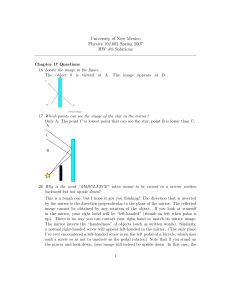
Chapter 4 Questions Perception of Color
... • The atmosphere refracts and scatters light into our eyes even after the sun has set. ...
... • The atmosphere refracts and scatters light into our eyes even after the sun has set. ...
Chapter 37 Wave Optics (I)
... When light is incident normally on the boundary between air (n=1) and glass (n=1.5), about 4% of the energy is reflected and 96% is transmitted. Thus, a camera with 6 lenses has 12 air-glass interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize ...
... When light is incident normally on the boundary between air (n=1) and glass (n=1.5), about 4% of the energy is reflected and 96% is transmitted. Thus, a camera with 6 lenses has 12 air-glass interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize ...
Light Tree.pdf - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... The concept of light tree is introduced in a wavelength routed optical network, which employs wavelength -division multiplexing (WDM). Light Tree was designed by Omar Ivan Huerta Cardoso. Cardoso designed a plastic tree with some water in it which is used to conduce the light from Light Emitting Dio ...
... The concept of light tree is introduced in a wavelength routed optical network, which employs wavelength -division multiplexing (WDM). Light Tree was designed by Omar Ivan Huerta Cardoso. Cardoso designed a plastic tree with some water in it which is used to conduce the light from Light Emitting Dio ...
The Photoelectric Effect in Practice WS Key
... of the electron. This is equal to the difference between the energy of the photon and the work function __________________________ of the atom. If the light has less energy than that amount, an electron will not be ejected/emitted/released __________________________ from the atom. 3. Ultraviolet lig ...
... of the electron. This is equal to the difference between the energy of the photon and the work function __________________________ of the atom. If the light has less energy than that amount, an electron will not be ejected/emitted/released __________________________ from the atom. 3. Ultraviolet lig ...
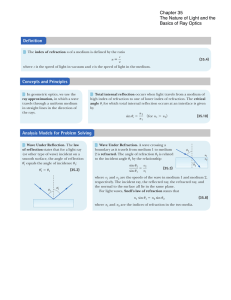
HW #8 Solutions
... of the light intensity is transmitted through the material. Since intensity is power per unit area, energy conservation requires that the reflected plus transmitted intensity (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is equal to the incident intensity. 15 Waves that are refracted towards the normal at a bou ...
... of the light intensity is transmitted through the material. Since intensity is power per unit area, energy conservation requires that the reflected plus transmitted intensity (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is equal to the incident intensity. 15 Waves that are refracted towards the normal at a bou ...
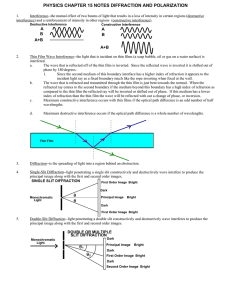
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
Topic 5 Core Questions
... Distance / time and frequency x wavelength. Substitute in values in standard units, show working out clearly and show the units on the answer. Triangles are a tool to help us re-arrange equations. Suspend the steel rod and hit it with a hammer. Use a frequency app to record the peak frequency (or a ...
... Distance / time and frequency x wavelength. Substitute in values in standard units, show working out clearly and show the units on the answer. Triangles are a tool to help us re-arrange equations. Suspend the steel rod and hit it with a hammer. Use a frequency app to record the peak frequency (or a ...
What Wavelength Was That?
... objects? • 4. What is a light wave? • 5.Are there any hands-on/minds-on activities I can do to learn more? ...
... objects? • 4. What is a light wave? • 5.Are there any hands-on/minds-on activities I can do to learn more? ...
Scribe notes 10/3 - Google Docs
... E5: Recent events suggest classical mechanics is insufficient for describing natural phenomenon. - Investigations by physicists into the nature of light - Speed of light = 186,000 miles/second (in a vacuum) - Light travels from Earth to the moon in 1-2 seconds/ from the Sun in 8 minutes First, light ...
... E5: Recent events suggest classical mechanics is insufficient for describing natural phenomenon. - Investigations by physicists into the nature of light - Speed of light = 186,000 miles/second (in a vacuum) - Light travels from Earth to the moon in 1-2 seconds/ from the Sun in 8 minutes First, light ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.