Photosynthesis in plants requires sunlight in addition
... spectral coverage is severely limited. Constructing a suitable LED-based plant grow light that adequately covers the high reaction yield portions of the photosynthesis absorption spectrum thus requires a number of LEDs emitting at different wavelengths. Electrospell’s broadband SpectrafillTM LEDs ge ...
... spectral coverage is severely limited. Constructing a suitable LED-based plant grow light that adequately covers the high reaction yield portions of the photosynthesis absorption spectrum thus requires a number of LEDs emitting at different wavelengths. Electrospell’s broadband SpectrafillTM LEDs ge ...
The electromagnetic spectrum
... The speed of light is 186,000 miles/second. How long does it take the light from a lightning strike to reach you if it is 186,000 miles away? A. Much, much less than 1 second B. 1 second C. 30 seconds D. 300 seconds ...
... The speed of light is 186,000 miles/second. How long does it take the light from a lightning strike to reach you if it is 186,000 miles away? A. Much, much less than 1 second B. 1 second C. 30 seconds D. 300 seconds ...
Final Exam
... b) From the angular width calculated above, determine the smallest details we can expect to resolve for an object located at 25 cm in front of our eyes, which is typically the closest distance that our eyes can still accommodate. State your answer in micrometers, µm. Make sure your answer is reasona ...
... b) From the angular width calculated above, determine the smallest details we can expect to resolve for an object located at 25 cm in front of our eyes, which is typically the closest distance that our eyes can still accommodate. State your answer in micrometers, µm. Make sure your answer is reasona ...
Pre-class 11
... particle-wave duality of light (and matter!) However, do not get confused with when to use the wave or the particle representation of the very same physical entity. It actually depends on the experiment (‘question’ or ‘measurement’)! We will see several experiments that should help you understand th ...
... particle-wave duality of light (and matter!) However, do not get confused with when to use the wave or the particle representation of the very same physical entity. It actually depends on the experiment (‘question’ or ‘measurement’)! We will see several experiments that should help you understand th ...
DUAL NATURE OF LIGHT WAVES A THEORETICAL PROOF
... ABSTRACT: According to Newton’s corpuscles theory of light, planks quantum theory light is particle nature and Maxwell Electromagnetic theory and Huygens wave theory light is wave nature. Some experiment shows light has particle nature and some experiment shows light has wave nature. Therefore accor ...
... ABSTRACT: According to Newton’s corpuscles theory of light, planks quantum theory light is particle nature and Maxwell Electromagnetic theory and Huygens wave theory light is wave nature. Some experiment shows light has particle nature and some experiment shows light has wave nature. Therefore accor ...
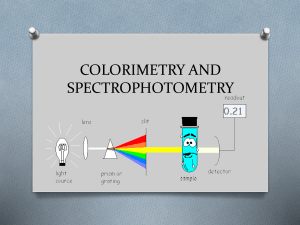
COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
... Colorimetry is the use of the human eye to determine the concentration of coloured solution Spectrophotometry is the use of instruments to make the same measurements. It extends the range of possible measurements beyond those that can be determined by the eye alone. ...
... Colorimetry is the use of the human eye to determine the concentration of coloured solution Spectrophotometry is the use of instruments to make the same measurements. It extends the range of possible measurements beyond those that can be determined by the eye alone. ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.