product in equation 19.11 represents the entire area of the rectangle enclosed by the thermodynamic path ABCDA and is shown as the cross-hatched are ...
THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 3·5 So far we have
... The negativ e sign is due to the sign conven tion that work done on a system is negative. This ensures that work done on a system increas es the energy of the system and work done by a system decreas es it. Now let us replace the electric heater with a paddle wheel (Fig. 3-50). As a result of the st ...
... The negativ e sign is due to the sign conven tion that work done on a system is negative. This ensures that work done on a system increas es the energy of the system and work done by a system decreas es it. Now let us replace the electric heater with a paddle wheel (Fig. 3-50). As a result of the st ...
Chapter 2
... we will develop the concept of temperature by considering what happens when two bodies are placed so that they can exchange energy. The most important property of the temperature is its tendency to become equal. For example, if we put a hot and a cold body into thermal contact, the temperature of th ...
... we will develop the concept of temperature by considering what happens when two bodies are placed so that they can exchange energy. The most important property of the temperature is its tendency to become equal. For example, if we put a hot and a cold body into thermal contact, the temperature of th ...
Polytropic Process
... If the volume compresses (delta V = final volume - initial volume < 0), then W < 0. That is, during isobaric compression the gas does negative work, or the environment does positive work. Restated, the environment does positive work on the gas. If the volume expands (delta V = final volume - initial ...
... If the volume compresses (delta V = final volume - initial volume < 0), then W < 0. That is, during isobaric compression the gas does negative work, or the environment does positive work. Restated, the environment does positive work on the gas. If the volume expands (delta V = final volume - initial ...
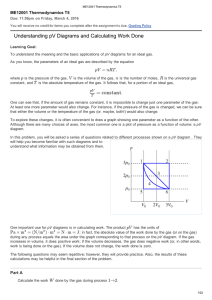
Understanding pV Diagrams and Calculating Work Done
... The first law of thermodynamics is the statement of the law of conservation of energy in its most general form. You can apply it to any situation in which you are concerned with changes in the internal energy of a system, with heat flow into or out of a system, and/or with work done by or on a syste ...
... The first law of thermodynamics is the statement of the law of conservation of energy in its most general form. You can apply it to any situation in which you are concerned with changes in the internal energy of a system, with heat flow into or out of a system, and/or with work done by or on a syste ...
A survey of statistical mechanics as it pertains to molecular simulation
... of statistical mechanics is devised to permit easy application of the postulates to nonisolated systems. This parallels the development of the formalism of thermodynamics, which begins by defining the entropy as a quantity that is maximized for an isolated system at equilibrium. Thermodynamics then ...
... of statistical mechanics is devised to permit easy application of the postulates to nonisolated systems. This parallels the development of the formalism of thermodynamics, which begins by defining the entropy as a quantity that is maximized for an isolated system at equilibrium. Thermodynamics then ...
Calorimetry - NC State University
... For a diatomic molecule there is contribution from rotations as well as translations. This means that as heat is added to the system the rotational levels can be populated in addition to an increase in molecular speed. The kinetic theory of gases considers only the speed. An approximate rule is that ...
... For a diatomic molecule there is contribution from rotations as well as translations. This means that as heat is added to the system the rotational levels can be populated in addition to an increase in molecular speed. The kinetic theory of gases considers only the speed. An approximate rule is that ...